

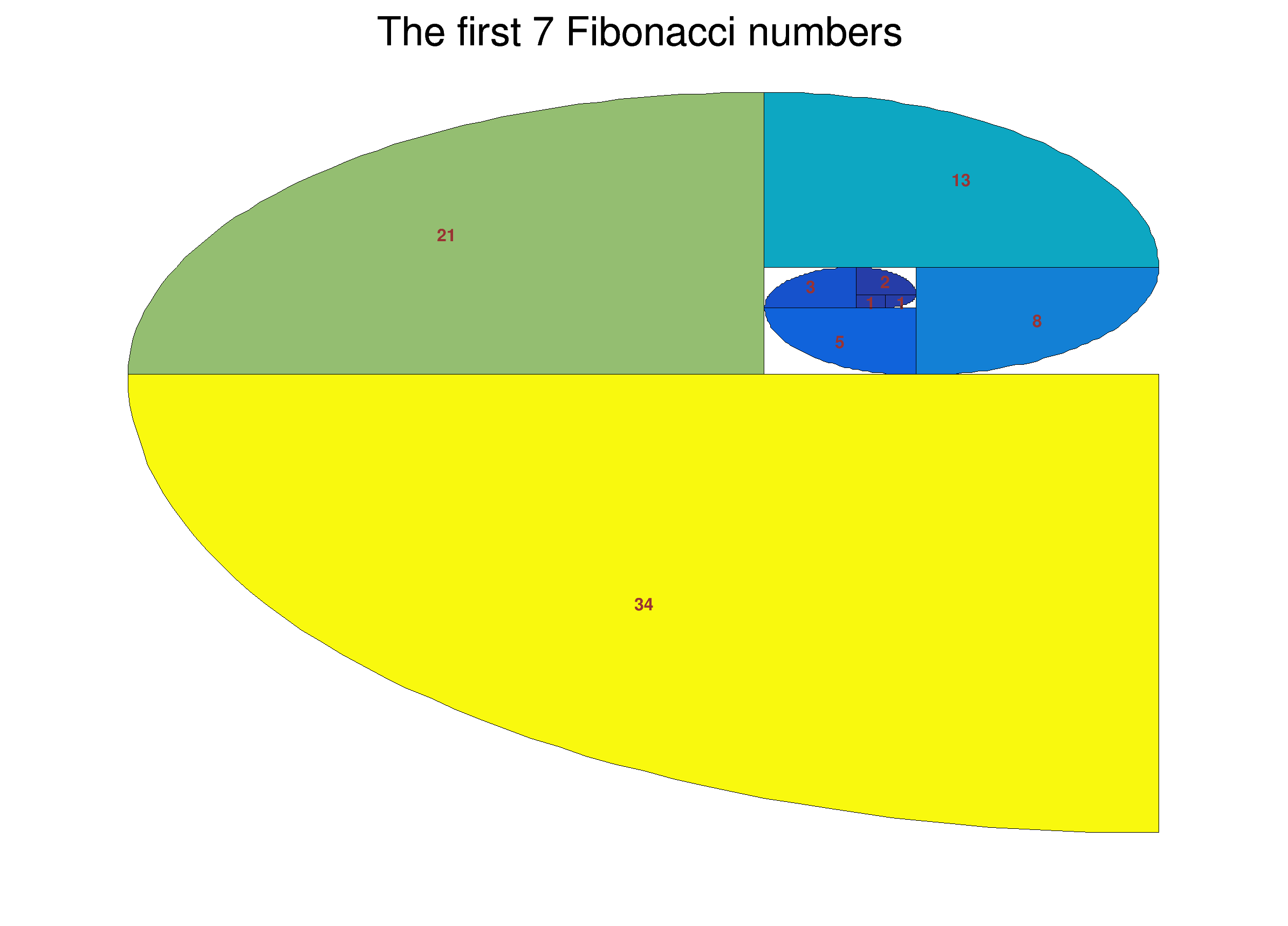
A TH2Poly build with Fibonacci numbers.
