With default parameters the macro will attempt to run the standard hist2workspace example and read the ROOT file that it produces.
The first ~100 lines define a new test statistic, then the main macro starts. You may want to control:
This uses a modified version of the profile likelihood ratio as a test statistic for upper limits (eg. test stat = 0 if muhat>mu).
Based on the observed data, one defines a set of parameter points to be tested based on the value of the parameter of interest and the conditional MLE (eg. profiled) values of the nuisance parameters.
At each parameter point, pseudo-experiments are generated using this fixed reference model and then the test statistic is evaluated. Note, the nuisance parameters are floating in the fits. For each point, the threshold that defines the 95% acceptance region is found. This forms a "Confidence Belt".
After constructing the confidence belt, one can find the confidence interval for any particular dataset by finding the intersection of the observed test statistic and the confidence belt. First this is done on the observed data to get an observed 1-sided upper limt.
Finally, there expected limit and bands (from background-only) are formed by generating background-only data and finding the upper limit. This is done by hand for now, will later be part of the RooStats tools.
On a technical note, this technique is NOT the Feldman-Cousins technique, because that is a 2-sided interval BY DEFINITION. However, like the Feldman-Cousins technique this is a Neyman-Construction. For technical reasons the easiest way to implement this right now is to use the FeldmanCousins tool and then change the test statistic that it is using.
Building the confidence belt can be computationally expensive. Once it is built, one could save it to a file and use it in a separate step.
We can use PROOF to speed things along in parallel, however, the test statistic has to be installed on the workers so either turn off PROOF or include the modified test statistic in your $ROOTSYS/roofit/roostats/inc directory, add the additional line to the LinkDef.h file, and recompile root.
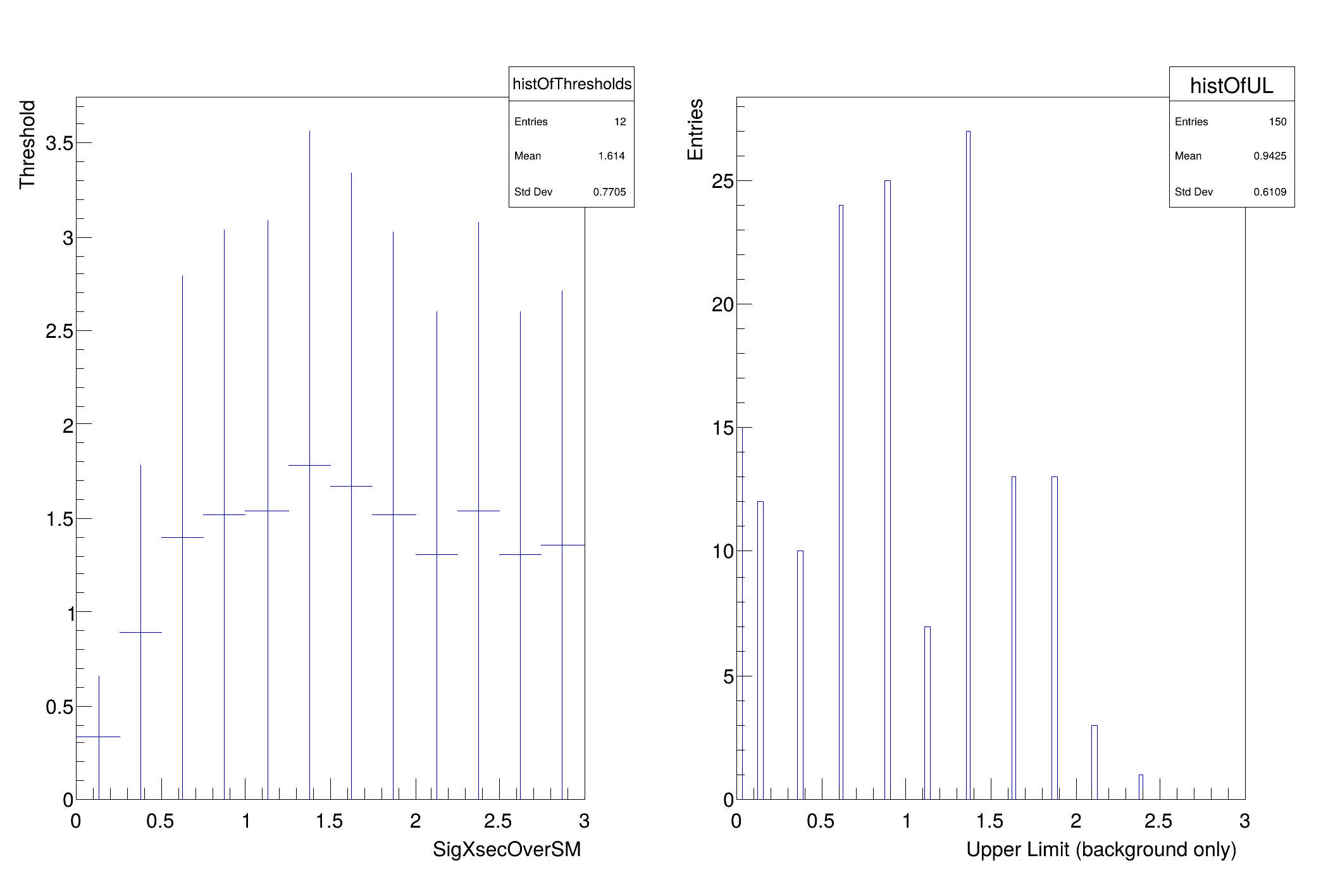
Note, if you have a boundary on the parameter of interest (eg. cross-section) the threshold on the one-sided test statistic starts off very small because we are only including downward fluctuations. You can see the threshold in these printouts:
