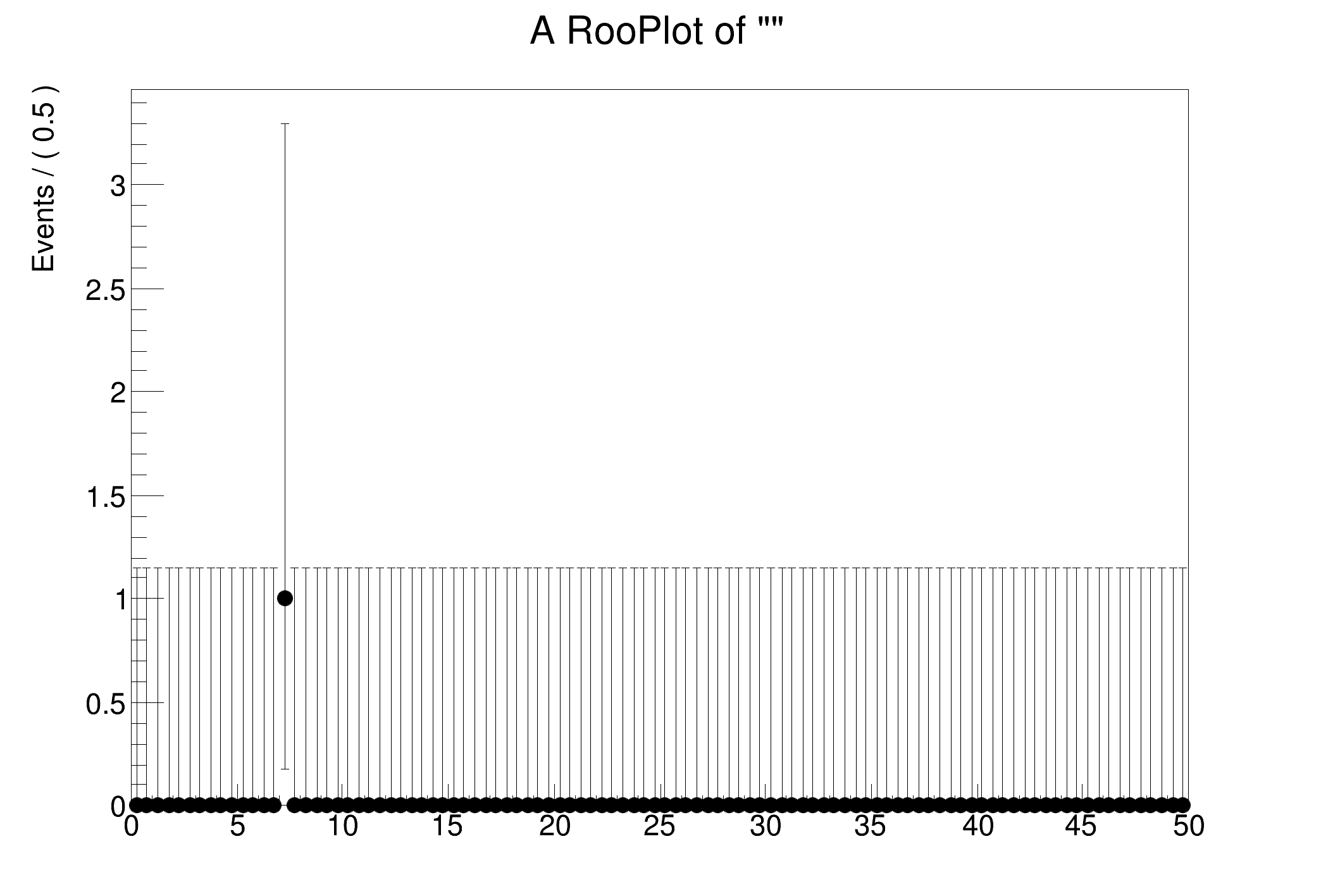
DataStore poisData (Generated From )
Contains 1 entries
Observables:
1) x = 7 L(0 - 50) ""
RooWorkspace() contents
variables
---------
(mu,x)
p.d.f.s
-------
RooPoisson::pois[ x=x mean=mean ] = 0.0224772
functions
--------
RooAddition::mean[ mu + b ] = 5.5
named sets
----------
poissonProblem_Observables:(x)
poissonProblem_POI:(mu)
=== Using the following for poissonProblem ===
Observables: RooArgSet:: = (x)
Parameters of Interest: RooArgSet:: = (mu)
PDF: RooPoisson::pois[ x=x mean=mean ] = 0.0224772
FeldmanCousins: ntoys per point: adaptive
FeldmanCousins: nEvents per toy will not fluctuate, will always be 1
FeldmanCousins: Model has no nuisance parameters
FeldmanCousins: # points to test = 100
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 1/100 total MC = 240 this test stat = 1.83324
mu=0.075 [-inf, 1.08573] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 2/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 1.6497
mu=0.225 [-inf, 0.949959] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 3/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 1.4816
mu=0.375 [-inf, 0.827185] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 4/100 total MC = 240 this test stat = 1.32721
mu=0.525 [-inf, 1.32721] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 5/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 1.1855
mu=0.675 [-inf, 2.73601] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 6/100 total MC = 240 this test stat = 1.05546
mu=0.825 [-inf, 1.72806] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 7/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.936198
mu=0.975 [-inf, 2.32979] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 8/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.826909
mu=1.125 [-inf, 1.424] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 9/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.726882
mu=1.275 [-inf, 1.2882] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 10/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.635479
mu=1.425 [-inf, 1.81453] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 11/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.552124
mu=1.575 [-inf, 1.66456] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 12/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.476298
mu=1.725 [-inf, 1.725] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 13/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.40728
mu=1.875 [-inf, 2.05965] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 14/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.345232
mu=2.025 [-inf, 1.9066] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 15/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.289405
mu=2.175 [-inf, 1.76244] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 16/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.239437
mu=2.325 [-inf, 1.7512] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 17/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.195006
mu=2.475 [-inf, 1.27174] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 18/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.155489
mu=2.625 [-inf, 1.99618] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 19/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.121494
mu=2.775 [-inf, 1.86244] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 20/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.0920776
mu=2.925 [-inf, 1.73057] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 21/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.0670922
mu=3.075 [-inf, 1.60585] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 22/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.0463567
mu=3.225 [-inf, 2.10098] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 23/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.0296823
mu=3.375 [-inf, 1.96524] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 24/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.0168841
mu=3.525 [-inf, 1.97094] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 25/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.00778646
mu=3.675 [-inf, 2.07549] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 26/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.00222463
mu=3.825 [-inf, 1.59677] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 27/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 4.47494e-05
mu=3.975 [-inf, 2.06902] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 28/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.00110295
mu=4.125 [-inf, 2.39501] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 29/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.00526396
mu=4.275 [-inf, 1.6175] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 30/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.0123995
mu=4.425 [-inf, 1.70627] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 31/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.0223862
