
 Example to illustrate the 2-d peak finder (class TSpectrum2).
Example to illustrate the 2-d peak finder (class TSpectrum2).
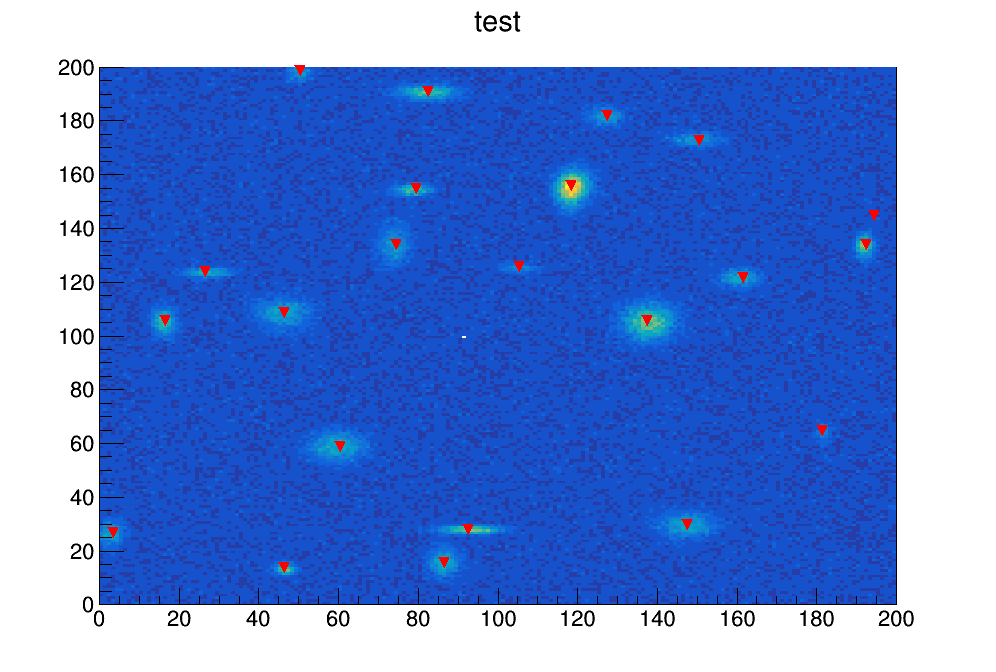
This script generates a random number of 2-d gaussian peaks The position of the peaks is found via TSpectrum2 To execute this example, do:
root > .x peaks2.C (generate up to 50 peaks by default)
root > .x peaks2.C(10) (generate up to 10 peaks)
root > .x peaks2.C+(200) (generate up to 200 peaks via ACLIC)
The script will iterate generating a new histogram having between 5 and the maximun number of peaks specified. Double Click on the bottom right corner of the pad to go to a new spectrum To Quit, select the "quit" item in the canvas "File" menu
for (
Int_t p=0;p<npeaks;p++) {
}
return result;
}
void findPeak2() {
printf("Generating histogram with %d peaks\n",npeaks);
delete h2;
h2 =
new TH2F(
"h2",
"test",nbinsx,xmin,xmax,nbinsy,ymin,ymax);
for (p=0;p<npeaks;p++) {
par[5*p+0] = gRandom->Uniform(0.2,1);
par[5*p+1] = gRandom->Uniform(xmin,xmax);
par[5*p+2] = gRandom->Uniform(dx,5*dx);
par[5*p+3] = gRandom->Uniform(ymin,ymax);
par[5*p+4] = gRandom->Uniform(dy,5*dy);
}
TF2 *f2 =
new TF2(
"f2",fpeaks2,xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax,5*npeaks);
if (!c1) c1 =
new TCanvas(
"c1",
"c1",10,10,1000,700);
for (p=0;p<npeaks;p++) {
for (pf=0;pf<nfound;pf++) {
if (diffx < 2*dx && diffy < 2*dy) ngood++;
}
}
if (ngood > nfound) ngood = nfound;
for (pf=0;pf<nfound;pf++) {
for (p=0;p<npeaks;p++) {
if (diffx < 2*dx && diffy < 2*dy) nf++;
}
if (nf == 0) nghost++;
}
printf("Gener=%d, Found=%d, Good=%d, Ghost=%d\n",npeaks,nfound,ngood,nghost);
printf("\nDouble click in the bottom right corner of the pad to continue\n");
}
}
void peaks2(
Int_t maxpeaks=50) {
for (int i=0; i<10; ++i) {
npeaks = (
Int_t)gRandom->Uniform(5,maxpeaks);
findPeak2();
}
}
- Author
- Rene Brun
Definition in file peaks2.C.



 Example to illustrate the 2-d peak finder (class TSpectrum2).
Example to illustrate the 2-d peak finder (class TSpectrum2). 