this tells you the values of the parameters being used to generate the pseudo-experiments and the threshold in this case is 0.011215. One would expect for 95% that the threshold would be ~1.35 once the cross-section is far enough away from 0 that it is essentially unaffected by the boundary. As one reaches the last points in the scan, the threshold starts to get artificially high. This is because the range of the parameter in the fit is the same as the range in the scan. In the future, these should be independently controlled, but they are not now. As a result the ~50% of pseudo-experiments that have an upward fluctuation end up with muhat = muMax. Because of this, the upper range of the parameter should be well above the expected upper limit... but not too high or one will need a very large value of nPointsToScan to resolve the relevant region. This can be improved, but this is the first version of this script.
Important note: when the model includes external constraint terms, like a Gaussian constraint to a nuisance parameter centered around some nominal value there is a subtlety. The asymptotic results are all based on the assumption that all the measurements fluctuate... including the nominal values from auxiliary measurements. If these do not fluctuate, this corresponds to an "conditional ensemble". The result is that the distribution of the test statistic can become very non-chi^2. This results in thresholds that become very large. This can be seen in the following thought experiment. Say the model is \( Pois(N | s + b)G(b0|b,sigma) \) where \( G(b0|b,sigma) \) is the external constraint and b0 is 100. If N is also 100 then the profiled value of b given s is going to be some trade off between 100-s and b0. If sigma is \( \sqrt(N) \), then the profiled value of b is probably 100 - s/2 So for s=60 we are going to have a profiled value of b~70. Now when we generate pseudo-experiments for s=60, b=70 we will have N~130 and the average shat will be 30, not 60. In practice, this is only an issue for values of s that are very excluded. For values of s near the 95% limit this should not be a big effect. This can be avoided if the nominal values of the constraints also fluctuate, but that requires that those parameters are RooRealVars in the model. This version does not deal with this issue, but it will be addressed in a future version.
