 |
ROOT 6.12/07 Reference Guide |
 |
ROOT 6.12/07 Reference Guide |
Advanced 3-dimensional spectra processing functions.
This class contains advanced spectra processing functions.
The algorithms in this class have been published in the following references:
[1] M.Morhac et al.: Background elimination methods for multidimensional coincidence gamma-ray spectra. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 401 (1997) 113-132.
[2] M.Morhac et al.: Efficient one- and two-dimensional Gold deconvolution and its application to gamma-ray spectra decomposition. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 401 (1997) 385-408.
[3] M. Morhac et al.: Efficient algorithm of multidimensional deconvolution and its application to nuclear data processing. Digital Signal Processing, Vol. 13, No. 1, (2003), 144-171.
[4] M.Morhac et al.: Identification of peaks in multidimensional coincidence gamma-ray spectra. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Research Physics A 443(2000), 108-125.
These NIM papers are also available as Postscript files from:
See also the online documentation and tutorials.
Definition at line 18 of file TSpectrum3.h.
Public Types | |
| enum | { kBackIncreasingWindow =0, kBackDecreasingWindow =1, kBackSuccessiveFiltering =0, kBackOneStepFiltering =1 } |
 Public Types inherited from TObject Public Types inherited from TObject | |
| enum | { kIsOnHeap = 0x01000000, kNotDeleted = 0x02000000, kZombie = 0x04000000, kInconsistent = 0x08000000, kBitMask = 0x00ffffff } |
| enum | { kSingleKey = BIT(0), kOverwrite = BIT(1), kWriteDelete = BIT(2) } |
| enum | EDeprecatedStatusBits { kObjInCanvas = BIT(3) } |
| enum | EStatusBits { kCanDelete = BIT(0), kMustCleanup = BIT(3), kIsReferenced = BIT(4), kHasUUID = BIT(5), kCannotPick = BIT(6), kNoContextMenu = BIT(8), kInvalidObject = BIT(13) } |
Public Member Functions | |
| TSpectrum3 () | |
| Constructor. More... | |
| TSpectrum3 (Int_t maxpositions, Double_t resolution=1) | |
| virtual | ~TSpectrum3 () |
| Destructor. More... | |
| virtual const char * | Background (const TH1 *hist, Int_t niter, Option_t *option="goff") |
| This function calculates background spectrum from source in h. More... | |
| const char * | Background (Double_t ***spectrum, Int_t ssizex, Int_t ssizey, Int_t ssizez, Int_t numberIterationsX, Int_t numberIterationsY, Int_t numberIterationsZ, Int_t direction, Int_t filterType) |
| This function calculates background spectrum from source spectrum. More... | |
| const char * | Deconvolution (Double_t ***source, const Double_t ***resp, Int_t ssizex, Int_t ssizey, Int_t ssizez, Int_t numberIterations, Int_t numberRepetitions, Double_t boost) |
| This function calculates deconvolution from source spectrum according to response spectrum The result is placed in the cube pointed by source pointer. More... | |
| TH1 * | GetHistogram () const |
| Int_t | GetNPeaks () const |
| Double_t * | GetPositionX () const |
| Double_t * | GetPositionY () const |
| Double_t * | GetPositionZ () const |
| virtual void | Print (Option_t *option="") const |
| Print the array of positions. More... | |
| virtual Int_t | Search (const TH1 *hist, Double_t sigma=2, Option_t *option="goff", Double_t threshold=0.05) |
| This function searches for peaks in source spectrum in hin The number of found peaks and their positions are written into the members fNpeaks and fPositionX. More... | |
| Int_t | SearchFast (const Double_t ***source, Double_t ***dest, Int_t ssizex, Int_t ssizey, Int_t ssizez, Double_t sigma, Double_t threshold, Bool_t markov, Int_t averWindow) |
| THREE-DIMENSIONAL CLASSICAL PEAK SEARCH FUNCTION This function searches for peaks in source spectrum using the algorithm based on smoothed second differences. More... | |
| Int_t | SearchHighRes (const Double_t ***source, Double_t ***dest, Int_t ssizex, Int_t ssizey, Int_t ssizez, Double_t sigma, Double_t threshold, Bool_t backgroundRemove, Int_t deconIterations, Bool_t markov, Int_t averWindow) |
| This function searches for peaks in source spectrum It is based on deconvolution method. More... | |
| void | SetResolution (Double_t resolution=1) |
