

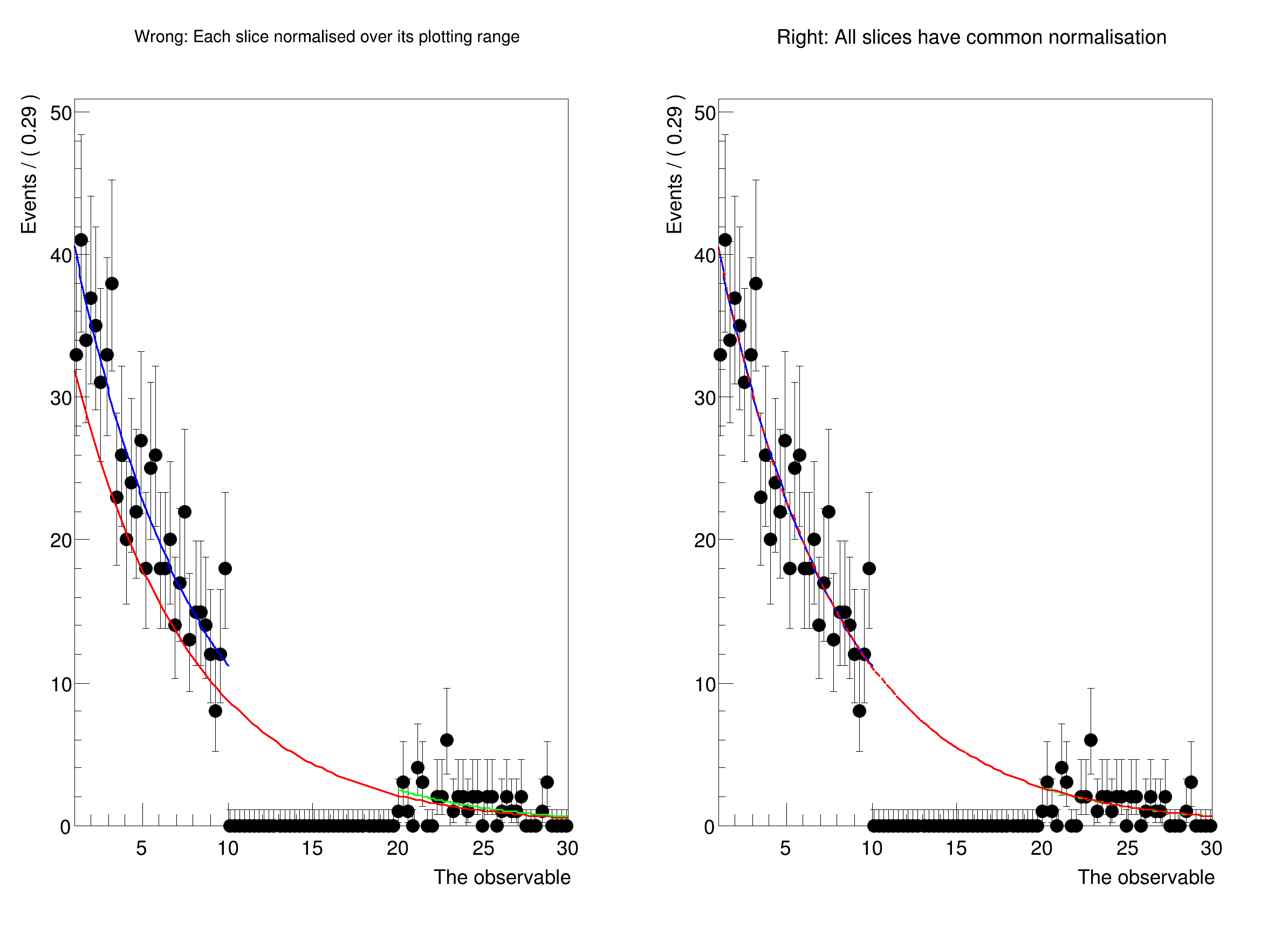
Plot a PDF in disjunct ranges, and get normalisation right.
Usually, when comparing a fit to data, one should first plot the data, and then the PDF. In this case, the PDF is automatically normalised to match the number of data events in the plot. However, when plotting only a sub-range, when e.g. a signal region has to be blinded, one has to exclude the blinded region from the computation of the normalisation.
In this tutorial, we show how to explicitly choose the normalisation when plotting using NormRange().
