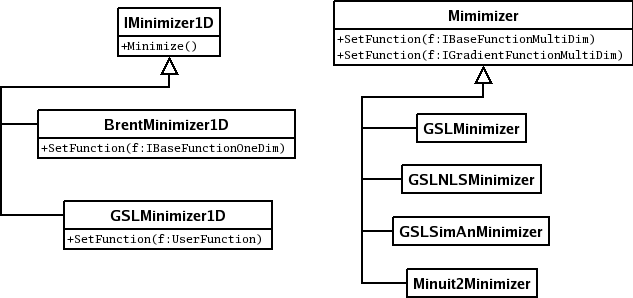
Class structure for function minimization
The algorithms provided by ROOT for numerical integration are implemented following the hierarchy shown in the next image. The left branch of classes are used for one dimensional minimization, while the right one is used for multidimensional minimization. In the case of multidimensional minimization we have also the classes TMinuit2Minimizer implemented using TMinuit, TFumiliMinimizer implemented using TFumili for least square or likelihood minimizations. We encourage the use of the GSL algorithms for one dimensional minimization and Minuit (TMinuit or Minuit2) for multi dimensional minimization.
Minimization in One Dimension
- BrentMinimizer1D: Implements the Brent method to minimize an IBaseFunctionOneDim. Example:
#include "Math/Functor.h" #include "Math/BrentMinimizer1D.h" double myfunc(double x ) { return 1 + -4*x + 1*x*x; } int NumericalMinimization(){ ROOT::Math::Functor1D func(&myfunc); ROOT::Math::BrentMinimizer1D bm; bm.SetFunction(func, -10,10); bm.Minimize(10,0,0); cout << "f(" << bm.XMinimum() << ") = " <<bm.FValMinimum() << endl; return 0; }
- GSLMinimizer1D: This class wraps two different methods from the GSL. The algorithms uspported are only bracketing algorithm which do not use derivatives information. The algorithms which can be choosen at construction time are GOLDENSECTION, which is the simplest method but the slowest and BRENT (the default one) which combines the golden section with a parabolic interpolation. Example:
#include "Math/Functor.h" #include "Math/GSLMinimizer1D.h" double myfunc(double x ) { return 1 + -4*x + 1*x*x; } int NumericalMinimization() { ROOT::Math::Functor1D func(&myfunc); // default (Brent) ROOT::Math::GSLMinimizer1D minBrent; minBrent.SetFunction(func,1,-10,10); minBrent.Minimize(100,0.01,0.01); std::cout << "Found minimum: x = " << minBrent.XMinimum() << " f(x) = " << minBrent.FValMinimum() << std::endl; // Golden Section ROOT::Math::GSLMinimizer1D minGold(ROOT::Math::Minim1D::kGOLDENSECTION); minGold.SetFunction(func,1,-10,10); minGold.Minimize(100,0.01,0.01); std::cout << "Found minimum: x = " << minGold.XMinimum() << " f(x) = " << minGold.FValMinimum() << std::endl; return 0; }
Minimization with Multidimensional Functions
- GSLMinimizer: The class implements the ROOT::Math::Minimizer interface and can be instantiated using the ROOT plugin manager (plugin name is "GSLMultiMin"). The varius minimization algorithms (conjugatefr, conjugatepr, bfgs, etc..) can be passed as enumerations and also as a string. The default algorithm is conjugatefr (Fletcher-Reeves conjugate gradient algorithm). Example:
#include "Math/GSLMinimizer.h" #include "Math/Functor.h" double RosenBrock(const double *xx ) { const Double_t x = xx[0]; const Double_t y = xx[1]; const Double_t tmp1 = y-x*x; const Double_t tmp2 = 1-x; return 100*tmp1*tmp1+tmp2*tmp2; } int NumericalMinimization() { // Choose method upon creation between: // kConjugateFR, kConjugatePR, kVectorBFGS, // kVectorBFGS2, kSteepestDescent ROOT::Math::GSLMinimizer min( ROOT::Math::kVectorBFGS ); min.SetMaxFunctionCalls(1000000); min.SetMaxIterations(100000); min.SetTolerance(0.001); ROOT::Math::Functor f(&RosenBrock,2); double step[2] = {0.01,0.01}; double variable[2] = { -1.,1.2}; min.SetFunction(f); // Set the free variables to be minimized! min.SetVariable(0,"x",variable[0], step[0]); min.SetVariable(1,"y",variable[1], step[1]); min.Minimize(); const double *xs = min.X(); cout << "Minimum: f(" << xs[0] << "," << xs[1] << "): " << RosenBrock(xs) << endl; return 0; }
- GSLNLSMinimizer: lass for Non Linear Least Square fitting It Uses the Levemberg-Marquardt algorithm from GSL.