| NOT USED resolution: determines resolution of the neighbouring peaks default value is 1 correspond to 3 sigma distance between peaks. More... | |
| const char * | SmoothMarkov (Double_t ***source, Int_t ssizex, Int_t ssizey, Int_t ssizez, Int_t averWindow) |
| This function calculates smoothed spectrum from source spectrum based on Markov chain method. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from TNamed Public Member Functions inherited from TNamed | |
| TNamed () | |
| TNamed (const char *name, const char *title) | |
| TNamed (const TString &name, const TString &title) | |
| TNamed (const TNamed &named) | |
| TNamed copy ctor. More... | |
| virtual | ~TNamed () |
| TNamed destructor. More... | |
| virtual void | Clear (Option_t *option="") |
| Set name and title to empty strings (""). More... | |
| virtual TObject * | Clone (const char *newname="") const |
| Make a clone of an object using the Streamer facility. More... | |
| virtual Int_t | Compare (const TObject *obj) const |
| Compare two TNamed objects. More... | |
| virtual void | Copy (TObject &named) const |
| Copy this to obj. More... | |
| virtual void | FillBuffer (char *&buffer) |
| Encode TNamed into output buffer. More... | |
| virtual const char * | GetName () const |
| Returns name of object. More... | |
| virtual const char * | GetTitle () const |
| Returns title of object. More... | |
| virtual ULong_t | Hash () const |
| Return hash value for this object. More... | |
| virtual Bool_t | IsSortable () const |
| virtual void | ls (Option_t *option="") const |
| List TNamed name and title. More... | |
| TNamed & | operator= (const TNamed &rhs) |
| TNamed assignment operator. More... | |
| virtual void | SetName (const char *name) |
| Set the name of the TNamed. More... | |
| virtual void | SetNameTitle (const char *name, const char *title) |
| Set all the TNamed parameters (name and title). More... | |
| virtual void | SetTitle (const char *title="") |
| Set the title of the TNamed. More... | |
| virtual Int_t | Sizeof () const |
| Return size of the TNamed part of the TObject. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from TObject Public Member Functions inherited from TObject | |
| TObject () | |
| TObject constructor. More... | |
| TObject (const TObject &object) | |
| TObject copy ctor. More... | |
| virtual | ~TObject () |
| TObject destructor. More... | |
| void | AbstractMethod (const char *method) const |
| Use this method to implement an "abstract" method that you don't want to leave purely abstract. More... | |
| virtual void | AppendPad (Option_t *option="") |
| Append graphics object to current pad. More... | |
| virtual void | Browse (TBrowser *b) |
| Browse object. May be overridden for another default action. More... | |
| ULong_t | CheckedHash () |
| Checked and record whether for this class has a consistent Hash/RecursiveRemove setup (*) and then return the regular Hash value for this object. More... | |
| virtual const char * | ClassName () const |
| Returns name of class to which the object belongs. More... | |
| virtual void | Delete (Option_t *option="") |
| Delete this object. More... | |
| virtual Int_t | DistancetoPrimitive (Int_t px, Int_t py) |
| Computes distance from point (px,py) to the object. More... | |
| virtual void | Draw (Option_t *option="") |
| Default Draw method for all objects. More... | |
| virtual void | DrawClass () const |
| Draw class inheritance tree of the class to which this object belongs. More... | |
| virtual TObject * | DrawClone (Option_t *option="") const |
Draw a clone of this object in the current selected pad for instance with: gROOT->SetSelectedPad(gPad). More... | |
| virtual void | Dump () const |
| Dump contents of object on stdout. More... | |
| virtual void | Error (const char *method, const char *msgfmt,...) const |
| Issue error message. More... | |
| virtual void | Execute (const char *method, const char *params, Int_t *error=0) |
| Execute method on this object with the given parameter string, e.g. More... | |
| virtual void | Execute (TMethod *method, TObjArray *params, Int_t *error=0) |