In mathematics, the Fibonacci sequence is a suite of integer in which every number is the sum of the two preceding one.
The first 10 Fibonacci numbers are:
1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, ...
This tutorial computes Fibonacci numbers and uses them to build a TH2Poly producing the "Fibonacci spiral" created by drawing circular arcs connecting the opposite corners of squares in the Fibonacci tiling.
void Arc(
int n,
double a,
double r,
double *px,
double *py);
void AddFibonacciBin(
TH2Poly *h2pf,
double N);
void Fibonacci(
int N=7) {
C->SetFrameLineWidth(0);
double f0 = 0.;
double ft;
AddFibonacciBin(h2pf,
f1);
for (
int i=0; i<=
N; i++) {
f0 = ft;
AddFibonacciBin(h2pf,
f1);
}
h2pf->
Draw(
"A COL L TEXT");
}
void Arc(
int n,
double a,
double r,
double *px,
double *py) {
for (
int i = 2; i<=
n-2; i++) {
}
}
void AddFibonacciBin(
TH2Poly *h2pf,
double N) {
double X1 = 0.;
double Y1 = 0.;
double X2 = 1.;
double Y2 = 1.;
static int MoveId = 0;
static double B = 0.;
const int NP = 50;
double px[NP];
double py[NP];
switch (MoveId) {
case 1:
px[0] = X1;
py[0] = Y2;
px[1] = X1;
py[1] = Y1;
px[NP-1] = X2;
py[NP-1] = Y2;
Arc(NP,3*pi2,(
double)
N,px,py);
break;
case 2:
px[0] = X1;
py[0] = Y1;
px[1] = X2;
py[1] = Y1;
px[NP-1] = X1;
py[NP-1] = Y2;
Arc(NP,0.,(
double)
N,px,py);
break;
case 3:
Y1 = B;
px[0] = X2;
py[0] = Y1;
px[1] = X2;
py[1] = Y2;
px[NP-1] = X1;
py[NP-1] = Y1;
Arc(NP,pi2,(
double)
N,px,py);
break;
case 4:
Y1 = B;
px[0] = X2;
py[0] = Y2;
px[1] = X1;
py[1] = Y2;
px[NP-1] = X2;
py[NP-1] = Y1;
Arc(NP,2*pi2,(
double)
N,px,py);
break;
}
if (MoveId==0) h2pf->
AddBin(X1,Y1,X2,Y2);
else h2pf->
AddBin(NP, px ,py);
h2pf->
Fill((X1+X2)/2.5, (Y1+Y2)/2.5,
N);
MoveId++;
if (MoveId==5) MoveId=1;
}
#define R(a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i)
Option_t Option_t TPoint TPoint const char GetTextMagnitude GetFillStyle GetLineColor GetLineWidth GetMarkerStyle GetTextAlign GetTextColor GetTextSize void char Point_t Rectangle_t WindowAttributes_t Float_t r
char * Form(const char *fmt,...)
Formats a string in a circular formatting buffer.
virtual void SetMarkerColor(Color_t mcolor=1)
Set the marker color.
void SetTitle(const char *title) override
Change (i.e.
void Draw(Option_t *option="") override
Draw this histogram with options.
virtual void SetStats(Bool_t stats=kTRUE)
Set statistics option on/off.
2D Histogram with Polygonal Bins
Int_t Fill(Double_t x, Double_t y) override
Increment the bin containing (x,y) by 1.
virtual Int_t AddBin(TObject *poly)
Adds a new bin to the histogram.
RooArgList L(Args_t &&... args)
Double_t Cos(Double_t)
Returns the cosine of an angle of x radians.
Double_t Sin(Double_t)
Returns the sine of an angle of x radians.
- Author
- Olivier Couet
Definition in file Fibonacci.C.