- GSLSimAnMinimizer: class for minimization using simulated annealing using the algorithm from GSL. Example:
#include "Math/GSLSimAnMinimizer.h" #include "Math/Functor.h" double RosenBrock(const double *xx ) { const Double_t x = xx[0]; const Double_t y = xx[1]; const Double_t tmp1 = y-x*x; const Double_t tmp2 = 1-x; return 100*tmp1*tmp1+tmp2*tmp2; } int NumericalMinimization() { ROOT::Math::GSLSimAnMinimizer min; min.SetMaxFunctionCalls(1000000); min.SetMaxIterations(100000); min.SetTolerance(0.001); ROOT::Math::Functor f(&RosenBrock,2); double step[2] = {0.01,0.01}; double variable[2] = { -1.,1.2}; min.SetFunction(f); // Set the free variables to be minimized! min.SetVariable(0,"x",variable[0], step[0]); min.SetVariable(1,"y",variable[1], step[1]); min.Minimize(); const double *xs = min.X(); cout << "Minimum: f(" << xs[0] << "," << xs[1] << "): " << RosenBrock(xs) << endl; return 0; }
- Minuit2Minimizer: Implements the Minuit2 Minimizer within the Minimizer interface. Example:
#include "Minuit2/Minuit2Minimizer.h" #include "Math/Functor.h" double RosenBrock(const double *xx ) { const Double_t x = xx[0]; const Double_t y = xx[1]; const Double_t tmp1 = y-x*x; const Double_t tmp2 = 1-x; return 100*tmp1*tmp1+tmp2*tmp2; } int NumericalMinimization() { // Choose method upon creation between: // kMigrad, kSimplex, kCombined, // kScan, kFumili ROOT::Minuit2::Minuit2Minimizer min ( ROOT::Minuit2::kMigrad ); min.SetMaxFunctionCalls(1000000); min.SetMaxIterations(100000); min.SetTolerance(0.001); ROOT::Math::Functor f(&RosenBrock,2); double step[2] = {0.01,0.01}; double variable[2] = { -1.,1.2}; min.SetFunction(f); // Set the free variables to be minimized! min.SetVariable(0,"x",variable[0], step[0]); min.SetVariable(1,"y",variable[1], step[1]); min.Minimize(); const double *xs = min.X(); cout << "Minimum: f(" << xs[0] << "," << xs[1] << "): " << RosenBrock(xs) << endl; return 0; }
Creating a Minimizer via the Plug-In Manager
There is an alternative better to create all the minimizer algorithms without using the classes directly. As all of them implement the ROOT::Math::Minimizer interface, we can instantiate them with any of the classes with the plug-in manager. This is done through the ROOT::Math::Factory class and its method CreateMinimizer. The method receives two string parameters. The first one is the name of the minimizer while the second is the name of the algorithm used if there is any, or an empty string if there is no possible choice. The next example shows all the possible combinations to this method for all the classes seen above. Example:
#include "Math/Minimizer.h" #include "Math/Factory.h" #include "Math/Functor.h" double RosenBrock(const double *xx ) { const Double_t x = xx[0]; const Double_t y = xx[1]; const Double_t tmp1 = y-x*x; const Double_t tmp2 = 1-x; return 100*tmp1*tmp1+tmp2*tmp2; } int NumericalMinimization() { ROOT::Math::Minimizer* min = ROOT::Math::Factory::CreateMinimizer("Minuit2", "Migrad"); // ROOT::Math::Minimizer* min = // ROOT::Math::Factory::CreateMinimizer("Minuit2", "Simplex"); // ROOT::Math::Minimizer* min = // ROOT::Math::Factory::CreateMinimizer("Minuit2", "Combined"); // ROOT::Math::Minimizer* min = // ROOT::Math::Factory::CreateMinimizer("Minuit2", "Scan"); // ROOT::Math::Minimizer* min = // ROOT::Math::Factory::CreateMinimizer("Minuit2", "Fumili"); // ROOT::Math::Minimizer* min = // ROOT::Math::Factory::CreateMinimizer("GSLMultiMin", "ConjugateFR"); // ROOT::Math::Minimizer* min = // ROOT::Math::Factory::CreateMinimizer("GSLMultiMin", "ConjugatePR"); // ROOT::Math::Minimizer* min = // ROOT::Math::Factory::CreateMinimizer("GSLMultiMin", "BFGS"); // ROOT::Math::Minimizer* min = // ROOT::Math::Factory::CreateMinimizer("GSLMultiMin", "BFGS2"); // ROOT::Math::Minimizer* min = // ROOT::Math::Factory::CreateMinimizer("GSLMultiMin", "SteepestDescent"); // ROOT::Math::Minimizer* min = // ROOT::Math::Factory::CreateMinimizer("GSLMultiFit", ""); // ROOT::Math::Minimizer* min = // ROOT::Math::Factory::CreateMinimizer("GSLSimAn", ""); min->SetMaxFunctionCalls(1000000); min->SetMaxIterations(100000); min->SetTolerance(0.001); ROOT::Math::Functor f(&RosenBrock,2); double step[2] = {0.01,0.01}; double variable[2] = { -1.,1.2}; min->SetFunction(f); // Set the free variables to be minimized! min->SetVariable(0,"x",variable[0], step[0]); min->SetVariable(1,"y",variable[1], step[1]); min->Minimize(); const double *xs = min->X(); cout << "Minimum: f(" << xs[0] << "," << xs[1] << "): " << RosenBrock(xs) << endl; return 0; }

