TGraph::SavesAs() for .csv, .tsv and .txt for
text output separated by comma, tab, and space, respectively.TGraph2DAsymmErrors to create TGraph2D with
asymmetric errors. 
ROOT version 6.28/00 was released on February 03, 2023.
For more information, see:
The following people have contributed to this new version:
Guilherme Amadio, CERN/SFT,
Rahul Balasubramanian, NIKHEF/ATLAS,
Bertrand Bellenot, CERN/SFT,
Jakob Blomer, CERN/SFT,
Patrick Bos, Netherlands eScience Center,
Rene Brun, CERN/SFT,
Carsten D. Burgard, TU Dortmund University/ATLAS,
Artem Busorgin,
Will Buttinger, RAL/ATLAS,
Philippe Canal, FNAL,
Olivier Couet, CERN/SFT,
Michel De Cian, EPFL/LHCb,
Hans Dembinski, TU Dortmund,
Simeon Ehrig, HZDR,
Mattias Ellert, Uppsala University,
Matthew Feickert, UW Madison/ATLAS,
Markus Frank, CERN/LHCb,
Oliver Freyermuth, U Bonn,
Gerri Ganis, CERN/SFT,
Andrei Gheata, CERN/SFT,
Sayandeep Ghosh, Jadavpur U Calcutta,
Konstantin Gizdov, University of Edinburgh/LHCb,
Max Goblirsch, CERN/ATLAS,
Stefan Gränitz,
Enrico Guiraud, CERN/SFT,
Stephan Hageboeck, CERN/IT,
Jonas Hahnfeld, CERN/SFT,
Ahmat Mahamat Hamdan, CERN/SFT,
Fernando Hueso-González, University of Valencia,
Pawan Johnson, Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur,
Subham Jyoti, ITER Bhubaneswar,
Ivan Kabadzhov, CERN/SFT,
Baidyanath Kundu, Princeton/SFT,
Giovanna Lazzari Miotto, CERN/SFT,
Yueh-Shun Li, National Central U Taiwan/CMS,
Sergey Linev, GSI,
Jerry Ling, Harvard University,
Javier Lopez-Gomez, CERN/SFT,
Enrico Lusiani, INFN/CMS,
Julia Mathe, CERN/SFT,
Pere Mato, CERN/SFT,
Lorenzo Moneta, CERN/SFT,
Nicolas Morange, CNRS/ATLAS,
Alja Mrak Tadel, UCSD/CMS,
Axel Naumann, CERN/SFT,
Duncan Ogilvie,
Hanna Olvhammar, CERN/SFT,
Vincenzo Eduardo Padulano, CERN/SFT and UPV,
Tapasweni Pathak,
Danilo Piparo, CERN/SFT,
David Poulton, Wits/SFT,
Fons Rademakers, CERN/SFT,
Jonas Rembser, CERN/SFT,
Mathias Schmitt,
Neel Shah, VJTI,
Petr Stepanov, Catholic University of America,
Enric Tejedor Saavedra, CERN/SFT,
Neel Shah, GSOC,
Sanjiban Sengupta, CERN/SFT,
Harshal Shende, GSOC,
Garima Singh, Princeton/SFT,
Surya Somayyajula, UW Madison,
Matevz Tadel, UCSD/CMS,
Vassil Vassilev, Princeton/CMS,
Andrii Verbytskyi, MPP Munich/ATLAS,
Wouter Verkerke, NIKHEF/ATLAS,
Frank Winklmeier, U Oregon/ATLAS,
Zef Wolffs, NIKHEF/ATLAS,
Jun Zhang
The deprecated types
ROOT::Experimental::TBufferMerger and
ROOT::Experimental::TBufferMergerFile are removed. Please
use their non-experimental counterparts ROOT::TBufferMerger
and ROOT::TBufferMergerFile instead.
ROOT::RVec::shrink_to_fit() has now been removed
after deprecation; it is not needed.
ROOT::RVec::emplace() has now been removed after
deprecation; please use ROOT::RVec::insert()
instead.
The deprecated function
ROOT::Detail::RDF::RActionImpl<Helper>::GetDataBlockCallback()
is removed; please use GetSampleCallback()
instead.
The deprecated RooFit containers RooHashTable,
RooNameSet, RooSetPair, and
RooList are removed. Please use STL container classes
instead, like std::unordered_map, std::set,
and std::vector.
The RooFit::FitOptions(const char*) command to steer
RooAbsPdf::fitTo()
with an option string was removed. This way of configuring the fit was
deprecated since at least since ROOT 5.02. Subsequently, the
RooMinimizer::fit(const char*) function and the RooMCStudy
constructor that takes an option string were removed as well.
The overload of RooAbsData::createHistogram that
takes integer parameters for the bin numbers is now deprecated and will
be removed in ROOT 6.30. This was done to avoid confusion with
inconsistent behavior when compared to other
createHistogram overloads. Please use the verson of
createHistogram that takes RooFit command
arguments.
The RooAbsData::valid() method to cache valid
entries in the variable range was removed. It was not implemented in
RooDataSet, so it never worked as intended. Related to it was the
RooDataHist::cacheValidEntries() function, which is removed
as well. The preferred way to reduce RooFit datasets to subranges is RooAbsData::reduce().
The longtime-deprecated
RooStats::HistFactory::EstimateSummary class is removed,
including the functions that use it. The information that it was meant
to store is managed by the
RooStats::HistFactory::Measurement object since many
years.
The RooSuperCategory::MakeIterator() function that
was deprecated since 6.22 is now removed. Please use range-based loops
to iterate over the category states.
The HybridCalculatorOriginal and
HypoTestInverterOriginal classes in RooStats that were
deprecated for a very long time aleady are removed. Please use
HybridCalculator and
HypoTestInverter.
The RooSimPdfBuilder that was deprecated in ROOT
5.20 and replaced by the RooSimWSTool is removed.
The RDataFrame factory functions MakeNumpyDataFrame,
MakeCsvDataFrame, MakeArrowDataFrame,
MakeNTupleDataFrame and MakeSqliteDataFrame
are now deprecated in favor of FromNumpy,
FromCSV, FromArrow, FromRNTuple
and FromSqlite respectively.
TDirectory::EncodeNameCycle() is deprecated; it
cannot be used safely. Use
name + ';' + std::to_string(cycle) instead.
The build option alien has been removed.
The build options gfal, gsl_shared,
jemalloc, monalisa,
pyroot_legacy, tcmalloc, and
xproofd have been deprecated. Please complain with
root-dev@cern.ch should you still need one!