| Execute method on this object with parameters stored in the TObjArray. More... | |
| virtual void | ExecuteEvent (Int_t event, Int_t px, Int_t py) |
| Execute action corresponding to an event at (px,py). More... | |
| virtual void | Fatal (const char *method, const char *msgfmt,...) const |
| Issue fatal error message. More... | |
| virtual TObject * | FindObject (const char *name) const |
| Must be redefined in derived classes. More... | |
| virtual TObject * | FindObject (const TObject *obj) const |
| Must be redefined in derived classes. More... | |
| virtual Option_t * | GetDrawOption () const |
| Get option used by the graphics system to draw this object. More... | |
| virtual const char * | GetIconName () const |
| Returns mime type name of object. More... | |
| virtual char * | GetObjectInfo (Int_t px, Int_t py) const |
| Returns string containing info about the object at position (px,py). More... | |
| virtual Option_t * | GetOption () const |
| virtual UInt_t | GetUniqueID () const |
| Return the unique object id. More... | |
| virtual Bool_t | HandleTimer (TTimer *timer) |
| Execute action in response of a timer timing out. More... | |
| Bool_t | HasInconsistentHash () const |
| Return true is the type of this object is known to have an inconsistent setup for Hash and RecursiveRemove (i.e. More... | |
| virtual void | Info (const char *method, const char *msgfmt,...) const |
| Issue info message. More... | |
| virtual Bool_t | InheritsFrom (const char *classname) const |
| Returns kTRUE if object inherits from class "classname". More... | |
| virtual Bool_t | InheritsFrom (const TClass *cl) const |
| Returns kTRUE if object inherits from TClass cl. More... | |
| virtual void | Inspect () const |
| Dump contents of this object in a graphics canvas. More... | |
| void | InvertBit (UInt_t f) |
| virtual Bool_t | IsEqual (const TObject *obj) const |
| Default equal comparison (objects are equal if they have the same address in memory). More... | |
| virtual Bool_t | IsFolder () const |
| Returns kTRUE in case object contains browsable objects (like containers or lists of other objects). More... | |
| R__ALWAYS_INLINE Bool_t | IsOnHeap () const |
| R__ALWAYS_INLINE Bool_t | IsZombie () const |
| void | MayNotUse (const char *method) const |
| Use this method to signal that a method (defined in a base class) may not be called in a derived class (in principle against good design since a child class should not provide less functionality than its parent, however, sometimes it is necessary). More... | |
| virtual Bool_t | Notify () |
| This method must be overridden to handle object notification. More... | |
| void | Obsolete (const char *method, const char *asOfVers, const char *removedFromVers) const |
| Use this method to declare a method obsolete. More... | |
| void | operator delete (void *ptr) |
| Operator delete. More... | |
| void | operator delete[] (void *ptr) |
| Operator delete []. More... | |
| void * | operator new (size_t sz) |
| void * | operator new (size_t sz, void *vp) |
| void * | operator new[] (size_t sz) |
| void * | operator new[] (size_t sz, void *vp) |
| TObject & | operator= (const TObject &rhs) |
| TObject assignment operator. More... | |
| virtual void | Paint (Option_t *option="") |
| This method must be overridden if a class wants to paint itself. More... | |
| virtual void | Pop () |
| Pop on object drawn in a pad to the top of the display list. More... | |
| virtual Int_t | Read (const char *name) |
| Read contents of object with specified name from the current directory. More... | |
| virtual void | RecursiveRemove (TObject *obj) |
| Recursively remove this object from a list. More... | |
| void | ResetBit (UInt_t f) |
| virtual void | SaveAs (const char *filename="", Option_t *option="") const |
| Save this object in the file specified by filename. More... | |
| virtual void | SavePrimitive (std::ostream &out, Option_t *option="") |
| Save a primitive as a C++ statement(s) on output stream "out". More... | |
| void | SetBit (UInt_t f, Bool_t set) |
| Set or unset the user status bits as specified in f. More... | |
| void | SetBit (UInt_t f) |