FeldmanCousins: ntoys per point = 499
FeldmanCousins: nEvents per toy will fluctuate about expectation
will use global observables for unconditional ensemble
RooArgSet:: = (nominalLumi,nom_alpha_syst1,nom_alpha_syst2,nom_alpha_syst3,nom_gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0,nom_gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1)
=== Using the following for ModelConfig ===
Observables: RooArgSet:: = (obs_x_channel1,channelCat)
Parameters of Interest: RooArgSet:: = (SigXsecOverSM)
Nuisance Parameters: RooArgSet:: = (alpha_syst2,alpha_syst3,gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0,gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1)
Global Observables: RooArgSet:: = (nominalLumi,nom_alpha_syst1,nom_alpha_syst2,nom_alpha_syst3,nom_gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0,nom_gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1)
PDF: RooSimultaneous::simPdf[ indexCat=channelCat channel1=model_channel1 ] = 0.190787
FeldmanCousins: Model has nuisance parameters, will do profile construction
FeldmanCousins: # points to test = 12
lookup index = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 1/12 total MC = 499 this test stat = 0
SigXsecOverSM=0.125 alpha_syst2=0.61993 alpha_syst3=0.233335 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0=1.03212 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1=1.04741 [-inf, 0.329584] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 2/12 total MC = 499 this test stat = 0
SigXsecOverSM=0.375 alpha_syst2=0.458263 alpha_syst3=0.183235 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0=1.02329 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1=1.03422 [-inf, 0.888912] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 3/12 total MC = 499 this test stat = 0
SigXsecOverSM=0.625 alpha_syst2=0.292479 alpha_syst3=0.126723 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0=1.01484 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1=1.02374 [-inf, 1.39758] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 4/12 total MC = 499 this test stat = 0
SigXsecOverSM=0.875 alpha_syst2=0.130655 alpha_syst3=0.0953602 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0=1.00646 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1=1.01288 [-inf, 1.51992] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 5/12 total MC = 499 this test stat = 0.000124169
SigXsecOverSM=1.125 alpha_syst2=-0.0146474 alpha_syst3=0.0173394 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0=0.999267 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1=1.003 [-inf, 1.54198] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 6/12 total MC = 499 this test stat = 0.0913576
SigXsecOverSM=1.375 alpha_syst2=-0.15078 alpha_syst3=-0.0572169 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0=0.99238 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1=0.993157 [-inf, 1.78377] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 7/12 total MC = 499 this test stat = 0.349003
SigXsecOverSM=1.625 alpha_syst2=-0.294555 alpha_syst3=-0.0932947 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0=0.985516 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1=0.983192 [-inf, 1.66921] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 8/12 total MC = 499 this test stat = 0.767692
SigXsecOverSM=1.875 alpha_syst2=-0.424297 alpha_syst3=-0.146312 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0=0.979248 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1=0.973447 [-inf, 1.5144] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 9/12 total MC = 499 this test stat = 1.34313
SigXsecOverSM=2.125 alpha_syst2=-0.546305 alpha_syst3=-0.198112 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0=0.973364 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1=0.963869 [-inf, 1.30266] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 10/12 total MC = 499 this test stat = 2.07172
SigXsecOverSM=2.375 alpha_syst2=-0.66027 alpha_syst3=-0.248685 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0=0.967841 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1=0.954463 [-inf, 1.5387] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 11/12 total MC = 499 this test stat = 2.9476
SigXsecOverSM=2.625 alpha_syst2=-0.766369 alpha_syst3=-0.29799 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0=0.962657 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1=0.945235 [-inf, 1.30108] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 12/12 total MC = 499 this test stat = 3.96711
SigXsecOverSM=2.875 alpha_syst2=-0.865262 alpha_syst3=-0.345965 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0=0.95779 gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1=0.936192 [-inf, 1.35603] in interval = 0
[#1] INFO:Eval -- 8 points in interval
95% interval on SigXsecOverSM is : [0.125, 1.875]
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- p.d.f. provides expected number of events, including extended term in likelihood.