This version adds the new rootreadspeed CLI tool. This
tool can be used to help identify bottlenecks in analysis runtimes, by
providing time and throughput measurements when reading ROOT files via
file systems or XRootD. More detailed information can be found in the
tool’s help information.
To see help information, install and source a recent enough version
of ROOT, and run the command rootreadspeed --help in your
terminal.
$ rootreadspeed --files <local-folder>/File1.root xrootd://<url-folder>/File2.root --trees Events --all-branches --threads 8llvm and clang have been upgraded to version 13. C++20 support will be provided as part of this release (not yet available for 6.28/00). cling has been upgraded to use llvm’s new just-in-time compilation engive ORCv2.
Cling checks pointer validity now only in interactive mode, improving performance for jitted code in batch systems.
This version of ROOT adds an LLVM JIT event listener to create perf
map files during runtime. This allows profiling of interpreted/JITted
code generated by cling. Instead of function addresses, the perf data
will contain full function names. In addition, stack frame pointers are
enabled in JITted code, so full stack traces can be generated. Debugging
is aided by switching off optimisations and adding frame pointers for
better stack traces. However, since both have a runtime cost, they are
disabled by default. Similar to LD_DEBUG and
LD_PROFILE for ld.so, the environment
variables CLING_DEBUG=1 and/or CLING_PROFILE=1
can be set to enable debugging and/or profiling.
std namespace is now
diagnosed. Specifically, given that ROOT injects
using namespace std directive, all the names in
the std namespace become available in the global scope.
However, in some circumstances users inadvertently introduce a
declaration that conflicts with a name in std making
references to the former declaration result in ambiguous lookup. A
fairly common case is trying to declare a global variable named
data which conflict with std::data
[C++17]. See ROOT-5971 for a
discussion. As of v6.28, such declarations result inroot [] int data;
ROOT_prompt_0:1:1: warning: 'data' shadows a declaration with the same name in the 'std' namespace; use '::data' to reference this declaration
int data;
^root [] .help editTFile by
TTreeProcessorMT.A new cross-protocol redirection has been added to allow files on EOS
mounts to be opened by TFile::Open via XRootD protocol
rather than via FUSE when that is possible. The redirection uses the
eos.url.xroot extended file attribute that is present on
files in EOS. The attribute can be viewed with
getfattr -n eos.url.xroot [file] on the command line. When
the URL passed into TFile::Open is a for a file on an EOS
mount, the extended attribute is used to attempt the redirection to
XRootD protocol. If the redirection fails, the file is opened using the
plain file path as before. This feature is controlled by the
pre-existing configuration option
TFile.CrossProtocolRedirects and is enabled by default. It
can be disabled by setting TFile.CrossProtocolRedirects to
0 in rootrc.
ROOT’s experimental successor of TTree has seen many updates during the last few months. Specifically, v6.28 includes the following changes:
Complete support for big-endian architectures (PR #10402).
Support for std::pair<T1, T2> and
std::tuple<Ts...> fields
Support for C array fields whose type is of the form
T[N]. Note that only single-dimension arrays are currently
supported.
Improvements to the ROOT file embedding (PR #10558). In
particular, a RNTupleReader or RDataFrame
object can be created from a TFile instance as
follows
auto f = TFile::Open("data.root");
auto ntpl = f->Get<ROOT::Experimental::RNTuple>("Events");
auto reader = ROOT::Experimental::RNTupleReader::Open(ntpl);
// or for RDataFrame
auto rdf = ROOT::Experimental::MakeNTupleDataFrame(ntpl);If buffered write is enabled, vector writes are used where possible. In particular, this yields important improvements in storage backends leveraging parallel writes, e.g. in object storages.
Large read/write throughput improvements in the experimental Intel DAOS backend.
RNTupleWriter::Fill() now returns the number of
uncompressed bytes written, which is align with TTree behavior.
Support for user-defined classes that behave as a collection via
the TVirtualCollectionProxy interface. Fields created via
RFieldBase::Create() automatically detect the presence of a
collection proxy at run-time. However, if RField<T>
(T being a class) is used instead, the trait
IsCollectionProxy<T> must be set for the given type
(see PR #11525 for
details). Note that associative collections are not yet
supported.
Some internal support for per field post-read callbacks. This functionality will be presented in upcoming releases through custom I/O rules.
Please, report any issues regarding the abovementioned features should you encounter them. RNTuple is still experimental and is scheduled to become production grade in 2024. Thus, we appreciate feedback and suggestions for improvement.
GraphAsymmErrors
action that fills a TGraphAsymmErrors object.RDatasetSpec
as an experimental class to specify the input dataset to an
RDataFrame.RDatasetSpec. The metadata of each sample can
then be retrieved during the execution by calling
DefinePerSample.SaveGraph,
where previously cling was getting wrong static
initialization.Graph
action (that fills a TGraph object) to properly handle containers and
non-container types.RCsvDS
class now allows users to specify column types, and can properly read
empty entries of csv files.Display operation would not show
the correct amount of entries requested by the user if called together
with other operations (PR).Stats results with
VariationsFor is now supported.MakeCsvDataFrame is now FromCSV. The old
wording is still available but deprecated.Sums and Means of
single-precision floating point values has been greatly improved by
employing Kahan summations.Vary and
VariationsFor operations) in distributed mode.Snapshot) is purposely made
lazy by the user, distributed RDataFrame now respects this and avoids
triggering the computations right away.Histo*D actions is now required in distributed mode. See
the relative
PR for more discussion.npartitions argument is not set by the user, the
default number of tasks created by a distributed RDataFrame is equal to
the number of cores specified by the user when connecting to the
cluster.std::exception and
derived) are now correctly propagated from the processes of the
computing nodes to the user side.dask version required to support
distributed RDataFrame is 2022.8.1, since a series of critical bugs
present before that version were hindering the normal execution of the
tool. Consequently, the minimum Python version needed to include
distributed RDataFrame in the ROOT build is Python 3.8. More information
in the relative github
issue.Stats and StdDev operations are now
available in distributed mode.GetColumnNames operation is now available in
distributed mode.TGraph::SavesAs() for .csv, .tsv and .txt for
text output separated by comma, tab, and space, respectively.TGraph2DAsymmErrors to create TGraph2D with
asymmetric errors. 
TLorentzVector can now convert to
ROOT::Math::PxPyPzEVector.Some improvements and small fixes to the internal object memory
management have been applied to the ROOT::Fit::Fitter
class.