| virtual void | SetDrawOption (Option_t *option="") |
| Set drawing option for object. More... | |
| virtual void | SetUniqueID (UInt_t uid) |
| Set the unique object id. More... | |
| virtual void | SysError (const char *method, const char *msgfmt,...) const |
| Issue system error message. More... | |
| R__ALWAYS_INLINE Bool_t | TestBit (UInt_t f) const |
| Int_t | TestBits (UInt_t f) const |
| virtual void | UseCurrentStyle () |
| Set current style settings in this object This function is called when either TCanvas::UseCurrentStyle or TROOT::ForceStyle have been invoked. More... | |
| virtual void | Warning (const char *method, const char *msgfmt,...) const |
| Issue warning message. More... | |
| virtual Int_t | Write (const char *name=0, Int_t option=0, Int_t bufsize=0) |
| Write this object to the current directory. More... | |
| virtual Int_t | Write (const char *name=0, Int_t option=0, Int_t bufsize=0) const |
| Write this object to the current directory. More... | |
Protected Attributes | |
| TH1 * | fHistogram |
| resulting histogram More... | |
| Int_t | fMaxPeaks |
| Maximum number of peaks to be found. More... | |
| Int_t | fNPeaks |
| number of peaks found More... | |
| Double_t * | fPosition |
| [fNPeaks] array of current peak positions More... | |
| Double_t * | fPositionX |
| [fNPeaks] X positions of peaks More... | |
| Double_t * | fPositionY |
| [fNPeaks] Y positions of peaks More... | |
| Double_t * | fPositionZ |
| [fNPeaks] Z positions of peaks More... | |
| Double_t | fResolution |
| NOT USED resolution of the neighboring peaks More... | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from TNamed Protected Attributes inherited from TNamed | |
| TString | fName |
| TString | fTitle |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from TObject Static Public Member Functions inherited from TObject | |
| static Long_t | GetDtorOnly () |
| Return destructor only flag. More... | |
| static Bool_t | GetObjectStat () |
| Get status of object stat flag. More... | |
| static void | SetDtorOnly (void *obj) |
| Set destructor only flag. More... | |
| static void | SetObjectStat (Bool_t stat) |
| Turn on/off tracking of objects in the TObjectTable. More... | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from TObject Protected Member Functions inherited from TObject | |
| virtual void | DoError (int level, const char *location, const char *fmt, va_list va) const |
| Interface to ErrorHandler (protected). More... | |
| void | MakeZombie () |
#include <TSpectrum3.h>
| anonymous enum |
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| kBackIncreasingWindow | |
| kBackDecreasingWindow | |
| kBackSuccessiveFiltering | |
| kBackOneStepFiltering | |
Definition at line 30 of file TSpectrum3.h.
| TSpectrum3::TSpectrum3 | ( | ) |
Constructor.
Definition at line 58 of file TSpectrum3.cxx.
Definition at line 80 of file TSpectrum3.cxx.
|
virtual |
Destructor.
Definition at line 97 of file TSpectrum3.cxx.
|
virtual |
This function calculates background spectrum from source in h.
The result is placed in the vector pointed by spectrum pointer.
Function parameters:
Definition at line 115 of file TSpectrum3.cxx.
| const char * TSpectrum3::Background | ( | Double_t *** | spectrum, |
| Int_t | ssizex, | ||
| Int_t | ssizey, | ||
| Int_t | ssizez, | ||
| Int_t | numberIterationsX, | ||
| Int_t | numberIterationsY, | ||
| Int_t | numberIterationsZ, | ||
| Int_t | direction, | ||
| Int_t | filterType | ||
| ) |
This function calculates background spectrum from source spectrum.
The result is placed to the array pointed by spectrum pointer.
Function parameters:
Goal: Separation of useful information (peaks) from useless information (background)
It is an extension of one-dimensional SNIP algorithm to another dimension. For details we refer to [2].
The algorithm is analogous to that for 2-dimensional data. For details we refer to TSpectrum2. New value in the estimated channel is calculated as \( a = \nu_{p-1}(i_1, i_2, i_3)\)
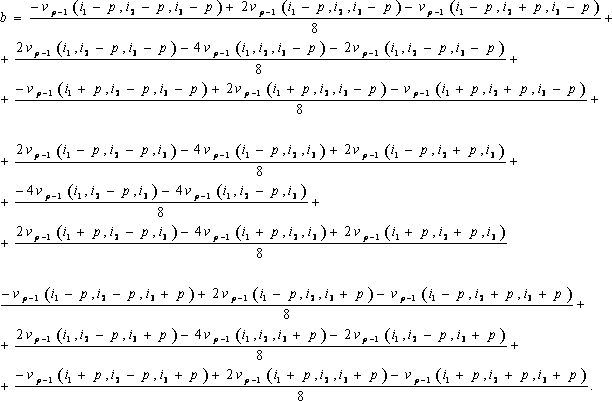
\[ \nu_p(i_1, i_2, i_3) = min (a,b) \]
where p = 1, 2, ..., number_of_iterations.