mu=4.575 [-inf, 1.79627] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 32/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.0351041
mu=4.725 [-inf, 2.04845] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 33/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.0504339
mu=4.875 [-inf, 2.94484] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 34/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.0682548
mu=5.025 [-inf, 3.0571] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 35/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.0888053
mu=5.175 [-inf, 2.27954] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 36/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.111493
mu=5.325 [-inf, 2.26305] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 37/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.136468
mu=5.475 [-inf, 2.03894] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 38/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.163629
mu=5.625 [-inf, 1.55152] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 39/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.192899
mu=5.775 [-inf, 1.81715] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 40/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.224207
mu=5.925 [-inf, 1.71475] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 41/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.257484
mu=6.075 [-inf, 2.75427] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 42/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.292951
mu=6.225 [-inf, 2.03573] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 43/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.330045
mu=6.375 [-inf, 1.92767] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 44/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.368932
mu=6.525 [-inf, 2.0544] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 45/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.409554
mu=6.675 [-inf, 2.14188] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 46/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.45186
mu=6.825 [-inf, 2.72294] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 47/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.495797
mu=6.975 [-inf, 2.03823] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 48/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.541318
mu=7.125 [-inf, 2.41011] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 49/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.588375
mu=7.275 [-inf, 1.83449] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 50/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.636924
mu=7.425 [-inf, 2.80213] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 51/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.686922
mu=7.575 [-inf, 1.82957] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 52/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.738329
mu=7.725 [-inf, 1.9093] in interval = 1
----> Doing a re-scan first
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 53/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.791008
mu=7.875 [-inf, 1.98986] in interval = 1
----> Doing a re-scan first
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 54/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.845195
mu=8.025 [-inf, 2.82912] in interval = 1
----> Doing a re-scan first
----> Doing a re-scan first
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 55/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.900613
mu=8.175 [-inf, 2.23216] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 56/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 0.957212
mu=8.325 [-inf, 1.51348] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 57/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 1.01518
mu=8.475 [-inf, 2.32128] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 58/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 1.07427
mu=8.625 [-inf, 4.56136] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 59/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 1.13452
mu=8.775 [-inf, 1.83847] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 60/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 1.19586
mu=8.925 [-inf, 1.80373] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 61/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 1.25841
mu=9.075 [-inf, 2.45852] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 62/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 1.32199
mu=9.225 [-inf, 1.95466] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 63/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 1.38662
mu=9.375 [-inf, 2.24328] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 64/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 1.45228
mu=9.525 [-inf, 2.50319] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 65/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 1.51895