GSLMultiFit class.TLinearMinimizer class).Support for providing the second derivatives (Hessian matrix) from
the model function is added to the Fitter class and the
corresponding function interfaces. The functionality it is then
propagated in the implementation of the FitMethod classes
and it is also added to the Minimizer classes for providing
a user computed Hessian of the objective functions to the minimizers.
Only Minuit2 (see below) has the capabilities of using this external
Hessian.
The GradFunctor class has been improved by providing a
new constructor taking an std::function implementing the
full gradient calculations instead of the single partial derivative.
The specialized methods for least-square/likelihood functions such as Fumili, Fumili2 and GSLMultiFit have been improved in case of binned likelihood fits, where a better approximation is used than before. This makes these method work better (conerging with less number of function calls) for these types of fits.
The support for using an External Hessian calculator has been added.
The external Hessian can be used for both the initial seeding, using
only the diagonal part, if the strategy is equal to 1 (the default
value) and in MnHesse, after the minimization, to compute
the covariance and correlation matrices.
The print log of Minuit2 has been improved, especially when printing vector and matrices with large number of parameters (when the print level = 3).
The ROOT::Math::KahanSum class was slightly
modified:
operator-= and operator+=
on a KahanSum were not symmetric, leading to slight
bit-wise inaccuracies. In fits, where such operations are done a lot of
times (e.g. through the offsetting mechanism in RooFit which subtracts a
constant KahanSum term after each likelihood evaluation),
this can add up to significant numerical divergence. An improved
algorithm was implemented, based on an algorithm for combining Kahan
sums and carry terms (Tian et al. 2012). (PR #11940)T and implicit type
T constructor in KahanSum made it hard to
debug KahanSum, because it is easy to overlook implicit
conversions in code, especially in lines where the type of the return
value is auto. These auto-conversions were removed. Where
necessary, they should be replaced with an explicit construction or
explicit conversion to double via Sum(). (PR #11941)operator== and
operator!= were added.The usage of TRef in the TFoamCell class
has ben replaced with array indices. This avoids, when generating a
large number of toys requiring a re-initialization of TFoam
an increase in the memory usage caused by TRef.
In previous releases, the default minimizer type that RooFit used was
hardcoded to be the original Minuit, while RooStats used
the default minimizer specified by
ROOT::Math::MinimizerOptions::DefaultMinimizerType(). Now
it is possible to centrally define the global minimizer for all RooFit
libraries via
ROOT::Math::MinimizerOptions::SetDefaultMinimizer(), or
alternatively in the .rootrc file by adding for example
Root.Fitter: Minuit2 to select Minuit2.
std::string in RooFit
interfacesThe following lesser-used RooFit functions now return a
std::string instead of a const char*,
potentially requiring the update of your code:
Before v6.28, it was ensured that no RooArgSet and
RooDataSet objects on the heap were located at an address
that had already been used for an instance of the same class before.
With v6.28, this is not guaranteed anymore. Hence, if your code uses
pointer comparisons to uniquely identify RooArgSet or RooDataSet
instances, please consider using the new
RooArgSet::uniqueId() or
RooAbsData::uniqueId().
In a binned likelihood fit, it is possible to skip the PDF normalization when the unnormalized binned PDF can be interpreted directly in terms of event yields. This is now done by default for HistFactory models, which results in great speedups for binned fits with many channels. Some RooFit users like ATLAS were already using this for a long time.
To disable this optimization when using the
hist2workspace executable, add the
-disable_binned_fit_optimization command line argument.
Directly in C++, you can also set the binnedFitOptimization
to false in the HistFactory configuration as follows:
RooStats::HistFactory::MakeModelAndMeasurementFast(measurement, {.binnedFitOptimization=false});If your compiler doesn’t support aggregate initialization with designators, you need to create and edit the configuration struct explicitely:
RooStats::HistFactory::HistoToWorkspaceFactoryFast::Configuration hfCfg;
hfCfg.binnedFitOptimization = false;
RooStats::HistFactory::MakeModelAndMeasurementFast(measurement, hfCfg);Copy assignment for RooAbsArgs was implemented in an unexpected and
inconsistent way. While one would expect that the copy assignment is
copying the object, it said in the documentation of
RooAbsArg::operator= that it will “assign all boolean and
string properties of the original bject. Transient properties and
client-server links are not assigned.” This contradicted with the
implementation, where the server links were actually copied too.
Furthermore, in RooAbsRealLValue, the assigment operator
was overloaded by a function that only assigns the value of another
RooAbsReal.
With all these inconsistencies, it was deemed safer to disable copy assignment of RooAbsArgs from now on.