[1] C. G Ryan et al.: SNIP, a statistics-sensitive background treatment for the quantitative analysis of PIXE spectra in geoscience applications. NIM, B34 (1988), 396-402./
[2] M.Morhac, J. Kliman, V. Matouoek, M. Veselsky, I. Turzo.: Background elimination methods for multidimensional gamma-ray spectra. NIM, A401 (1997) 113-132.
Example 1- script Back3.c :
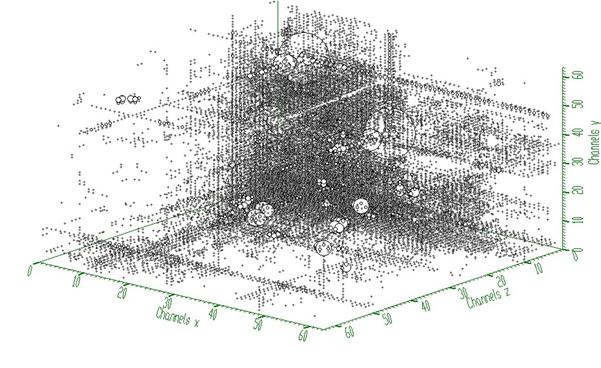
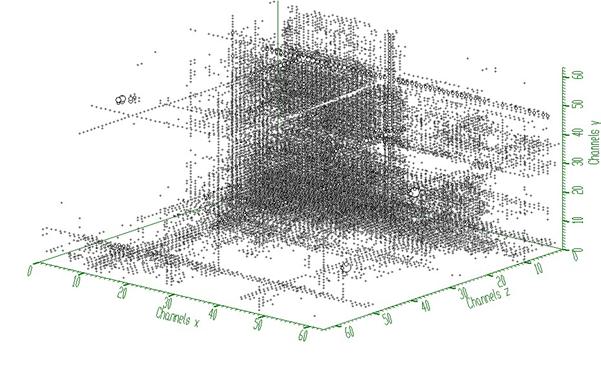
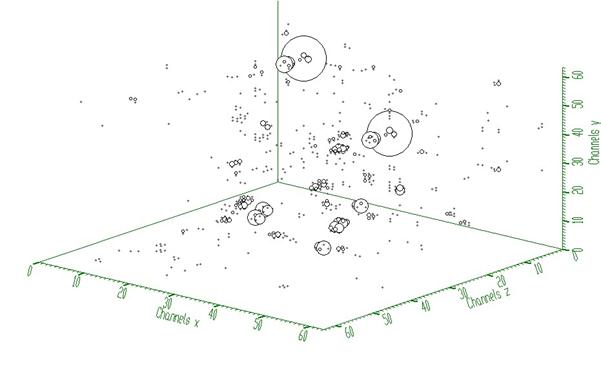
Example to illustrate the background estimator (class TSpectrum3). To execute this example, do:
root > .x Back3.C
Definition at line 384 of file TSpectrum3.cxx.
| const char * TSpectrum3::Deconvolution | ( | Double_t *** | source, |
| const Double_t *** | resp, | ||
| Int_t | ssizex, | ||
| Int_t | ssizey, | ||
| Int_t | ssizez, | ||
| Int_t | numberIterations, | ||
| Int_t | numberRepetitions, | ||
| Double_t | boost | ||
| ) |
This function calculates deconvolution from source spectrum according to response spectrum The result is placed in the cube pointed by source pointer.
Function parameters:
Goal: Improvement of the resolution in spectra, decomposition of multiplets
Mathematical formulation of the 3-dimensional convolution system is
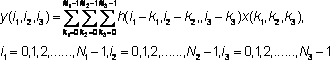
where h(i,j,k) is the impulse response function, x, y are input and output fields, respectively, \( N_1, N_2, N3\), are the lengths of x and h fields
[1] M.Morhac, J. Kliman, V. Matouoek, M. Veselsky, I. Turzo.: Efficient one- and two-dimensional Gold deconvolution and its application to gamma-ray spectra decomposition. NIM, A401 (1997) 385-408.
