

tutorial demonstrating and validates the RooJeffreysPrior class
Jeffreys's prior is an 'objective prior' based on formal rules. It is calculated from the Fisher information matrix.
Read more: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jeffreys_prior
The analytic form is not known for most PDFs, but it is for simple cases like the Poisson mean, Gaussian mean, Gaussian sigma.
This class uses numerical tricks to calculate the Fisher Information Matrix efficiently. In particular, it takes advantage of a property of the 'Asimov data' as described in Asymptotic formulae for likelihood-based tests of new physics Glen Cowan, Kyle Cranmer, Eilam Gross, Ofer Vitells http://arxiv.org/abs/arXiv:1007.1727
This Demo has four parts:
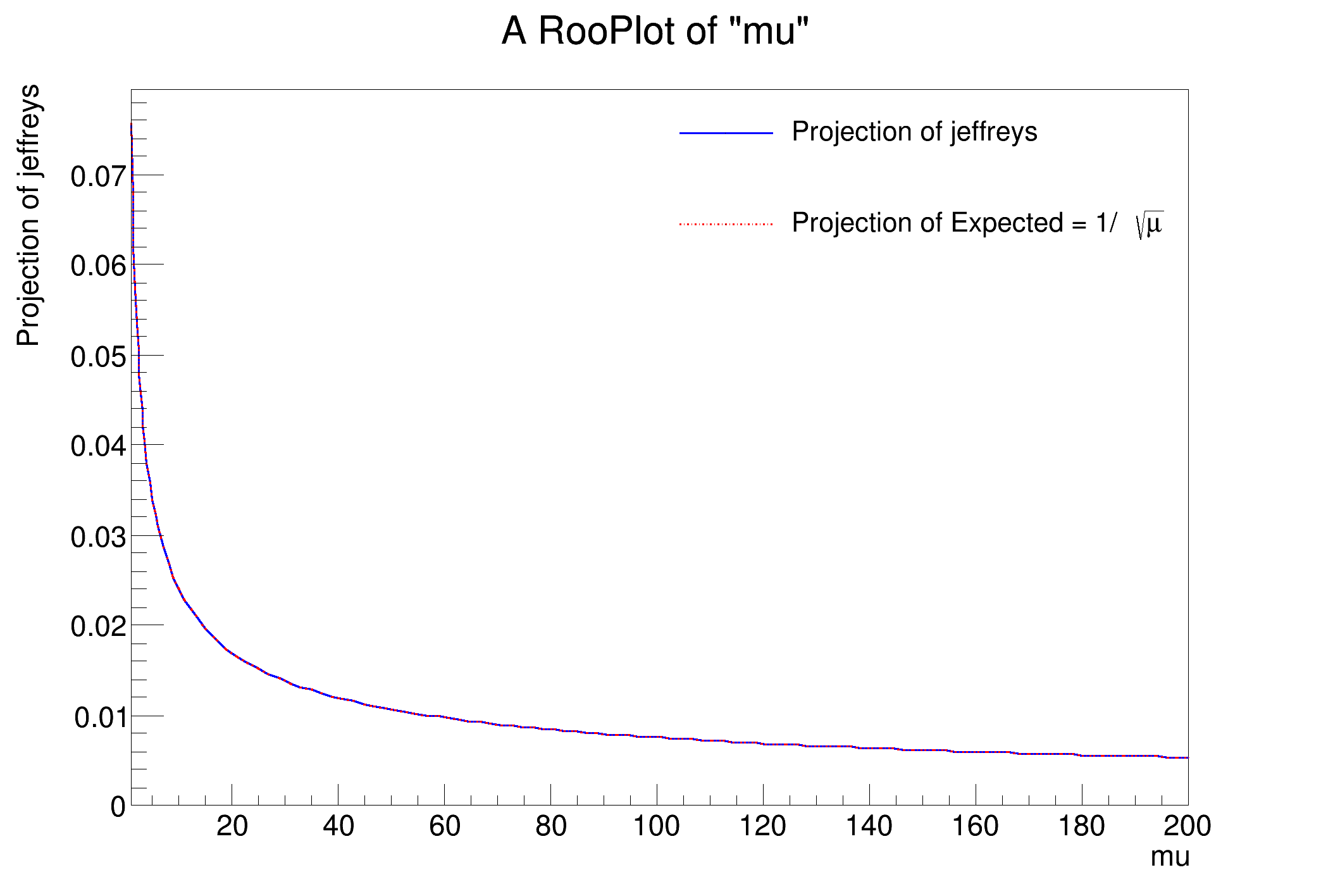
- TestJeffreysPriorDemo – validates Poisson mean case 1/sqrt(mu)
- TestJeffreysGaussMean – validates Gaussian mean case
- TestJeffreysGaussSigma – validates Gaussian sigma case 1/sigma
- TestJeffreysGaussMeanAndSigma – demonstrates 2-d example
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- p.d.f. provides expected number of events, including extended term in likelihood.
