With default parameters the macro will attempt to run the standard hist2workspace example and read the ROOT file that it produces.
The actual heart of the demo is only about 10 lines long.
The MCMCCalculator is a Bayesian tool that uses the Metropolis-Hastings algorithm to efficiently integrate in many dimensions. It is not as accurate as the BayesianCalculator for simple problems, but it scales to much more complicated cases.
␛[1mRooFit v3.60 -- Developed by Wouter Verkerke and David Kirkby␛[0m
Copyright (C) 2000-2013 NIKHEF, University of California & Stanford University
All rights reserved, please read http://roofit.sourceforge.net/license.txt
[#1] INFO:Minization -- p.d.f. provides expected number of events, including extended term in likelihood.
[#1] INFO:Minization -- createNLL: caching constraint set under name CONSTR_OF_PDF_simPdf_FOR_OBS_channelCat:obs_x_channel1 with 6 entries
[#1] INFO:Minization -- Including the following contraint terms in minimization: (lumiConstraint,alpha_syst1Constraint,alpha_syst2Constraint,alpha_syst3Constraint,gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0_constraint,gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1_constraint)
[#1] INFO:Minization -- The following global observables have been defined: (nom_alpha_syst2,nom_alpha_syst3,nom_gamma_stat_channel1_bin_0,nom_gamma_stat_channel1_bin_1)
Metropolis-Hastings progress: ....................................................................................................
[#1] INFO:Eval -- Proposal acceptance rate: 27.377%
[#1] INFO:Eval -- Number of steps in chain: 27377
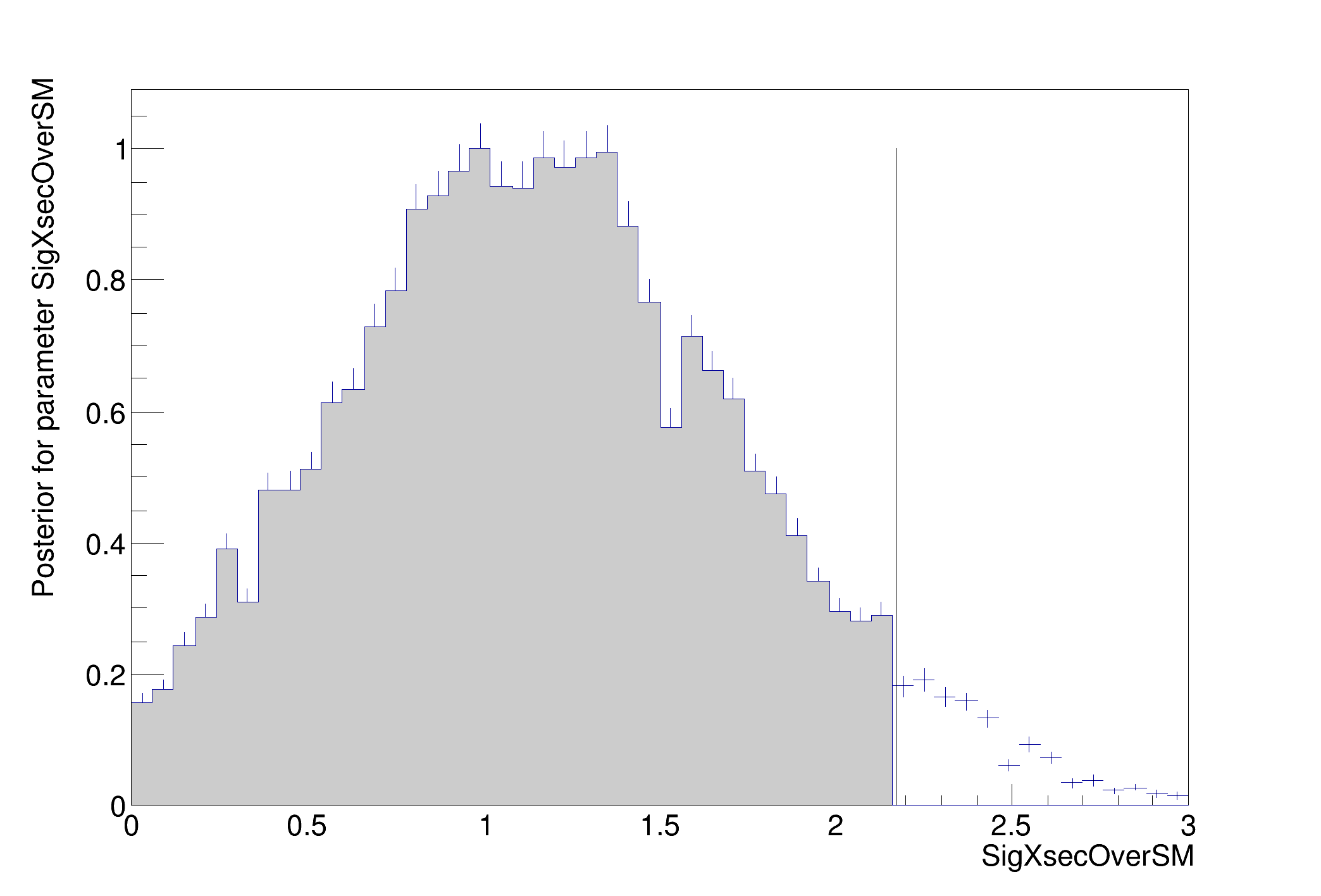
>>>> RESULT : 95% interval on SigXsecOverSM is : [0, 2.17276]
struct BayesianMCMCOptions {
double confLevel = 0.95;
int intervalType = 2;
double maxPOI = -999;
double minPOI = -999;
int numIters = 100000;
int numBurnInSteps = 100;