mu=9.675 [-inf, 3.02403] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 66/100 total MC = 240 this test stat = 1.58659
mu=9.825 [-inf, 1.60365] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 67/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 1.6552
mu=9.975 [-inf, 3.20706] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 68/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 1.72474
mu=10.125 [-inf, 2.42844] in interval = 1
[#0] PROGRESS:Generation -- generated toys: 500 / 1440
[#0] PROGRESS:Generation -- generated toys: 1000 / 1440
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 69/100 total MC = 2160 this test stat = 1.79519
mu=10.275 [-inf, 1.79519] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 70/100 total MC = 240 this test stat = 1.86654
mu=10.425 [-inf, 1.86654] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 71/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 1.93876
mu=10.575 [-inf, 2.67618] in interval = 1
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 72/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 2.01184
mu=10.725 [-inf, 1.40678] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 73/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 2.08575
mu=10.875 [-inf, 1.86151] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 74/100 total MC = 240 this test stat = 2.16048
mu=11.025 [-inf, 1.7642] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 75/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 2.23601
mu=11.175 [-inf, 1.59869] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 76/100 total MC = 240 this test stat = 2.31232
mu=11.325 [-inf, 1.66448] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 77/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 2.38941
mu=11.475 [-inf, 1.26987] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 78/100 total MC = 240 this test stat = 2.46724
mu=11.625 [-inf, 1.40071] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 79/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 2.54582
mu=11.775 [-inf, 1.86704] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 80/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 2.62511
mu=11.925 [-inf, 1.93623] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 81/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 2.70511
mu=12.075 [-inf, 1.43268] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 82/100 total MC = 240 this test stat = 2.7858
mu=12.225 [-inf, 1.49357] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 83/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 2.86717
mu=12.375 [-inf, 1.55534] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 84/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 2.94921
mu=12.525 [-inf, 1.12614] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 85/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 3.03185
mu=12.675 [-inf, 2.29398] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 86/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 3.11523
mu=12.825 [-inf, 1.7457] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 87/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 3.1991
mu=12.975 [-inf, 1.8108] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 88/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 3.28355
mu=13.125 [-inf, 2.51742] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 89/100 total MC = 240 this test stat = 3.36896
mu=13.275 [-inf, 1.40455] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 90/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 3.45474
mu=13.425 [-inf, 2.01076] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 91/100 total MC = 240 this test stat = 3.5411
mu=13.575 [-inf, 2.07893] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 92/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 3.62804
mu=13.725 [-inf, 2.14777] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 93/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 3.71554
mu=13.875 [-inf, 1.16754] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 94/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 3.80359
mu=14.025 [-inf, 1.70395] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 95/100 total MC = 240 this test stat = 3.89219
mu=14.175 [-inf, 1.76612] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 96/100 total MC = 240 this test stat = 3.98132
mu=14.325 [-inf, 1.32819] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 97/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 4.07097
mu=14.475 [-inf, 1.38331] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 98/100 total MC = 80 this test stat = 4.16114
mu=14.625 [-inf, 1.43935] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 99/100 total MC = 240 this test stat = 4.25182
mu=14.775 [-inf, 1.49612] in interval = 0
NeymanConstruction: Prog: 100/100 total MC = 240 this test stat = 4.343
mu=14.925 [-inf, 2.08888] in interval = 0
[#1] INFO:Eval -- 68 points in interval
is this point in the interval? 0
interval is [0.525, 10.575]
Real time 0:00:03, CP time 3.010