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- Including the following constraint terms in minimization: (lumiConstraint,alpha_syst1Constraint,alpha_syst2Constraint,alpha_syst3Constraint,gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0_constraint,gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1_constraint)
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- The global observables are not defined , normalize constraints with respect to the parameters (Lumi,SigXsecOverSM,alpha_syst1,alpha_syst2,alpha_syst3,gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0,gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1)
[#1] INFO:Fitting -- RooAbsPdf::fitTo(simPdf) fixing normalization set for coefficient determination to observables in data
[#1] INFO:Fitting -- using CPU computation library compiled with -mavx512
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- RooProfileLL::evaluate(RooEvaluatorWrapper_Profile[SigXsecOverSM]) Creating instance of MINUIT
[#1] INFO:Fitting -- RooAddition::defaultErrorLevel(nll_simPdf_obsData) Summation contains a RooNLLVar, using its error level
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- RooProfileLL::evaluate(RooEvaluatorWrapper_Profile[SigXsecOverSM]) determining minimum likelihood for current configurations w.r.t all observable
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- RooProfileLL::evaluate(RooEvaluatorWrapper_Profile[SigXsecOverSM]) minimum found at (SigXsecOverSM=1.12136)
.
Will use these parameter points to generate pseudo data for bkg only
1) 0x7ec5380 RooRealVar:: alpha_syst2 = 0.710958 +/- 0.914123 L(-5 - 5) "alpha_syst2"
2) 0x7ec5890 RooRealVar:: alpha_syst3 = 0.261478 +/- 0.929174 L(-5 - 5) "alpha_syst3"
3) 0x7ec5df0 RooRealVar:: gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0 = 1.03677 +/- 0.0462911 L(0 - 1.25) "gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0"
4) 0x7ec6350 RooRealVar:: gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1 = 1.05318 +/- 0.0761263 L(0 - 1.5) "gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1"
5) 0x7ec68b0 RooRealVar:: SigXsecOverSM = 0 +/- 0 L(0 - 3) B(12) "SigXsecOverSM"
-2 sigma band 3.97984e-316
-1 sigma band 0.105 [Power Constraint)]
median of band 0.855
+1 sigma band 1.605
+2 sigma band 2.085
observed 95% upper-limit 1.875
CLb strict [P(toy>obs|0)] for observed 95% upper-limit 0.966667
CLb inclusive [P(toy>=obs|0)] for observed 95% upper-limit 0.966667
{
filename =
"results/example_combined_GaussExample_model.root";
cout << "will run standard hist2workspace example" << endl;
gROOT->ProcessLine(
".! prepareHistFactory .");
gROOT->ProcessLine(
".! hist2workspace config/example.xml");
cout << "\n\n---------------------" << endl;
cout << "Done creating example input" << endl;
cout << "---------------------\n\n" << endl;
}
} else
if (!file) {
cout <<
"StandardRooStatsDemoMacro: Input file " <<
filename <<
" is not found" << endl;
return;
}
cout << "workspace not found" << endl;
return;
}
cout << "data or ModelConfig was not found" << endl;
return;
}
fc.AdditionalNToysFactor(
0.5);
if (!
mc->GetPdf()->canBeExtended()) {
if (
data->numEntries() == 1)
fc.FluctuateNumDataEntries(
false);
else
cout << "Not sure what to do about this model" << endl;
}
}
if (
mc->GetGlobalObservables()) {
cout << "will use global observables for unconditional ensemble" << endl;
mc->GetGlobalObservables()->Print();
}
}
std::unique_ptr<RooAbsReal>
nll{
mc->GetPdf()->createNLL(*
data)};
std::unique_ptr<RooAbsReal> profile{
nll->createProfile(*
mc->GetParametersOfInterest())};
profile->getVal();
if (
mc->GetNuisanceParameters())
cout << "\nWill use these parameter points to generate pseudo data for bkg only" << endl;
double CLb = 0;
histOfUL->GetXaxis()->SetTitle(
"Upper Limit (background only)");
histOfUL->GetYaxis()->SetTitle(
"Entries");
w->loadSnapshot(
"paramsToGenerateData");
std::unique_ptr<RooDataSet>
toyData;
if (!