};
BayesianMCMCOptions optMCMC;
void StandardBayesianMCMCDemo(const char *infile = "", const char *workspaceName = "combined",
const char *modelConfigName = "ModelConfig", const char *dataName = "obsData")
{
const char *filename = "";
if (!strcmp(infile, "")) {
filename = "results/example_combined_GaussExample_model.root";
if (!fileExist) {
#ifdef _WIN32
cout << "HistFactory file cannot be generated on Windows - exit" << endl;
return;
#endif
cout << "will run standard hist2workspace example" << endl;
gROOT->ProcessLine(
".! prepareHistFactory .");
gROOT->ProcessLine(
".! hist2workspace config/example.xml");
cout << "\n\n---------------------" << endl;
cout << "Done creating example input" << endl;
cout << "---------------------\n\n" << endl;
}
} else
filename = infile;
cout << "StandardRooStatsDemoMacro: Input file " << filename << " is not found" << endl;
return;
}
if (!w) {
cout << "workspace not found" << endl;
return;
}
ModelConfig *mc = (ModelConfig *)w->
obj(modelConfigName);
if (!data || !mc) {
cout << "data or ModelConfig was not found" << endl;
return;
}
SequentialProposal sp(0.1);
MCMCCalculator mcmc(*data, *mc);
mcmc.SetConfidenceLevel(optMCMC.confLevel);
mcmc.SetProposalFunction(sp);
mcmc.SetNumIters(optMCMC.numIters);
mcmc.SetNumBurnInSteps(optMCMC.numBurnInSteps);
if (optMCMC.intervalType == 0)
mcmc.SetIntervalType(MCMCInterval::kShortest);
if (optMCMC.intervalType == 1)
mcmc.SetLeftSideTailFraction(0.5);
if (optMCMC.intervalType == 2)
mcmc.SetLeftSideTailFraction(0.);
if (optMCMC.minPOI != -999)
firstPOI->
setMin(optMCMC.minPOI);
if (optMCMC.maxPOI != -999)
firstPOI->
setMax(optMCMC.maxPOI);
MCMCInterval *interval = mcmc.GetInterval();
MCMCIntervalPlot plot(*interval);
plot.Draw();
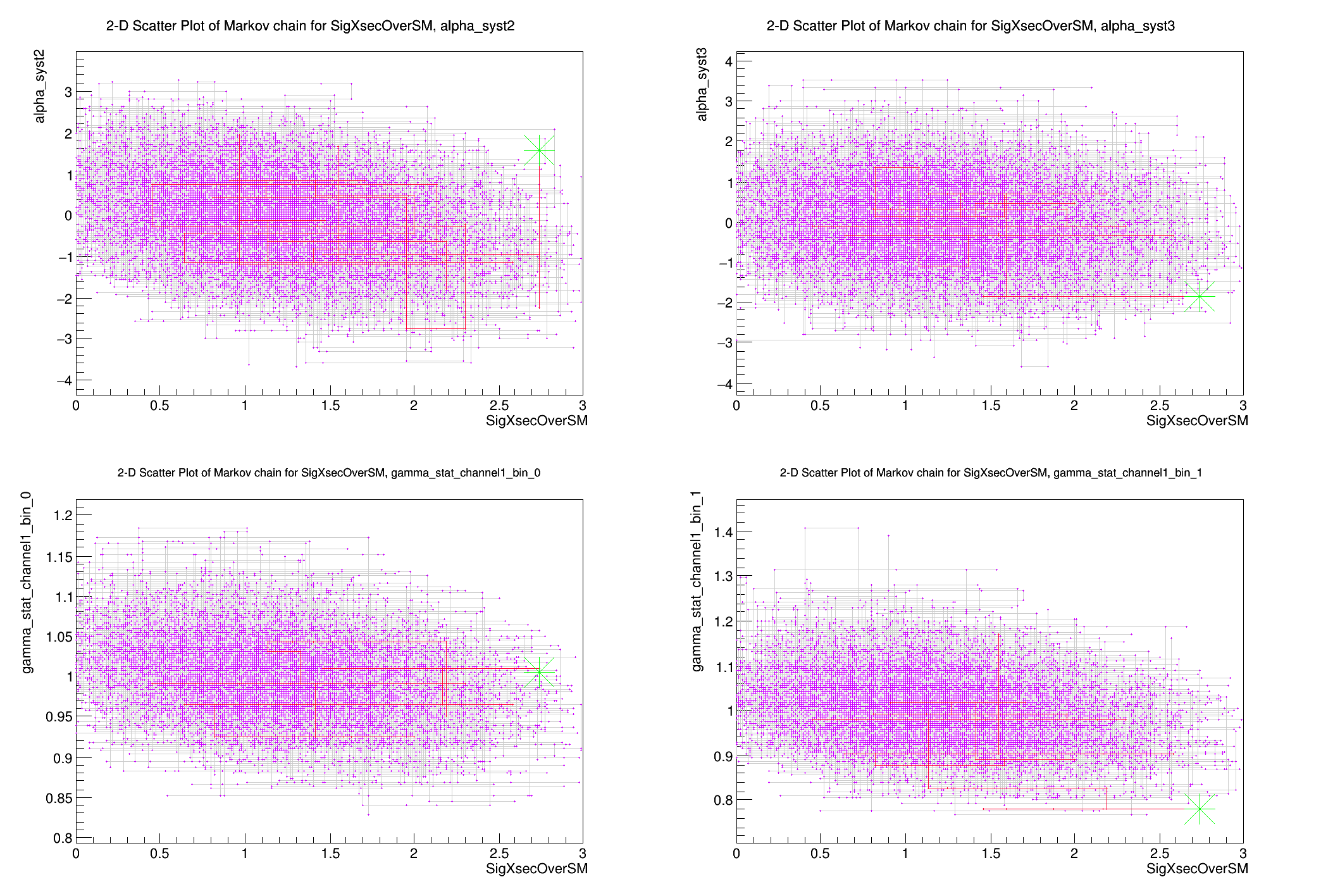
const RooArgSet *list = mc->GetNuisanceParameters();
}
TIterator *it = mc->GetNuisanceParameters()->createIterator();