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- RooAbsMinimizerFcn::setOptimizeConst: activating const optimization
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- The following expressions have been identified as constant and will be precalculated and cached: (u)
Minuit2Minimizer: Minimize with max-calls 500 convergence for edm < 1 strategy 1
Minuit2Minimizer : Valid minimum - status = 0
FVAL = -360.517018598809159
Edm = 4.13877261906962124e-17
Nfcn = 22
mu = 100 +/- 9.98317 (limited)
[#1] INFO:Fitting -- RooAbsPdf::fitTo(p) Calculating sum-of-weights-squared correction matrix for covariance matrix
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- RooAbsMinimizerFcn::setOptimizeConst: deactivating const optimization
RooDataHist::genData[x] = 100 bins (100 weights)
RooFitResult: minimized FCN value: -360.517, estimated distance to minimum: 3.66543e-18
covariance matrix quality: Full, accurate covariance matrix
Status : MINIMIZE=0 HESSE=0 HESSE=0
Floating Parameter FinalValue +/- Error
-------------------- --------------------------
mu 1.0000e+02 +/- 1.00e+01
variance = 100.016
stdev = 10.0008
jeffreys = 0.0999921
[#1] INFO:NumericIntegration -- RooRealIntegral::init(jeffreys_Int[mu]) using numeric integrator RooAdaptiveGaussKronrodIntegrator1D to calculate Int(mu)
[#1] INFO:NumericIntegration -- RooRealIntegral::init(Expected_Int[mu]) using numeric integrator RooRombergIntegrator to calculate Int(mu)
void rs302_JeffreysPriorDemo()
{
w.factory(
"Uniform::u(x[0,1])");
w.factory(
"mu[100,1,200]");
w.factory(
"ExtendPdf::p(u,mu)");
std::unique_ptr<RooDataHist> asimov{
w.pdf(
"p")->generateBinned(*
w.var(
"x"), ExpectedData())};
std::unique_ptr<RooFitResult> res{
w.pdf(
"p")->fitTo(*asimov, Save(), SumW2Error(
kTRUE))};
asimov->Print();
res->Print();
w.defineSet(
"poi",
"mu");
auto legend =
plot->BuildLegend();
}
void TestJeffreysGaussMean()
{
w.factory(
"Gaussian::g(x[0,-20,20],mu[0,-5.,5],sigma[1,0,10])");
w.factory(
"n[10,.1,200]");
w.factory(
"ExtendPdf::p(g,n)");
w.var(
"sigma")->setConstant();
w.var(
"n")->setConstant();
std::unique_ptr<RooDataHist> asimov{
w.pdf(
"p")->generateBinned(*
w.var(
"x"),
ExpectedData())};
asimov->Print();
res->Print();
w.defineSet(
"poi",
"mu");
pi.getParameters(*temp)->
Print();
auto legend =
plot->BuildLegend();
}
void TestJeffreysGaussSigma()
{
w.factory(
"Gaussian::g(x[0,-20,20],mu[0,-5,5],sigma[1,1,5])");
w.factory(
"n[100,.1,2000]");
w.factory(
"ExtendPdf::p(g,n)");
w.var(
"mu")->setConstant();
w.var(
"n")->setConstant();
w.var(
"x")->setBins(301);
std::unique_ptr<RooDataHist> asimov{
w.pdf(
"p")->generateBinned(*
w.var(
"x"),
ExpectedData())};
asimov->Print();
res->Print();
w.defineSet(
"poi",
"sigma");
pi.getParameters(*temp)->
Print();
auto legend =
plot->BuildLegend();
}
void TestJeffreysGaussMeanAndSigma()
{
w.factory(
"Gaussian::g(x[0,-20,20],mu[0,-5,5],sigma[1,1.,5.])");
w.factory(
"n[100,.1,2000]");
w.factory(
"ExtendPdf::p(g,n)");
w.var(
"n")->setConstant();
w.var(
"x")->setBins(301);
std::unique_ptr<RooDataHist> asimov{
w.pdf(
"p")->generateBinned(*
w.var(
"x"),
ExpectedData())};
asimov->Print();
res->Print();
w.defineSet(
"poi",
"mu,sigma");
pi.getParameters(*temp)->
Print();
TH1 *Jeff2d = pi.createHistogram(
"2dJeffreys", *
w.var(
"mu"),
Binning(10, -5., 5),
YVar(*
w.var(
"sigma"),
Binning(10, 1., 5.)));
}
winID h TVirtualViewer3D TVirtualGLPainter char TVirtualGLPainter plot
void Print(Option_t *options=nullptr) const override
This method must be overridden when a class wants to print itself.
RooArgSet is a container object that can hold multiple RooAbsArg objects.
RooGenericPdf is a concrete implementation of a probability density function, which takes a RooArgLis...
Implementation of Jeffrey's prior.
A RooPlot is a plot frame and a container for graphics objects within that frame.
Persistable container for RooFit projects.
TH1 is the base class of all histogram classes in ROOT.
void Draw(Option_t *option="") override
Draw this histogram with options.
Double_t Determinant() const override
TMatrixTSym< Element > & Invert(Double_t *det=nullptr)
Invert the matrix and calculate its determinant Notice that the LU decomposition is used instead of B...
virtual TObject * DrawClone(Option_t *option="") const
Draw a clone of this object in the current selected pad with: gROOT->SetSelectedPad(c1).
virtual void Draw(Option_t *option="")
Default Draw method for all objects.
RooCmdArg YVar(const RooAbsRealLValue &var, const RooCmdArg &arg={})
RooCmdArg Save(bool flag=true)
RooCmdArg SumW2Error(bool flag)
RooCmdArg ExpectedData(bool flag=true)
RooCmdArg Binning(const RooAbsBinning &binning)
RooCmdArg LineColor(Color_t color)
RooCmdArg LineStyle(Style_t style)
VecExpr< UnaryOp< Sqrt< T >, VecExpr< A, T, D >, T >, T, D > sqrt(const VecExpr< A, T, D > &rhs)
The namespace RooFit contains mostly switches that change the behaviour of functions of PDFs (or othe...
- Author
- Kyle Cranmer
Definition in file rs302_JeffreysPriorDemo.C.