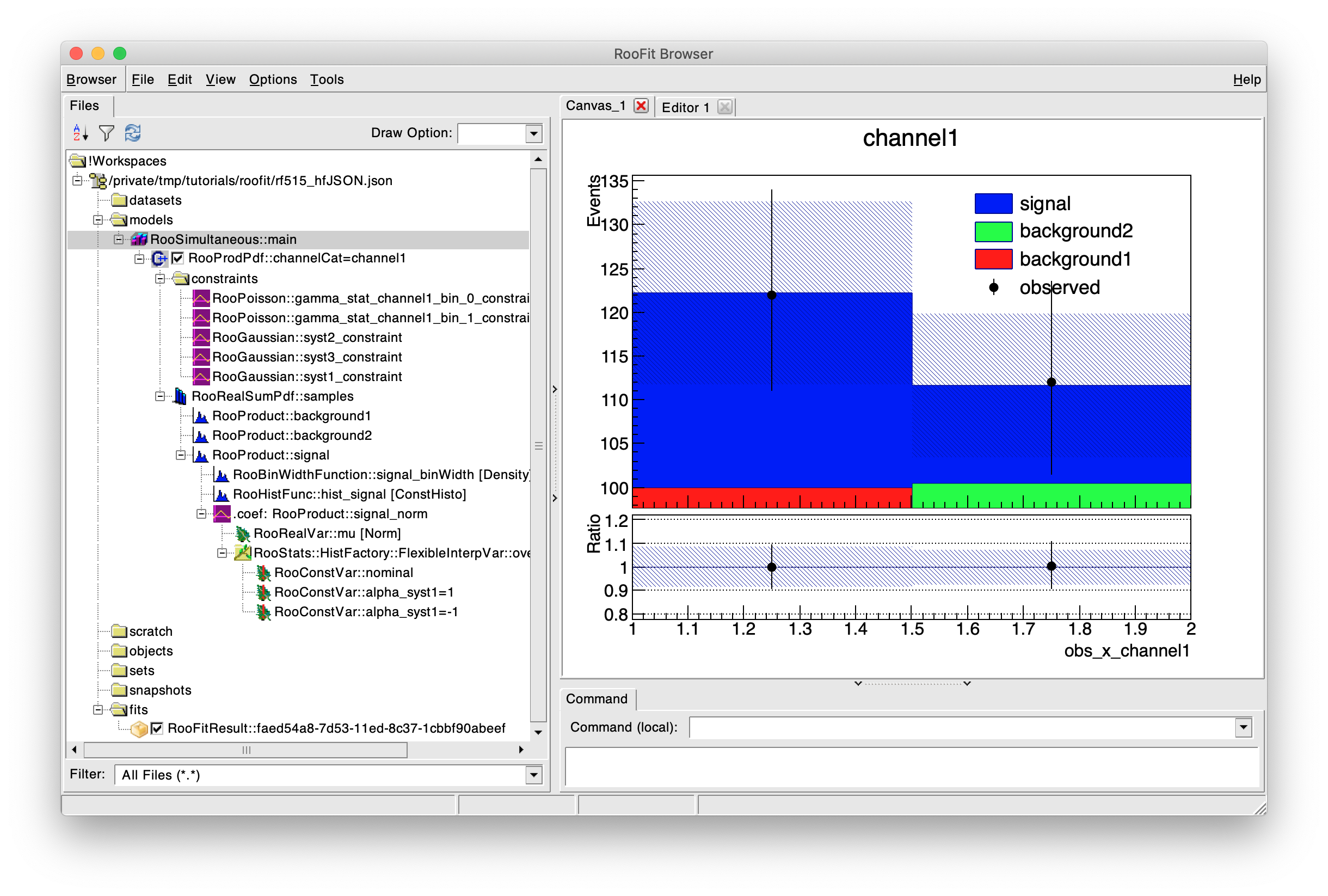
This experimental new feature utilises the technology from ROOT’s
familiar TBrowser in order to create an interface for
graphically exploring and visualizing the content of a workspace, as
well as perform basic fitting operations with the models and
datasets.
The original HistoToWorkspaceFactory produced models
that consisted of a Poisson term for each bin. In this “number counting
form” the dataset has one row and the collumns corresponded to the
number of events for each bin. This led to severe performance problems
in statistical tools that generated pseudo-experiments and evaluated
likelihood ratio test statistics.
Nowadays, everyone uses the faster
HistoToWorkspaceFactoryFast implementation that produces a
model in the “standard form” where the dataset has one row for each
event, and the column corresponds to the value of the observable in the
histogram.
Therefore, the original HistoToWorkspaceFactory is now
removed to avoid confusion and maintainance burden.
As printed out by the HistFactory in a warning message for a long
time already, setting the Const attribute to the
<NormFactor> tag is deprecated and it will be
ignored. Instead, add
<ParamSetting Const="True"> myparam </ParamSetting>
to your top-level XML’s <Measurement> entry.
This deprecation implied that the constant parameter flag in the
RooStats:HistFactory::NormFactor class had no effect as
well. To avoid ambiguity in the future, the possibility to set and
retrieve this flag with NormFactor::SetConst() and
NormFactor::GetConst() was removed, as well as the
Sample::AddNormFactor(std::string Name, double Val, double Low, double High, bool Const)
overload. Also, the aforementioned deprecation warning is not printed
anymore.
RooAbsMinimizerFcn and RooMinimizerFcn from
the public interfaceThe RooAbsMinimizerFcn class and its implementation
RooMinimizerFcn were removed from the public interface.
These classes are implementation details of the RooMinimizer and should
not be used in your code. In the unlikely case that this causes any
problem for you, please open a GitHub issue requesting to extend the
RooMinimizer by the needed functionality.
RooAbsBinning interface for bin index lookupsThe RooAbsBinning interface for bin index lookups was
changed to enable vectorized implementations. Instead of having the
override RooAbsBinning::binNumber(), the binning
implementations now have to override the
RooAbsBinning::binNumbers() function to evaluate the bin
indices of multiple values in one function call.
RooAbsRealLValue::inRange()So far, the RooAbsRealLValue::inRange() function used
the following undocumented convention to check whether a value
x is in the range with limits a and
b: test if [x - eps * x, x + eps * x] overlaps
with [a, b], where the parameter eps is
defined as max(epsRel * x, epsAbs).
The values of the relative and absolute epsilons were inconsistent among the overloads:
epsRel = 1e-8, epsAbs = 0epsRel = 0, epsAbs = 1e-6epsRel = 0, epsAbs = 1e-6With this release, the default absolute and relative epsilon is zero
to avoid confusion. You can change them with
RooNumber::setRangeEpsRel(epsRel) and
RooNumber::setRangeEpsAbs(epsAbs).
A large number of new features have been added in the TMVA SOFIE
library. The list of all operators supported in the RModel
class is the one provided below for the ONNX parser.
The interface of RModel::Generate has been changed
to
RModel::Generate(Options options = Options::kDefault, int batchsize = 1)`where Options is a new enumeration having 3 different
values:
kDefault = 0x0 : default case, a session class is
generated and the weights are stored in a separate .dat
file (in text format).kNoSession = 0x1 : no session class is generated and
the internal intermediate tensors are declared in the global namespace
TMVA_SOFIE_$ModelName.kNoWeightFile = 0x2 the weight values are not written
in a separate .dat file, but they are included in the
generated header file.In addition, the RModel::Generate function takes as an
additional optional argument the batch size (default is = 1) and the
inference code can then be generated for the desired batch size.
The ONNX parser supports now several new ONNX operators. The list of the current supported ONNX operators is the following:
In addition a Custom (user defined) operator is supported. An example
of using a Custom operator is the program
tmva/pymva/test/EmitCustomModel.cxx.
The ONNX parser supports also the fusing of the operators MatMul + Add in a Gemm operator and fusing Conv + Add and ConvTranspose + Add.
The Keras parser supports now model with input batch size not defined
(e.g bathsize=-1), and by default the model is generated
with batchsize=1. The Keras parser supports now in addition
to the Dense layer the Conv2D layer, several activation functions (Relu,
Selu, Sigmoid, Softmax, Tanh, LeakyRelu) and these other layers:
BatchNormalization, Reshape, Convatenate, Add, Subtract, Multiply.