mc->GetPdf()->canBeExtended()) {
if (
data->numEntries() == 1)
toyData = std::unique_ptr<RooDataSet>{
mc->GetPdf()->generate(*
mc->GetObservables(), 1)};
else
cout << "Not sure what to do about this model" << endl;
} else {
toyData = std::unique_ptr<RooDataSet>{
mc->GetPdf()->generate(*
mc->GetObservables(), Extended())};
}
std::unique_ptr<RooDataSet>
one{
mc->GetPdf()->generate(*
mc->GetGlobalObservables(), 1)};
std::unique_ptr<RooArgSet> allVars{
mc->GetPdf()->getVariables()};
allVars->assign(*values);
} else {
for (
auto const&
tt :
simPdf->indexCat()) {
std::unique_ptr<RooArgSet>
globtmp{
pdftmp->getObservables(*
mc->GetGlobalObservables())};
}
}
} else {
break;
}
}
}
c1->SaveAs(
"one-sided_upper_limit_output.pdf");
for (
int i = 1; i <=
cumulative->GetNbinsX(); ++i) {
if (bins[i] < 0.5)
}
cout <<
"-1 sigma band " <<
band1sigDown <<
" [Power Constraint)]" << endl;
cout <<
"\nobserved 95% upper-limit " <<
interval->UpperLimit(*
firstPOI) << endl;
cout << "CLb strict [P(toy>obs|0)] for observed 95% upper-limit " << CLb << endl;
cout <<
"CLb inclusive [P(toy>=obs|0)] for observed 95% upper-limit " <<
CLbinclusive << endl;
}
Option_t Option_t TPoint TPoint const char GetTextMagnitude GetFillStyle GetLineColor GetLineWidth GetMarkerStyle GetTextAlign GetTextColor GetTextSize void char Point_t Rectangle_t WindowAttributes_t Float_t Float_t Float_t Int_t Int_t UInt_t UInt_t Rectangle_t Int_t Int_t Window_t TString Int_t GCValues_t GetPrimarySelectionOwner GetDisplay GetScreen GetColormap GetNativeEvent const char const char dpyName wid window const char font_name cursor keysym reg const char only_if_exist regb h Point_t winding char text const char depth char const char Int_t count const char ColorStruct_t color const char filename
Option_t Option_t TPoint TPoint const char GetTextMagnitude GetFillStyle GetLineColor GetLineWidth GetMarkerStyle GetTextAlign GetTextColor GetTextSize void data
R__EXTERN TSystem * gSystem
Abstract base class for binned and unbinned datasets.
Abstract interface for all probability density functions.
RooArgSet is a container object that can hold multiple RooAbsArg objects.
Container class to hold unbinned data.
Variable that can be changed from the outside.
Facilitates simultaneous fitting of multiple PDFs to subsets of a given dataset.
ConfidenceBelt is a concrete implementation of the ConfInterval interface.
The FeldmanCousins class (like the Feldman-Cousins technique) is essentially a specific configuration...
ModelConfig is a simple class that holds configuration information specifying how a model should be u...
PointSetInterval is a concrete implementation of the ConfInterval interface.
ProfileLikelihoodTestStat is an implementation of the TestStatistic interface that calculates the pro...
Holds configuration options for proof and proof-lite.
ToyMCSampler is an implementation of the TestStatSampler interface.
Persistable container for RooFit projects.
TObject * Get(const char *namecycle) override
Return pointer to object identified by namecycle.
A ROOT file is an on-disk file, usually with extension .root, that stores objects in a file-system-li...
static TFile * Open(const char *name, Option_t *option="", const char *ftitle="", Int_t compress=ROOT::RCompressionSetting::EDefaults::kUseCompiledDefault, Int_t netopt=0)
Create / open a file.
1-D histogram with a float per channel (see TH1 documentation)
virtual Bool_t AccessPathName(const char *path, EAccessMode mode=kFileExists)
Returns FALSE if one can access a file using the specified access mode.
double nll(double pdf, double weight, int binnedL, int doBinOffset)
The namespace RooFit contains mostly switches that change the behaviour of functions of PDFs (or othe...
Namespace for the RooStats classes.
double SignificanceToPValue(double Z)
returns p-value corresponding to a 1-sided significance