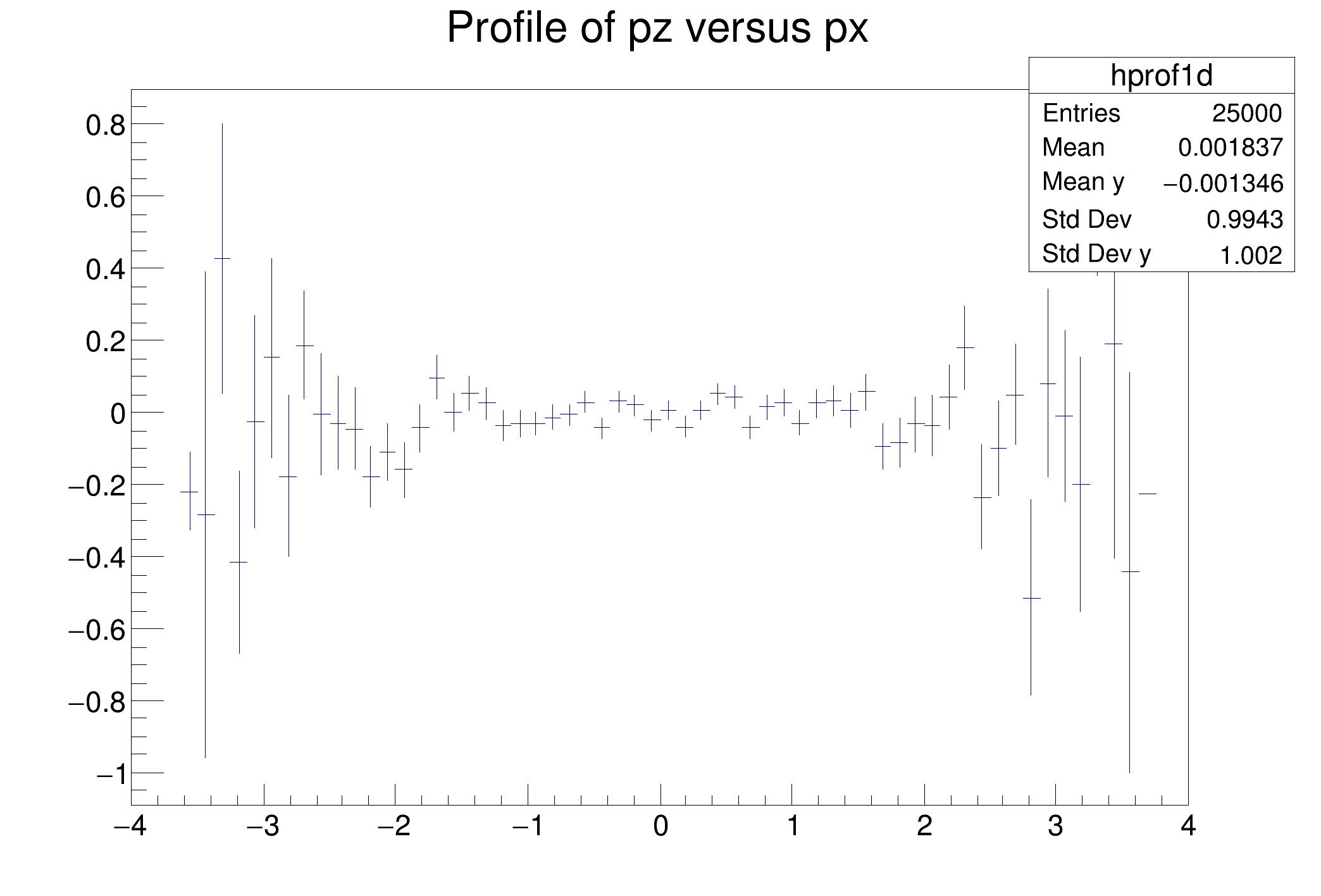
This tutorial illustrates how to use TProfiles in combination with the RDataFrame. See the documentation of TProfile and TProfile2D to better understand the analogy of this code with the example one.
import ROOT
def fill_tree(treeName, fileName):
d.Define("px", "gRandom->Gaus()")\
.Define("py", "gRandom->Gaus()")\
.Define("pz", "sqrt(px * px + py * py)")\
.Snapshot(treeName, fileName)
fileName = "df003_profiles_py.root"
treeName = "myTree"
fill_tree(treeName, fileName)
columns = ROOT.vector('string')()
columns.push_back("px")
columns.push_back("py")
columns.push_back("pz")
hprof1d = d.Profile1D(("hprof1d", "Profile of pz versus px", 64, -4, 4))
hprof2d = d.Profile2D(("hprof2d", "Profile of pz versus px and py", 40, -4, 4, 40, -4, 4, 0, 20))
c1 = ROOT.TCanvas("c1", "Profile histogram example", 200, 10, 700, 500)
hprof1d.Draw()
c1.SaveAs("df003_c1.png")
c2 = ROOT.TCanvas("c2", "Profile2D histogram example", 200, 10, 700, 500)
hprof2d.Draw()
c2.SaveAs("df003_c2.png")
print("Saved figures to df003_*.png")
ROOT's RDataFrame offers a high level interface for analyses of data stored in TTree,...

 Use TProfiles with RDataFrame.
Use TProfiles with RDataFrame.