Models with Dropout layers are supported in case the Dropout is used
only during training and not inference.
For model having operators not yet supported in the Keras parser it
is then reccomended to convert the Keras model to ONNX
using the python tf2onnx tool.
If using PyTorch it is recommended to save the model directly in
ONNX format instad of the native .pt format by
using the torch.onnx.export function of PyTorch. The
support for parsing directly .pt files is limited to the
Gemm, Conv, Relu, Selu, Sigmoid and Transpose operators.
The SOFIE inference is now integrated with RDataFrame, where a model
can be evaluated on the columns of an input TTree with
RDataFrame using the adapter functor class
SofieFunctor. Examples of using SOFIE with
RDataFrame are the new tutorials (in the
tutorials/tmva directory)
TMVA_SOFIE_RDataFrame.C or
TMVA_SOFIE_RDataFrame.py.
TMVA_SOFIE_RDataFrame_JIT.C is an example where the SOFIE
model is generated and compiled at runtime using ROOT Cling and
evaluated using RDataFrame.
RSofieReader is a new class, which takes as input a
model file (in ONNX, Keras, PyTorch or ROOT format) and generates and
compiles the C++ code for the inference at run time using the ROOT
JITing capabilities of CLING. An example of using this class is the
tutorial TMVA_SOFIE_RSofieReader.C.
New Pythonizations are available for TMVA allowing to replace the
option string passed to several TMVA functions such as the
TMVA::Factory constructor, the
DataLoader::PrepareTrainingAndTestTree and
Factory::BookMethod using Python function arguments. For
example instead of writing an option string
"NTrees=500:BoostType=AdaBoost" one can use in Python
NTrees=500,BoostType='AdaBoost'. The new tmva tutorials
TMVA_Higgs_Classification.py,
TMVA_CNN_Classificaion.py and
TMVA_RNN_Classificaton.py provide examples of using these
new pythonizations.
Implement the option “File”: The current file name is painted on
the bottom right of each plot if the option File is set on
via gStyle->SetOptFile().
In matplolib one can use the “Default X-Points” feature to plot X/Y graphs: If one doesn’t specify the points in the x-axis, they will get the default values 0, 1, 2, 3, (etc. depending on the length of the y-points). The matplotlib script will be:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
points = np.array([3, 8, 1, 10, 5, 7])
plt.plot(ypoints)
plt. show()It is now possible to do the same with the ROOT TGraph:
double y[6] = {3, 8, 1, 10, 5, 7};
auto g = new TGraph(6,y);
g->Draw();REve now uses RenderCore to visualize 3D objects in
JavaScript, replacing the use of Three.js. RenderCore is an
open source WebGL rendering engine maintained by University of Ljubljana
and tailored to the needs of the REve visualization framework. The
minimized version is now included in ROOT source as built-in. REve with
use of RendeCore gains:



ROOT::Experimental::RGeomViewer viewer(geom);
viewer.SaveImage("rootgeom.jpeg", 800, 600);This runs normal WebGL rendering in headless web browser (Chrome or Firefox) and creates png or jpeg image out of it.
rootssh script
for tunnel to remote sessionrootssh shell script to simplify use of
web-based widgets on remote nodes: [localnode] rootssh user@remotenode
[remotenode] root --web -e 'new TBrowser'Script automatically configures ssh tunnel between local and remote nodes, one the remote node unix socket with strict 0700 mode is used. When ROOT running on remote node wants to display new web widget, script will automatically start web browser on local node with appropriate URL, accessing widget via configured ssh tunnel.
tutorial/tmva directory. Tutorials like
TMVA_Higgs_Classification.py shows the new pythonizations
available in TMVA and new TMVA_SOFIE_... tutorials show th
eusage of SOFIE in both C++ or Python.__cplusplus preprocessor macro w.r.t. when ROOT was
configured.override..rootlogon.py file will be searched both in the
current working directory and in the user’s home directory. This file is
the Python equivalent of rootlogon.C and can be used to
tweak ROOT settings when using PyROOT.TFile now enables its usage as
a Python context manager:from ROOT import TFile
with TFile("file1.root", "recreate") as outfile:
hout = ROOT.TH1F(...)
outfile.WriteObject(hout, "myhisto")TDirectory::TContext now
enables its usage as a Python context manager:with TDirectory.TContext():
# Open some file here
file = ROOT.TFile(...)
# Retrieve contents from the file
histo = file.Get("myhisto")
# After the 'with' statement, the current directory is restored to ROOT.gROOTstd::vector contents at the
prompt.[#9069] - impossible to use type-erased write API to write an existing object
[#9507] - Not
possible anymore to build roottest standalone
[#9145] - [DF] Various improvements in SaveGraph
[#9607] - [MSVC][std:c++latest][permissive-] root failed to build on MSVC
[#9600] - Missing dependency when building roottest as part of ROOT.
[#9740] - Crash after zoom and unzoom with secondary axes
[#8363] -
RDataFrame::GraphAsymmErrors
[#9763] - Image artifact with zoombox on 1D hist if SetFillStyle 0 on Ubuntu
[#9556] - [DF] Prettier, more helpful graphviz computation graph representations
[#9870] - By default, bars are invisible in bar plots
[#9596] - doxygen gets confused with ClassDef and Streamer
[#9846] - PyROOT Conversion from int32 numpy array
to Int_t * doesn’t work on 32-bit platforms
[#9697] - PCM file not found
[#9900] -
rootcling does not properly detect the class doc when using
a ClassDefOverride
[#9898] - [DF] Allow use of aliases RVecI, RVecD, etc. in ROOT.Numba.Declare
[#7151] - More convenience when constructing TGraphs
[#7483] - [cling] Decls in an unnamed namespace cannot be looked up after a unload-load cycle
[#9993] - Distributed RDataFrame doesn’t respect lazy instant actions
[#9989] - Writing TObject-derived objects to file does not store the object’s title
[#9850] - [cling] Crash unloading a templated function containing a lambda expression
[#10013] - stack-use-after-scope in treetreeplayertestUnit
[#10012] - heap-use-after-free in TTree
[#10056] - [cling-docu] raw help
[#10015] - heap-use-after-free in TThread
[#10011] - heap-buffer-overflow in RNtuple
[#10057] - Capture CTRL+L in ROOT prompt to clear
[#9561] - [DF] Teach CSV datasource to handle NaN values
[#9939] - Hadd super slow since TFileMerger modification
[#10067] - [doxy] upgrade to Mathjax3
[#10090] - TRint changes in 6.26.00 break existing use cases
[#10133] - [textinput] CTRL+T eats prompt label
[#10135] - [textinput] CTRL+D missing newline after quitting.