[2] Morhac M., Matouoek V., Kliman J., Efficient algorithm of multidimensional deconvolution and its application to nuclear data processing, Digital Signal Processing 13 (2003) 144.
response function (usually peak) should be shifted to the beginning of the coordinate system (see Fig. 1)
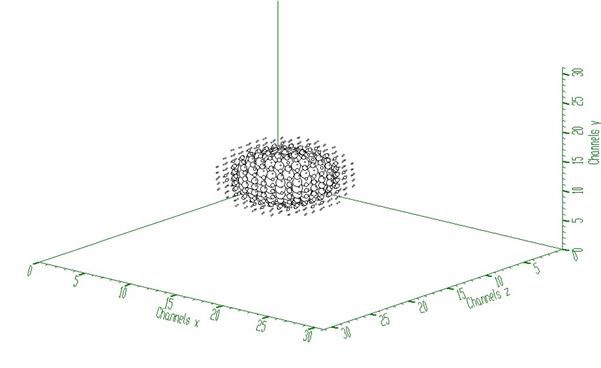
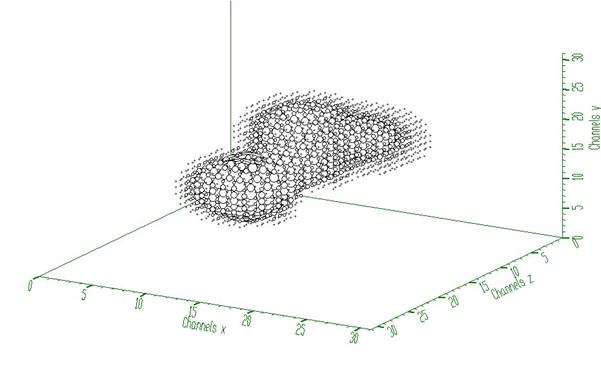
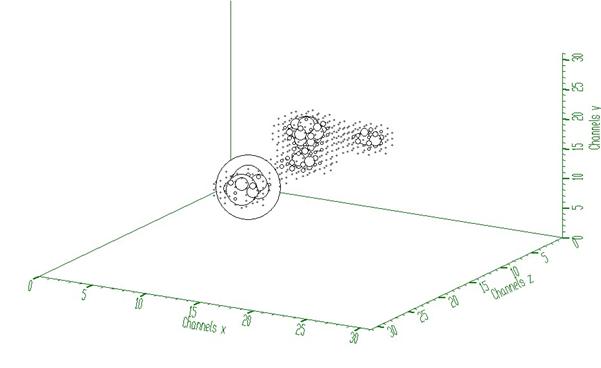
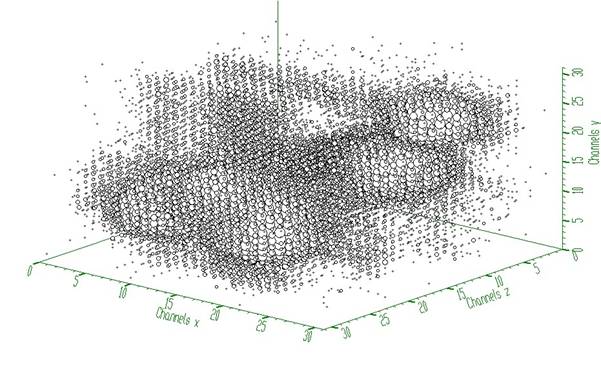
Example to illustrate the Gold deconvolution (class TSpectrum3). To execute this example, do:
root > .x Decon3.C
This example illustrates repeated Gold deconvolution with boosting. After every 10 iterations we apply power function with exponent = 2 to the spectrum given in Fig. 2.
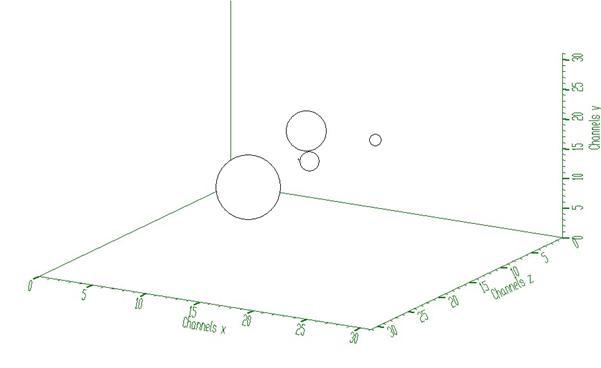
Example to illustrate the Gold deconvolution (class TSpectrum3). To execute this example, do:
root > .x Decon3_hr.C
Definition at line 1592 of file TSpectrum3.cxx.
|
inline |
Definition at line 43 of file TSpectrum3.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 44 of file TSpectrum3.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 45 of file TSpectrum3.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 46 of file TSpectrum3.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 47 of file TSpectrum3.h.
