

A hypothesis testing example based on number counting with background uncertainty.
A hypothesis testing example based on number counting with background uncertainty.
NOTE: This example is like HybridInstructional, but the model is more clearly generalizable to an analysis with shapes. There is a lot of flexibility for how one models a problem in RooFit/RooStats. Models come in a few common forms:
- standard form: extended PDF of some discriminating variable m: eg: P(m) ~ S*fs(m) + B*fb(m), with S+B events expected in this case the dataset has N rows corresponding to N events and the extended term is Pois(N|S+B)
- fractional form: non-extended PDF of some discriminating variable m: eg: P(m) ~ s*fs(m) + (1-s)*fb(m), where s is a signal fraction in this case the dataset has N rows corresponding to N events and there is no extended term
- number counting form: in which there is no discriminating variable and the counts are modeled directly (see HybridInstructional) eg: P(N) = Pois(N|S+B) in this case the dataset has 1 row corresponding to N events and the extended term is the PDF itself.
Here we convert the number counting form into the standard form by introducing a dummy discriminating variable m with a uniform distribution.
This example:
- demonstrates the usage of the HybridCalcultor (Part 4-6)
- demonstrates the numerical integration of RooFit (Part 2)
- validates the RooStats against an example with a known analytic answer
- demonstrates usage of different test statistics
- explains subtle choices in the prior used for hybrid methods
- demonstrates usage of different priors for the nuisance parameters
The basic setup here is that a main measurement has observed x events with an expectation of s+b. One can choose an ad hoc prior for the uncertainty on b, or try to base it on an auxiliary measurement. In this case, the auxiliary measurement (aka control measurement, sideband) is another counting experiment with measurement y and expectation tau*b. With an 'original prior' on b, called \( \eta(b) \) then one can obtain a posterior from the auxiliary measurement \( \pi(b) = \eta(b) * Pois(y|tau*b) \). This is a principled choice for a prior on b in the main measurement of x, which can then be treated in a hybrid Bayesian/Frequentist way. Additionally, one can try to treat the two measurements simultaneously, which is detailed in Part 6 of the tutorial.
This tutorial is related to the FourBin.C tutorial in the modeling, but focuses on hypothesis testing instead of interval estimation.
More background on this 'prototype problem' can be found in the following papers:
-----------------------------------------
Part 3
Z_Bi p-value (analytic): 0.00094165
Z_Bi significance (analytic): 3.10804
Real time 0:00:00, CP time 0.030
[#0] WARNING:Eval -- RooStatsUtils::MakeNuisancePdf - no constraints found on nuisance parameters in the input model
[#0] WARNING:Eval -- RooStatsUtils::MakeNuisancePdf - no constraints found on nuisance parameters in the input model
-----------------------------------------
Part 4
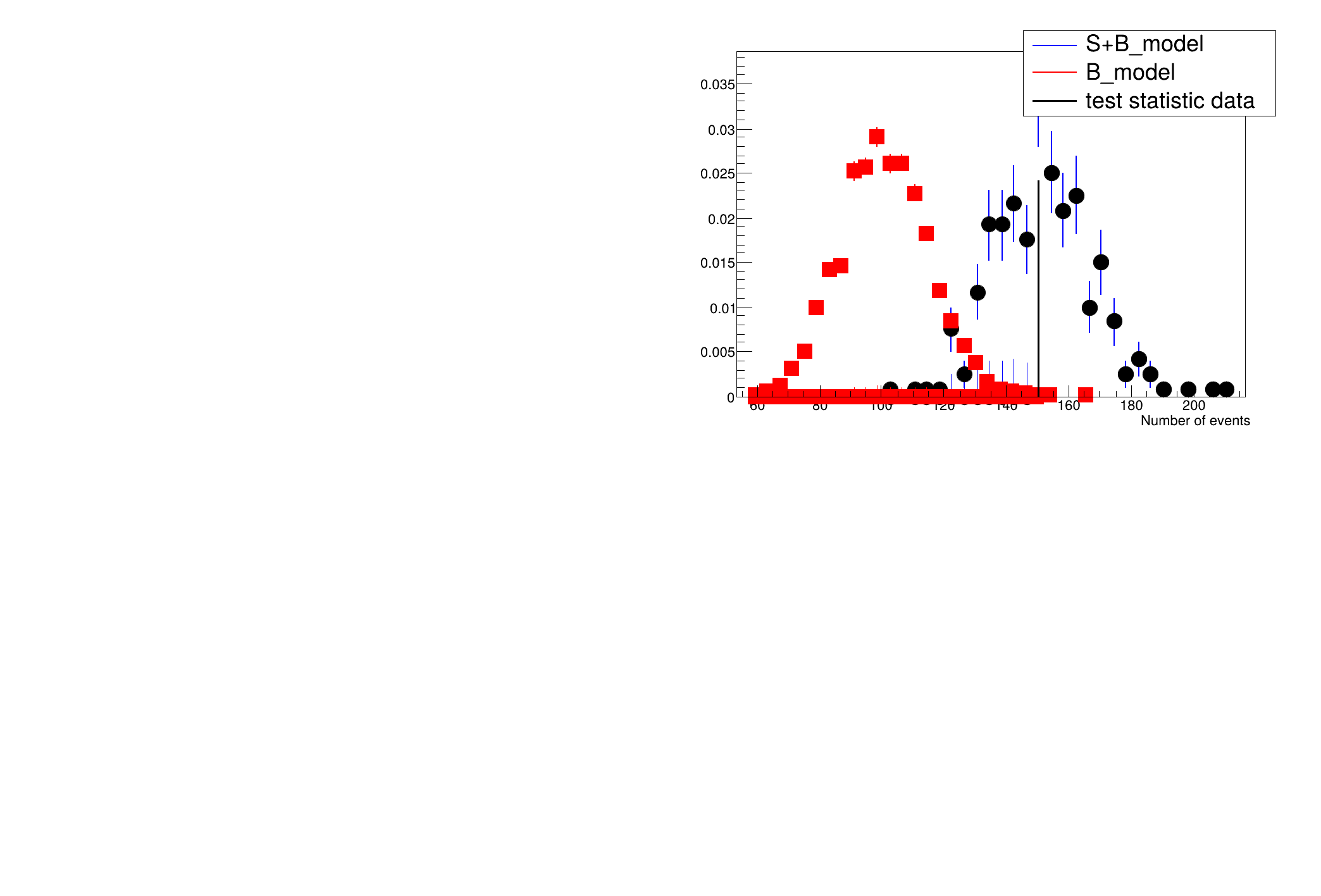
Results HypoTestCalculator_result:
- Null p-value = 0.001 +/- 0.000408044
- Significance = 3.09023 +/- 0.121186 sigma
- Number of Alt toys: 300
- Number of Null toys: 6000
- Test statistic evaluated on data: 150
- CL_b: 0.001 +/- 0.000408044
- CL_s+b: 0.573333 +/- 0.0285553
- CL_s: 573.333 +/- 235.682
Real time 0:00:04, CP time 4.600
public:
{
for (
int i = 0; i <
data.numEntries(); i++) {
value +=
data.get(i)->getRealValue(fColumnName.c_str());
}
}
virtual const TString GetVarName()
const {
return fColumnName; }