Thanks to Marc Escalier for asking how to do this correctly.
{
RooRealVar tau(
"tau",
"The exponent", -0.1337, -10., -0.1);
x.setRange(
"full", 1, 30);
x.setRange(
"left", 1, 10);
x.setRange(
"right", 20, 30);
std::unique_ptr<RooDataSet>
data{expo.generate(
x, 1000)};
std::unique_ptr<RooAbsData> blindedData{
data->reduce(CutRange(
"left,right"))};
tau.setVal(-2.);
expo.removeStringAttribute("fitrange");
std::cout << "Now plotting with unique normalisation for each slice." << std::endl;
blindedData->plotOn(plotFrame);
std::cout << "\n\nNow plotting with correct norm ranges:" << std::endl;
blindedData->plotOn(plotFrameWithNormRange);
plotFrameWithNormRange->
Draw();
}
Option_t Option_t TPoint TPoint const char GetTextMagnitude GetFillStyle GetLineColor GetLineWidth GetMarkerStyle GetTextAlign GetTextColor GetTextSize void data
A RooPlot is a plot frame and a container for graphics objects within that frame.
static RooPlot * frame(const RooAbsRealLValue &var, double xmin, double xmax, Int_t nBins)
Create a new frame for a given variable in x.
void Draw(Option_t *options=nullptr) override
Draw this plot and all of the elements it contains.
RooRealVar represents a variable that can be changed from the outside.
void Draw(Option_t *option="") override
Draw a canvas.
TVirtualPad * cd(Int_t subpadnumber=0) override
Set current canvas & pad.
void Divide(Int_t nx=1, Int_t ny=1, Float_t xmargin=0.01, Float_t ymargin=0.01, Int_t color=0) override
Automatic pad generation by division.
RooCmdArg Title(const char *name)
RooCmdArg PrintLevel(Int_t code)
RooCmdArg NormRange(const char *rangeNameList)
RooCmdArg LineColor(Color_t color)
RooCmdArg LineStyle(Style_t style)
The namespace RooFit contains mostly switches that change the behaviour of functions of PDFs (or othe...
[#1] INFO:Eval -- RooRealVar::setRange(x) new range named 'full' created with bounds [1,30]
[#1] INFO:Eval -- RooRealVar::setRange(x) new range named 'left' created with bounds [1,10]
[#1] INFO:Eval -- RooRealVar::setRange(x) new range named 'right' created with bounds [20,30]
[#1] INFO:Eval -- RooRealVar::setRange(x) new range named 'fit_nll_expo_expoData_left' created with bounds [1,10]
[#1] INFO:Eval -- RooRealVar::setRange(x) new range named 'fit_nll_expo_expoData_right' created with bounds [20,30]
[#1] INFO:Fitting -- RooAbsOptTestStatistic::ctor(nll_expo_expoData) constructing test statistic for sub-range named left,right
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- RooAbsMinimizerFcn::setOptimizeConst: activating const optimization
[#1] INFO:Minimization -- RooAbsMinimizerFcn::setOptimizeConst: deactivating const optimization
Now plotting with unique normalisation for each slice.
[#1] INFO:Plotting -- RooAbsPdf::plotOn(expo) only plotting range 'full', curve is normalized to data in given range
[#1] INFO:Plotting -- RooAbsPdf::plotOn(expo) only plotting range 'left', curve is normalized to data in given range
[#1] INFO:Plotting -- RooAbsPdf::plotOn(expo) only plotting range 'right', curve is normalized to data in given range
Now plotting with correct norm ranges:
[#1] INFO:Plotting -- RooAbsPdf::plotOn(expo) only plotting range 'left'
[#1] INFO:Plotting -- RooAbsPdf::plotOn(expo) p.d.f. curve is normalized using explicit choice of ranges 'left,right'
[#1] INFO:Plotting -- RooAbsPdf::plotOn(expo) only plotting range 'right'
[#1] INFO:Plotting -- RooAbsPdf::plotOn(expo) p.d.f. curve is normalized using explicit choice of ranges 'left,right'
[#1] INFO:Plotting -- RooAbsPdf::plotOn(expo) only plotting range 'full'
[#1] INFO:Plotting -- RooAbsPdf::plotOn(expo) p.d.f. curve is normalized using explicit choice of ranges 'left,right'
- Date
- March 2020
- Author
- Stephan Hageboeck
Definition in file rf212_plottingInRanges_blinding.C.


