

Multidimensional models: working with parametrized ranges to define non-rectangular regions for fitting and integration
{
y.setRange(
"R", ylo, yhi);
z.setRange("R", zlo, zhi);
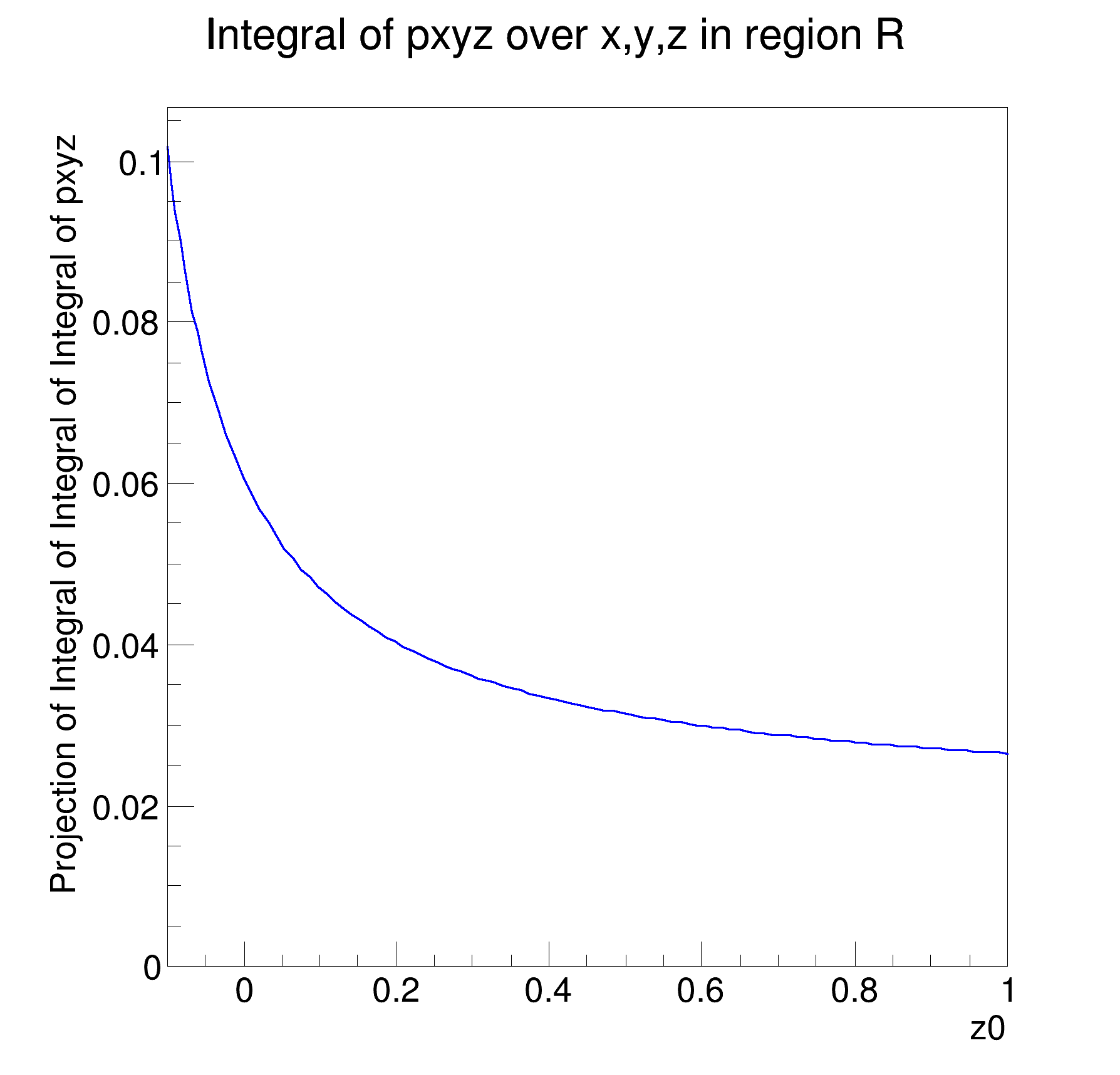
RooPlot *frame = z0.
frame(Title(
"Integral of pxyz over x,y,z in region R"));
intPdf->plotOn(frame);
new TCanvas(
"rf313_paramranges",
"rf313_paramranges", 600, 600);
gPad->SetLeftMargin(0.15);
return;
}
RooArgSet is a container object that can hold multiple RooAbsArg objects.
A RooPlot is a plot frame and a container for graphics objects within that frame.
static RooPlot * frame(const RooAbsRealLValue &var, double xmin, double xmax, Int_t nBins)
Create a new frame for a given variable in x.
void Draw(Option_t *options=nullptr) override
Draw this plot and all of the elements it contains.
RooPolynomial implements a polynomial p.d.f of the form.
RooProdPdf is an efficient implementation of a product of PDFs of the form.
RooRealVar represents a variable that can be changed from the outside.
virtual void SetTitleOffset(Float_t offset=1)
Set distance between the axis and the axis title.
The namespace RooFit contains mostly switches that change the behaviour of functions of PDFs (or othe...
[#1] INFO:NumericIntegration -- RooRealIntegral::init(pxyz_Int[z|R]_Norm[x,y,z]_Int[y|R]_Int[x|R]) using numeric integrator RooIntegrator1D to calculate Int(x)
[#1] INFO:NumericIntegration -- RooRealIntegral::init(pxyz_Int[z|R]_Norm[x,y,z]_Int[y|R]) using numeric integrator RooIntegrator1D to calculate Int(y)
- Date
- July 2008
- Author
- Wouter Verkerke
Definition in file rf313_paramranges.C.