Print the array of positions.
Reimplemented from TNamed.
Definition at line 126 of file TSpectrum3.cxx.
|
virtual |
This function searches for peaks in source spectrum in hin The number of found peaks and their positions are written into the members fNpeaks and fPositionX.
Function parameters:
threshold: (default=0.05) peaks with amplitude less than threshold*highest_peak are discarded.
if option is not equal to "goff" (goff is the default), then a polymarker object is created and added to the list of functions of the histogram. The histogram is drawn with the specified option and the polymarker object drawn on top of the histogram. The polymarker coordinates correspond to the npeaks peaks found in the histogram. A pointer to the polymarker object can be retrieved later via:
Definition at line 160 of file TSpectrum3.cxx.
| Int_t TSpectrum3::SearchFast | ( | const Double_t *** | source, |
| Double_t *** | dest, | ||
| Int_t | ssizex, | ||
| Int_t | ssizey, | ||
| Int_t | ssizez, | ||
| Double_t | sigma, | ||
| Double_t | threshold, | ||
| Bool_t | markov, | ||
| Int_t | averWindow | ||
| ) |
THREE-DIMENSIONAL CLASSICAL PEAK SEARCH FUNCTION This function searches for peaks in source spectrum using the algorithm based on smoothed second differences.
Function parameters:
Definition at line 3152 of file TSpectrum3.cxx.
| Int_t TSpectrum3::SearchHighRes | ( | const Double_t *** | source, |
| Double_t *** | dest, | ||
| Int_t | ssizex, | ||
| Int_t | ssizey, | ||
| Int_t | ssizez, | ||
| Double_t | sigma, | ||
| Double_t | threshold, | ||
| Bool_t | backgroundRemove, | ||
| Int_t | deconIterations, | ||
| Bool_t | markov, | ||
| Int_t | averWindow | ||
| ) |
This function searches for peaks in source spectrum It is based on deconvolution method.
First the background is removed (if desired), then Markov spectrum is calculated (if desired), then the response function is generated according to given sigma and deconvolution is carried out. It returns number of found peaks.
Function parameters:
Goal: to identify automatically the peaks in spectrum with the presence of the continuous background, one- and two-fold coincidences (ridges) and statistical fluctuations - noise.
The common problems connected with correct peak identification in three-dimensional coincidence spectra are
[1] M.A. Mariscotti: A method for identification of peaks in the presence of background and its application to spectrum analysis. NIM 50 (1967), 309-320.
[2] M.Morhac, J. Kliman, V. Matouoek, M. Veselsky, I. Turzo.:Identification of peaks in multidimensional coincidence gamma-ray spectra. NIM, A443 (2000) 108-125.
[3] Z.K. Silagadze, A new algorithm for automatic photo-peak searches. NIM A 376 (1996), 451.
SearchHighRes function provides users with the possibility to vary the input parameters and with the access to the output deconvolved data in the destination spectrum. Based on the output data one can tune the parameters.
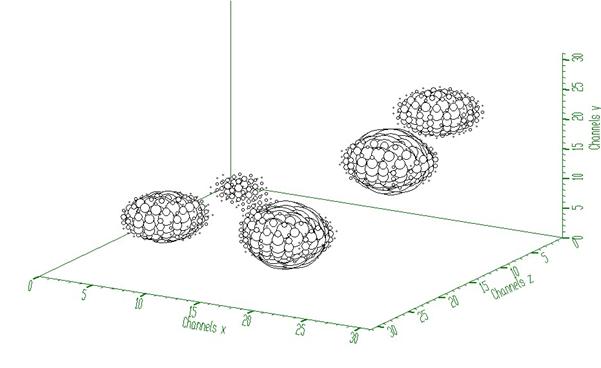
Example to illustrate high resolution peak searching function (class TSpectrum3). To execute this example, do:
root > .x Search3.C
Definition at line 1931 of file TSpectrum3.cxx.
