| virtual | ~KelvinFunctions() |
| static double | Bei(double x) |
| static double | Ber(double x) |
| static double | DBei(double x) |
| static double | DBer(double x) |
| static double | DKei(double x) |
| static double | DKer(double x) |
| static double | F1(double x) |
| static double | F2(double x) |
| static double | G1(double x) |
| static double | G2(double x) |
| static double | Kei(double x) |
| ROOT::Math::KelvinFunctions | KelvinFunctions() |
| ROOT::Math::KelvinFunctions | KelvinFunctions(const ROOT::Math::KelvinFunctions&) |
| static double | Ker(double x) |
| static double | M(double x) |
| static double | N(double x) |
| ROOT::Math::KelvinFunctions& | operator=(const ROOT::Math::KelvinFunctions&) |
| static double | Phi(double x) |
| static double | Theta(double x) |
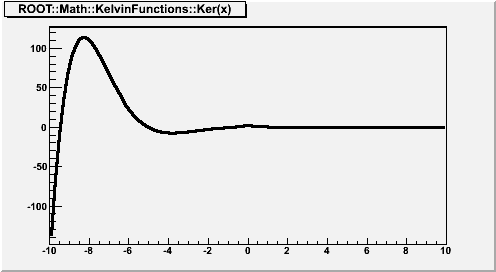
where x is real, and
is the zeroth-order modified Bessel function of the second kind. If x < fgMin (=20), Ker(x) is computed according to its polynomial approximation
where
is the Euler-Mascheroni constant,
for x < 0 and is otherwise zero, and
For x > fgMin, Ker(x) is computed according to its asymptotic expansion:
where
See also F2(x) and G2(x).
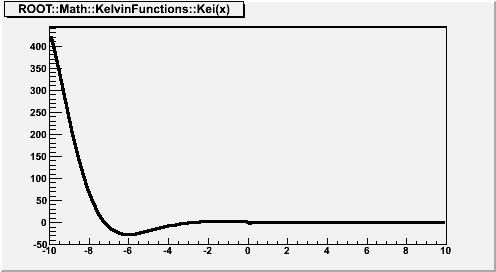
where x is real, and
is the zeroth-order modified Bessel function of the second kind. If x < fgMin (=20), Kei(x) is computed according to its polynomial approximation
where
is the Euler-Mascheroni constant,
for x < 0 and is otherwise zero, and
For x > fgMin, Kei(x) is computed according to its asymptotic expansion:
where
See also F2(x) and G2(x).