[#10136] - [textinput] Esc,L and Esc,U not finding word boundary
[#10066] - [doxy] qch and tag as compressed files
[#10170] - Crashes when reading a ttree with a friend
[#8549] - A
crash when opening a ttree and its friend on
TFile::Close()
[#10017] - Failures due to “incompatible ASan runtimes”
[#10107] - [RF] v6-26-00-patches branch fails to build on ubuntu 18.04
[#10147] - Compile macro inside temp build directory
[#10180] - [textinput] segmentation violation on Undo shortcut
[#10131] - Open too many different non-versioned layouts for pair
[#10182] - [textinput] Undo buffer misses one entry in the actual sequence
[#10008] - [RF] heap-use-after-free in RooAbsData
[#10216] - [DF] EnableImplicitMT() prevents reading TTree in sub-directory from XrootD file
[#10137] - [textinput] forward search
[#10209] - [textinput] right or left arrow introduce stray characters while history search
[#10266] - TGraph2D interpolation hangs for degenerate points
[#10279] -
TAxis::ChangeLabel documentation
[#10283] - [CMake] Imported targets improperly forwarded
[#10299] -
TColor::GetColorTransparent() does not re-use previously
defined transparent colors
[#10278] - [RF] RooDataSet incorrectly loads RooCategory values from TTree branch of type Short_t
[#10225] -
TChain doesn’t recognise ROOT::VecOps::RVec<double>
as a column type
[#10233] - RDataFrame RDataFrame.Redefine does not work with Snapshot
[#10065] - [MetaSema/TApplication] outdated .help message
[#10298] - /bin/sh: 166: bin/thisroot.sh: Bad substitution
[#10327] - [RBrowser] Garbled output at prompt
[#10297] - RVec’s swap is broken when RVec is adopting memory
[#10260] -
RBrowser should support Safari
[#10265] -
“Same” option not working in RBrowser
[#10282] - [RF] Crash in reading some RooWorkspaces after recent TStreamerInfo update
[#10357] - [I/O] Race condition when reading vectors with custom allocators with TTreeProcessorMT
[#9242] - [TMVA][RDF] Tutorials for ML inference in RDF
[#9196] - [RF] Possible memory leak when running upper-limits with toys
[#8323] - [RF] Possible heap fragmentation because of RooDataSet with memory pool
[#9491] - TGraph SaveAs .csv
[#10157] - [DF] Histo1D pythonization should allow template arguments
[#10353] - Thread-safety issue in TClassEdit (StdLen)? [6.24.06]
[#9954] -
[RF] Disable RooFit banner with
CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS option __ROOFIT_NOBANNER by
default
[#10385] - [RF] verbose printout of some RooFit classes broken
[#6951] -
[RF] Broken weights after reducing RooDataSet created with
RooAbsPdf::generate()
[#8806] -
Interpreter prints unexpected values when auto is used for
pointer types
[#10390] - Wrong file names created in distributed Snapshot
[#10430] -
df105_WBosonAnalysis.py does not convert in notebook using
nbconvert
[#10404] -
Broken interaction between TThreadExecutor and
TSeq with specified beginning/range
[#10386] - Cling crash on valid c++ code (stack variable pointer).
[#10041] - Allow GraphAsymmErrors to accept systematic variations
[#9321] -
[RF] Segfault in RooProduct::Print("v")
[#10452] - Cling symbols not exported in win32 and win64
[#10503] - Failure to build master branch due to xrootd SHA256 checksum mismatch
[#10323] - [ntuple] Verify object (de-)serialization with EBO
[#8063] - Gracefully error out if application compiling against ROOT is using a different C++ standard than the one with which ROOT was built
[#8787] - [RF] RooDataSet columns added with addColumns method not copied correctly in reduce
[#10473] - [RF] Crash when RooSimultaneous does not contain a pdf for each value of the index category
[#8015] - [RF] Bug in building a combined RooDataHist
[#10351] -
macOS 12: TViewPubDataMembers uses deprecated
std::iterator
[#10478] -
runtime_cxxmodules fails to build with GCC12
[#10389] -
RBrowser does not list in-memory objects when written
objects are present in TDirectory context
[#9070] - [RF] Inconsistent behavior when editing constraint terms in HistFactory models
[#10528] - “bits/utility.h” not found. root does not build from source in Arch linux.
[#10497] - [docu] unexpected end of XML file
[#10449] - Recursion limits hit in pruning/serialisation of distributed RDF graph
[#8232] - Improve startup time of distributed RDataFrame application
[#10548] - Use of undeclared identifier on Mac ARM
[#10572] - Compiler warnings on macOS
[#10383] - [ntuple] Properly support big-endian architectures
[#10545] -
Teach Vary to accept Stats
[#6347] - [ntuple] Off-by-one-byte error when deserializing arrays as RVecs
[#10586] - [TMVA][SOFIE]Generated headers are missing include guards
[#10466] -
[ntuple] GetViewCollection semantics are unclear
[#10538] - [RF] AdditionalData is not exported to XML
[#10604] - External XrootD built from git commit is not detected
[#10324] -
[ntuple] Add I/O support for std::pair
[#10440] -
[RF] Making two times RooMinimizer::contour does not give
back the same plot
[#10557] -
[RF] Inconsistent behavior of RooAbsPdf::createChi2() and
RooChi2Var
[#10681] - Some TMath function help is missing
[#10732] - CMSSW build fails with root master 4c13caa0ac
[#8186] - [RF] HistFactory ignores ParamSetting values when creating the Asimov dataset
[#8901] - RNTuple: Can not create a Field for a user class with anonymous enum
[#10632] -
[ntuple] Add I/O support for std::tuple
[#10748] -
RBrowser attempts and fails to launch TBrowser
despite --web=server:xxxx
[#7965] - [RF] RooAddPdf constructor not properly picked up by RooWSFactoryTool
[#7748] - [RF] Clarify usage of RooParametricStepFunction
[#10814] - Error in REveBox.cxx while building root 6.26.04
[#8374] - [RF] Modernise RooRealSumFunc after #8368
[#7809] - [RF] Constructors RooProdPdf and RooProduct
[#8059] - [RF] HistFactory: Incorrect default value for NormFactor
[#7825] - [RF] RooAddition and RooRealSumFunc largely duplicate each other
[#10403] - Update civetweb to 1.16 once it’s released
[#10719] - [ntuple] Enable page vector writes
[#10840] -
[RF] HistFactory PreprocessFunction::PrintXML() needs to
escape special characters to produce valid XML
[#10869] - [RF] sPlot does not work with RooAddPdf in 6.26/04
[#9360] - [RF] Update Python version of rf408 tutorial
[#7252] - [RF] RooAddPdf can fit, but not generate negative coefficients
[#10919] - Histograms copy constructor has wrong implementation
[#7702] - [DF] Allow running on a subset of the entries also in multi-thread runs
[#8080] - [ntuple, daos] Improve DAOS object mapping
[#8615] -
[RF] Add documentation for RooAbsData::Expected
[#10931] - [RF] Improve the position of the legend in the RooMCStudy output
[#10988] -
[RF] RooAddPdf::fixCoefRange cache issue with