NOT USED resolution: determines resolution of the neighbouring peaks default value is 1 correspond to 3 sigma distance between peaks.
Higher values allow higher resolution (smaller distance between peaks. May be set later through SetResolution.
Definition at line 227 of file TSpectrum3.cxx.
| const char * TSpectrum3::SmoothMarkov | ( | Double_t *** | source, |
| Int_t | ssizex, | ||
| Int_t | ssizey, | ||
| Int_t | ssizez, | ||
| Int_t | averWindow | ||
| ) |
This function calculates smoothed spectrum from source spectrum based on Markov chain method.
The result is placed in the array pointed by spectrum pointer.
Function parameters:
Goal: Suppression of statistical fluctuations the algorithm is based on discrete Markov chain, which has very simple invariant distribution
\[ U_2 = \frac{p_{1.2}}{p_{2,1}}U_1, U_3 = \frac{p_{2,3}}{p_{3,2}}U_2 U_1, ... , U_n = \frac{p_{n-1,n}}{p_{n,n-1}}U_{n-1} ... U_2 U_1 \]
\(U_1\) being defined from the normalization condition \( \sum_{i=1}^{n} U_i = 1\) n is the length of the smoothed spectrum and
\[ p_{i,i\pm1} = A_i \sum_{k=1}^{m} exp\left[\frac{y(i\pm k)-y(i)}{y(i\pm k)+y(i)}\right] \]
is the probability of the change of the peak position from channel i to the channel i+1. \(A_i\) is the normalization constant so that \( p_{i,i-1}+p_{i,i+1}=1\) and m is a width of smoothing window. We have extended this algorithm to three dimensions.
[1] Z.K. Silagadze, A new algorithm for automatic photo-peak searches. NIM A 376 (1996), 451-.
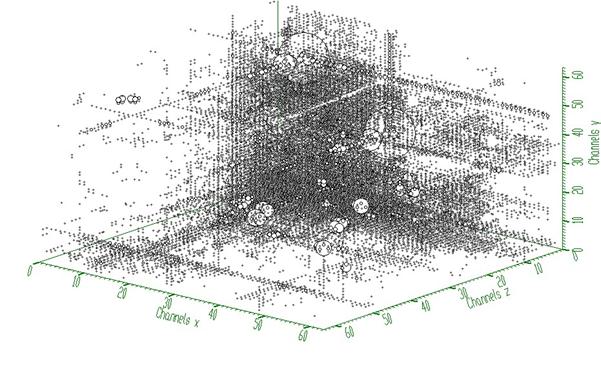
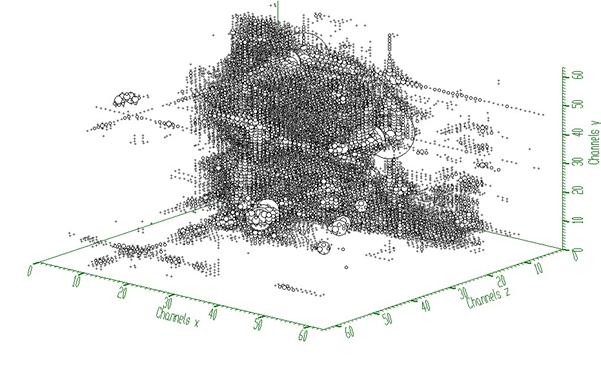
Example to illustrate the Markov smoothing (class TSpectrum3). To execute this example, do:
root > .x SmoothMarkov3.C
Definition at line 859 of file TSpectrum3.cxx.
|
protected |
resulting histogram
Definition at line 27 of file TSpectrum3.h.
|
protected |
Maximum number of peaks to be found.
Definition at line 20 of file TSpectrum3.h.
|
protected |
number of peaks found
Definition at line 21 of file TSpectrum3.h.
|
protected |
[fNPeaks] array of current peak positions
Definition at line 22 of file TSpectrum3.h.
|
protected |
[fNPeaks] X positions of peaks
Definition at line 23 of file TSpectrum3.h.
|
protected |
[fNPeaks] Y positions of peaks
Definition at line 24 of file TSpectrum3.h.
|
protected |
[fNPeaks] Z positions of peaks
Definition at line 25 of file TSpectrum3.h.
|
protected |
NOT USED resolution of the neighboring peaks
Definition at line 26 of file TSpectrum3.h.