int iPad = 1;
plot.DrawChainScatter(*firstPOI, *nuis);
}
cout <<
"\n>>>> RESULT : " << optMCMC.confLevel * 100 <<
"% interval on " << firstPOI->
GetName() <<
" is : [" << interval->LowerLimit(*firstPOI) << ", " << interval->UpperLimit(*firstPOI) << "] " << endl;
}
R__EXTERN TSystem * gSystem
RooAbsData is the common abstract base class for binned and unbinned datasets.
RooArgSet is a container object that can hold multiple RooAbsArg objects.
RooRealVar represents a fundamental (non-derived) real valued object.
void setMin(const char *name, Double_t value)
Set minimum of name range to given value.
void setMax(const char *name, Double_t value)
Set maximum of name range to given value.
The RooWorkspace is a persistable container for RooFit projects.
RooAbsData * data(const char *name) const
Retrieve dataset (binned or unbinned) with given name. A null pointer is returned if not found.
void Print(Option_t *opts=0) const
Print contents of the workspace.
TObject * obj(const char *name) const
Return any type of object (RooAbsArg, RooAbsData or generic object) with given name)
A ROOT file is a suite of consecutive data records (TKey instances) with a well defined format.
static TFile * Open(const char *name, Option_t *option="", const char *ftitle="", Int_t compress=ROOT::RCompressionSetting::EDefaults::kUseGeneralPurpose, Int_t netopt=0)
Create / open a file.
Iterator abstract base class.
virtual TObject * Next()=0
virtual const char * GetName() const
Returns name of object.
virtual Bool_t AccessPathName(const char *path, EAccessMode mode=kFileExists)
Returns FALSE if one can access a file using the specified access mode.
Template specialisation used in RooAbsArg:
Namespace for the RooStats classes.
Int_t CeilNint(Double_t x)



 Standard demo of the Bayesian MCMC calculator
Standard demo of the Bayesian MCMC calculator