createIntegral
[#10759] -
root-config fails if spaces are part of
ROOTSYS path
[#11026] - Integer overflow in TEntryList
[#10872] - [DF] Wrong entries are loaded from friend trees with distributed RDF
[#11067] - [RF] RooImproperIntegrator1D does not propagate RooNumIntConfig to RooIntegrator1D
[#11061] - [RF] Segfault for RooMomentMorph for ROOT>6.24
[#8777] - [RF] Migration from RooAbsCollection and RooLinkedList legacy iterators to range-based loops
[#11080] - Backport the fix on computation of the radiation and nuclear interaction lengths to v6.24
[#11128] - Clang can’t build ROOT anymore due to a new added diagnostic about undefined behavior
[#11186] -
[RF] heap-use-after-free and stack-use-after-return for
RooFit::UniqueId
[#10009] - [RF] heap-use-after-free for RooAbsRealWrapper
[#10016] - heap-buffer-overflow in TRandom3
[#9859] -
[RF] Avoid printing false warning when passing both
FillColor/FillStyle and VisualizeError to
RooAbsReal::plotOn()
[#11130] - ROOT doesn’t compile with new nlohmann-json version 3.11.0
[#11215] -
[I/O] Cannot create a std::pair<int, int> branch at
prompt
[#11239] - Build failure on Ubuntu22.04, when ROOT builds FTGL itself
[#11222] - [DF] gtest-tree-dataframe-test-dataframe-snapshot fails with AddressSanitizer
[#11236] -
build failure because of nlohmann_json
[#11154] - [math][fit] FitResult is empty or corrupted after FitData class is deleted
[#11050] - C++ exceptions are not correctly propagated by Dask
[#11124] - Several improvements of df103_NanoAODHiggsAnalysis.C
[#11207] -
[DF] Bad interaction between Alias and TTree
sub-branches
[#11272] -
Segfault in TGeoMixture::ComputeDerivedQuantities
[#10645] - [TTreeReader] Cannot read Float16_t branch
[#11260] -
TTreeReaderArray does not support
Double32_t
[#11259] -
genreflex crash in TMetaUtils::ReSubstTemplateArg with
gcc12 headers
[#11250] - Draw options “X+” and “Y+” not working with TMultiGraph
[#11312] - Build failure with nlohmann/json 3.11
[#11280] - [TGaxis] wrong secondary axis defined with TF1, erratic behavior of SetNdivisions
[#10742] -
READ_WITHOUT_GLOBALREGISTRATION has no effect on remote
files
[#11383] - Deadlock in ErrorHandler when invoked at library initialization time.
[#10092] - PyROOT Crash when passing functor to template method
[#11396] - [RF] Buggy range overlap check in createNLL when SplitRange option is used
[#11414] - [RF] Renaming dataset fails when total number of dataset in workspace reached 10
[#11330] - [core] kNotDeleted mechanism is broken on some platforms
[#10828] -
TH1::Merge does not extend axes properly for certain
histograms with labels
[#11333] -
THnSparse::Add() does not preserve weights
[#11233] - cmake Pythonizations in build directory don’t get updated in incremental builds
[#10382] - [TNDArrayT] Backward incompatibility: Error reading from ROOT Files created with earlier versions - Streamer bug
[#11447] - [RF] NLL from RooSimultaneous doesn’t give the expected value in multi-range fits
[#11421] - [RF] RooCmdArg pythonization drops temporary RooArgSets too early
[#11436] - Missing StreamerInfo in file containing nested collection that is non-split but stored member wise
[#10799] - Python 3.11 failures
[#9741] -
[RF] RooPlot::pullHist only uses upper range
[#8808] - [RF] Updates to RooFit tutorials necessary before the next release
[#11418] - [RF] Wrong CmdArg name in documentation of RooAbsPdf class
[#11437] - [cmake] Build tries to compile incompatible pythonization sources with Python 2
[#11508] -
[DF] Wrong entries processed with a Range with
begin+stride
[#11390] - Display does not respect parameters if another operation is booked before printing
[#11344] -
pyroot Do not silently set
EXTRA_CLING_ARGS to -O2
[#8962] - SetClusterPrefetch(true) breaks BulkIO with more than one basket
[#11515] -
Error in TInterpreter::Calc with no output stack in
seemingly random distributed rdf test execution
[#11048] - Resolve the alerts produced by “LGTM analysis: Python”
[#11456] -
Documentation of TH1::GetRMS does not mention the fact that
it is not the RMS anymore
[#10510] - modules_idx_deps CMakeCache.txt variable grows boundless (and does not update properly for module that are turned off)
[#11221] - [RF] AddressSanitizer failures in two RooFit tests
[#11136] -
Misleading warning with builtin_clang=OFF
[#11191] - TBrowser does not show TGeo volume names
[#11581] -
Broken pythonization of
std::vector<const char*>
[#11182] - h2root/g2root man pages should be excluded from install when fortran is disabled
[#11569] -
[VecOps] Sum(vec_of_bool) should not return a
bool
[#11519] - TBrowser non-ascii text scrambles on windows
[#10991] - [RF] Batch mode with RooSimultaneous introduces spurious parameters
[#10559] - [ntuple] Fix low-level TFile embedding
[#11578] -
[RF] Parameter desync in integral of RooRealSumPdf when
using batchmode
[#11634] - extend the TGaxis so that nice “arrows” could be added on its ends
[#11295] - [gui] Variable Explorer GUI class
[#10870] - Improvements to debug/perf symbols for jitted code
[#11672] -
[ntuple] Make RNTupleWriter::Fill() return the number of
bytes written
[#11523] -
[ntuple] Support the storage of collections that use legacy
TVirtualCollectionProxy
[#11686] - Missing Rint dependency for rootcling
[#10958] - [ntuple,daos] Allow multiple ntuples to be stored in a DAOS container
[#10039] -
TFile’s ctor’s error message should point to TFile::Open
when filename contains “://”
[#11738] -
[RF] ROOT v6.26/08 plots wrong pull distribution with
RooPlot::pullHist
[#11723] -
[IO] TFile::DrawMap plots can be improved
[#11476] - [RF] RooAddPdf still emits unexpected errors about missing normalization sets
[#11757] - [RF] Documentation for the RooVoigtian
[#10868] - [RF] Wrong integral for RooPoisson if integrated from a > 0 to infinity
[#11732] - [ntuple] C-style array members of a user-defined class are stored/retrieved as a scalar
[#11663] - TTask: unsafe cast in ExecuteTasks
[#8231] - [RF] Fitting RooSimultaneous with Range option not accounting for range on the indexCat
[#11482] -
[RF] plotSamplingHint can cause evaluation outside the
“safe” range of an observable
[#11747] - Frame of a TPad can sometimes be deleted ‘twice’
[#11837] -
Spurious error message when reading a char from a
TTreeReader<signed char>
[#11853] - Large memory usage / leak when using GetBasketSerialised
[#11730] - [ntuple] Allow users to specify a per-field read callback function
[#10875] -
_HAS_CONDITIONAL_EXPLICIT=0 won’t work with VS 2022
17.4
[#9845] - [RF] Various flaws in the RooLagrangianMorphFunc
[#11875] -
[RF] RooAbsPdf::fitTo: would it be possible to add an
option to control maximal number of calls?