private:
string fColumnName;
protected:
};
{
w->factory(
"Uniform::f(m[0,1])");
w->factory(
"ExtendPdf::px(f,sum::splusb(s[0,0,100],b[100,0.1,300]))");
w->factory(
"Poisson::py(y[100,0.1,500],prod::taub(tau[1.],b))");
w->factory(
"PROD::model(px,py)");
w->factory(
"Uniform::prior_b(b)");
double p_Bi = NumberCountingUtils::BinomialWithTauObsP(150, 100, 1);
double Z_Bi = NumberCountingUtils::BinomialWithTauObsZ(150, 100, 1);
cout << "-----------------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "Part 3" << endl;
std::cout <<
"Z_Bi p-value (analytic): " <<
p_Bi << std::endl;
std::cout <<
"Z_Bi significance (analytic): " <<
Z_Bi << std::endl;
w->defineSet(
"obs",
"m");
w->defineSet(
"poi",
"s");
std::unique_ptr<RooDataSet>
data{
w->pdf(
"px")->generate(*
w->set(
"obs"), 150)};
b_model.SetParametersOfInterest(*
w->set(
"poi"));
w->var(
"s")->setVal(0.0);
sb_model.SetParametersOfInterest(*
w->set(
"poi"));
w->var(
"s")->setVal(50.0);
w->factory(
"Gaussian::gauss_prior(b,y, expr::sqrty('sqrt(y)',y))");
w->factory(
"Lognormal::lognorm_prior(b,y, expr::kappa('1+1./sqrt(y)',y))");
hc1.ForcePriorNuisanceAlt(*
w->pdf(
"py"));
hc1.ForcePriorNuisanceNull(*
w->pdf(
"py"));
cout << "-----------------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "Part 4" << endl;
return;
hc2.ForcePriorNuisanceAlt(*
w->pdf(
"py"));
hc2.ForcePriorNuisanceNull(*
w->pdf(
"py"));
cout << "-----------------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "Part 5" << endl;
return;
}
double Double_t
Double 8 bytes.
#define ClassDef(name, id)
ROOT::Detail::TRangeCast< T, true > TRangeDynCast
TRangeDynCast is an adapter class that allows the typed iteration through a TCollection.
Option_t Option_t TPoint TPoint const char GetTextMagnitude GetFillStyle GetLineColor GetLineWidth GetMarkerStyle GetTextAlign GetTextColor GetTextSize void data
Option_t Option_t TPoint TPoint const char GetTextMagnitude GetFillStyle GetLineColor GetLineWidth GetMarkerStyle GetTextAlign GetTextColor GetTextSize void value
Abstract base class for binned and unbinned datasets.
RooArgSet is a container object that can hold multiple RooAbsArg objects.
static RooMsgService & instance()
Return reference to singleton instance.
Same purpose as HybridCalculatorOriginal, but different implementation.
This class provides the plots for the result of a study performed with any of the HypoTestCalculatorG...
HypoTestResult is a base class for results from hypothesis tests.
< A class that holds configuration information for a model using a workspace as a store
NumEventsTestStat is a simple implementation of the TestStatistic interface used for simple number co...
TestStatistic class that returns -log(L[null] / L[alt]) where L is the likelihood.
TestStatistic is an interface class to provide a facility for construction test statistics distributi...
ToyMCSampler is an implementation of the TestStatSampler interface.
Persistable container for RooFit projects.
void Divide(Int_t nx=1, Int_t ny=1, Float_t xmargin=0.01, Float_t ymargin=0.01, Int_t color=0) override
Automatic pad generation by division.
void Start(Bool_t reset=kTRUE)
Start the stopwatch.
void Stop()
Stop the stopwatch.
void Print(Option_t *option="") const override
Print the real and cpu time passed between the start and stop events.
The namespace RooFit contains mostly switches that change the behaviour of functions of PDFs (or othe...
MsgLevel
Verbosity level for RooMsgService::StreamConfig in RooMsgService.
Namespace for the RooStats classes.
- Authors
- Kyle Cranmer, Wouter Verkerke, and Sven Kreiss
Definition in file HybridStandardForm.C.


