




Shadow generation
You can generate a shadow with a z-buffer map in a twostep process.
- Move the camera to the light position. Generate the graphic. Save
the zbuffer.
- Render the graphic (a point is under shadow if its z, as seen from the light, is less than the z saved in the first step).
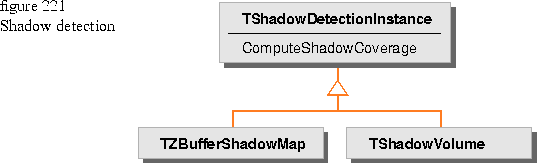
This method requires that you define and create a shadow detection instance to determine the percentage of a pixel area being covered by shadows. Figure 221 shows a shadow detection class with two derived classes. The two derived classes represent different implementations for shadow detection. TZBufferShadowMap uses shadow map algorithms in its implementation; whereas, TShadowVolume accumulates geometry instances for the intersection check.
The declaration of ComputeShadowCoverage looks like this:
double ComputeShadowCoverage( const ShadingSample& shadeSample );
You can install a shadow detection instance by deriving a light source and implementing its functions as shown in Figure 222.
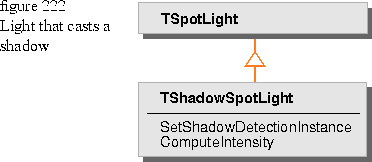
The implementation of ComputeIntensity does the following:
- Request the shadow detection instance to compute the shadow coverage based on TShadingSample and TSceneBundle.
- Requests TSpotLight to compute intensity as if no shadow were involved.
- Modifies the light intensity accordingly.
[Contents]
[Previous]
[Next]
 Click the icon to mail questions or corrections about this material to Taligent personnel.
Click the icon to mail questions or corrections about this material to Taligent personnel.
Copyright©1995 Taligent,Inc. All rights reserved.
Generated with WebMaker