[#11913] -
TExec::SavePrimitive fails when string args used inside
command
[#11916] -
TColor::SaveColor sometimes does not store color
[#11933] - [cling] Crash when dictionary headers can not be found
[#11758] -
[ntuple] Improve the definition and use of
RNTupleLocators
[#10520] - [ntuple] Fix moving of complex elements in collections
[#11954] - [RF] RooFit variables fail comparisons in edge cases
[#11907] - thread local gDirectory not properly updated when another delete the file its point to.
[#12020] - [RF] Cannot generate nested RooSimultaneous from prototype category data
[#11927] - PyROOT: bad CPU performance for 6.27 (dev3 LCG nightly slot at cvmfs)
[#11930] -
Failure in TClass::GetMethodWithPrototype
[#11937] -
macOS linking -flat_namespace changes user-facing
behavior
[#11971] - Is this line surplus to requirements? (or am I missing its purpose?)
[#12170] - Crash when training a PyTorch model within PyMVA
[#12164] - Strange behaviour in interpreter in master/6.28 when initialising vectors
[ROOT-5219] -
Improve error message for incomplete input to
TROOT::ProcessLine()
[ROOT-5805] -
RooHist does not correctly handle negative scale
factor
[ROOT-8040] -
RooAbsData reduce with CutRange not applying
cut to unselected variables
[ROOT-8827] -
TTreeReaderArray<T> does not work for VLEN branches
whose length branch is not of type int
[ROOT-9649] -
Wrong normalization of variable-bin-width RooHistPdf
plotted in range
[ROOT-9687] - value printing of automatic variable is broken (off by one level of indirection?)
[ROOT-9752] - NLL values when fitting with ranges
[ROOT-10088] - lsb_release is not specified as a ROOT dependency
[ROOT-11023] -
RDataFrame Remove global state in
ROOT::RDF::SaveGraph
Published on March 21, 2023
rootreadspeed --help has “random” linebreaks?# syntax in TChain::AddRVec<T> is broken for
non-trivially-constructible TsgPad->SetLogx is
combined with Draw("same")TTime class is not splitablePublished on May 7, 2023
"TEXT90 COLZ" does not workRDF::FromCSV gives wrong output with colTypes
specifiedRVec<bool> shows wrong valuesgDirectory macro should include global-namespace
qualificationGetClass(<typedef>) works only at the second tryRooDataSetRooLinearVar not used in plot projection
integralsstd.bits/uses_allocator_args.h requires feature
cplusplus20Published on August 28, 2023
HistFactory model file twice gives strange
results since ROOT 6.26.02TTreeCache scales (very) poorly with number of
baskets/clusters.TClass object managed in case of multi-threaded
‘rapid’ set of dlopen/dlclose on same library.<filesystem> with runtime modulesHistFactory workspaces incompatible between versions
6.26 and 6.28std::map in a Debug build using recent
versions of GCCTDirectoryFile::lsTRootBrowser: Histogramming leafs which are
functions failsClingConfig.cmake.tmp to the
external LLVM library directory, causing configuration failurebuiltin_llvm=OFF due to unintend libbsd
linkingbuiltin_llvm=OFF: CommandLine Error:
Option ‘W’ registered more than once!core/clib/inc/strlcpy.h incompatible with
latest glibcstd::unique_ptrTFile with very large number of
directories.input_line_1:1:…Snapshot actions writes to uninitialized
memoryPublished on October 13, 2023
Published on November 27, 2023
This release also addresses a security issue. More details will follow.
Published on January 30, 2024
Besides the items below, this patch release features some
improvements relative to run time performance. Firstly, the memory
footprint of the plugin manager has been reduced. Moreover, the
mechanism by which symbols are looked up by the interpreter was
improved, avoiding to open and close a large number of libraries at
startup, which improves considerably the user experience as well as cpu
efficiency on batch jobs. More verbose output is now provided if wrong
settings are used for the web-based widgets, the loopback device is
always used and only one connection is allowed to
RBrowser.
List of issues solved:
Published on February 12, 2026
This release comes with some minor fixes, for example for TMVA. Moreover, it addresses the following problems:
This patch release removes the RooPower and
RooExpPoly classes from this release branch. It is an
unfortunate but unavoidable change: different classes with the same name
were used in the CMS collaboration since at least the Higgs discovery.
This name collision caused massive problems in backwards compatibility
and was blocking CMS from picking up ROOT 6.28+ for statistical
analysis. These classes were only introduced with ROOT 6.28.00 and were
not widely advertised, so you should not be affected by this removal. If
you were using one of these classes, please copy the sources from a
previous ROOT tag in your analysis as a temporary solution, and report
this unsupported usecase by opening a GitHub issue. Based on the
feedback to this patch release, the RooPower and
RooExpPoly classes will either be removed or renamed in
ROOT 6.32.