

Use Simulation Based Inference (SBI) in RooFit.
This tutorial shows how to use SBI in ROOT. As reference distribution we choose a simple uniform distribution. The target distribution is chosen to be gaussian with different mean values. The classifier is trained to discriminate between the reference and target distribution. We see how the neural networks generalize to unknown mean values.
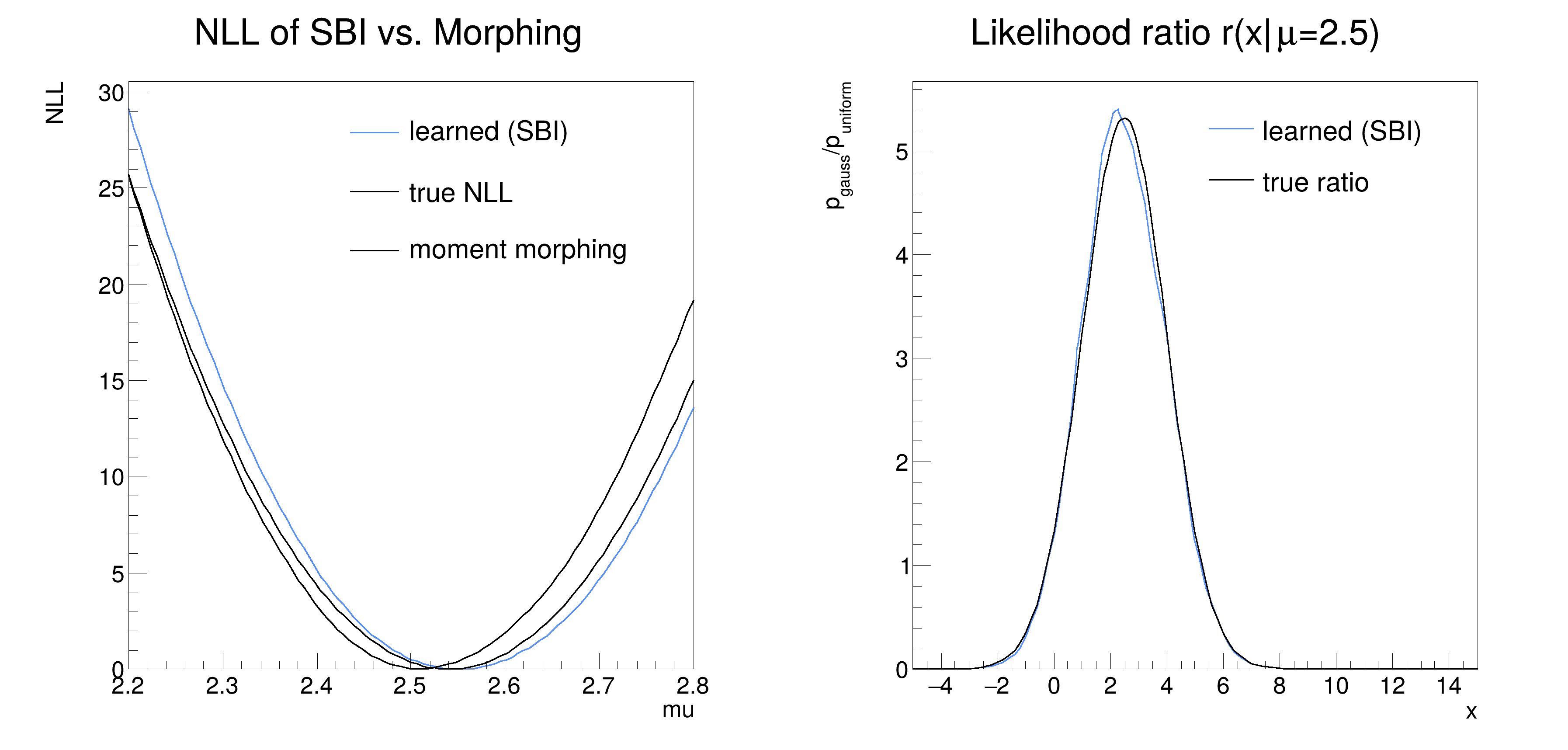
We compare the approach of using the likelihood ratio trick to morphing.
An introduction of SBI can be found in https://arxiv.org/pdf/2010.06439.
A short recap: The idea of SBI is to fit a surrogate model to the data, in order to really learn the likelihood function instead of calculating it. Therefore, a classifier is trained to discriminate between samples from a target distribution (here the Gaussian) $$x\sim p(x|\theta)$$ and a reference distribution (here the Uniform) $$x\sim p_{ref}(x|\theta)$$.
The output of the classifier $$\hat{s}(\theta)$$ is a monotonic function of the likelihood ration and can be turned into an estimate of the likelihood ratio via $$\hat{r}(\theta)=\frac{1-\hat{s}(\theta)}{\hat{s}(\theta)}.$$ This is called the likelihood ratio trick.
In the end we compare the negative logarithmic likelihoods of the learned, morphed and analytical likelihood with minuit and as a plot.
import numpy as np
import ROOT
n_samples = 10000
n_grid = 5
hist = workspace[f"g{i}"].generateBinned([x_var], n_samples)
def __init__(self, workspace):
self.classifier =
MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes=(20, 20), max_iter=1000, random_state=42)
self.data_model = None
self.data_ref = None
self.X_train = None
self.y_train = None
self.workspace = workspace
ws = self.workspace
data_test_model = []
samples_gaussian = ws[model].generate([ws[x], ws[mu]], n_samples).
to_numpy()
self._training_mus = samples_gaussian[mu]
ws = self.workspace
samples_uniform = ws[model].generate(ws[x], n_samples)
)
thetas_model = self._training_mus.
reshape(-1, 1)
thetas_reference = self._training_mus.
reshape(-1, 1)
self.classifier.fit(self.X_train, self.y_train)
n_samples_train = n_samples * 5
ws.factory(f
"Gaussian::gauss(x[-5,15], mu[0,4], {sigma})")
ws["mu"].setVal(mu_observed)
obs_data = ws["gauss"].generate(ws["x"], 1000)
return ws
mu_observed = 2.5
sigma = 1.5
workspace =
build_ws(mu_observed, sigma)
x_var = workspace["x"]
mu_var = workspace["mu"]
gauss = workspace["gauss"]
uniform = workspace["uniform"]
obs_data = workspace["obs_data"]
sbi_model = model
X[:, 0] = x
X[:, 1] = mu
return prob / (1 - prob)
nll_morph = workspace["morph"].createNLL(obs_data)
frame1 =
mu_var.frame(Title=
"NLL of SBI vs. Morphing;mu;NLL", Range=(2.2, 2.8))
frame2 =
x_var.frame(Title=
"Likelihood ratio r(x|#mu=2.5);x;p_{gauss}/p_{uniform}")
single_canvas = True
c =
ROOT.TCanvas(
"",
"", 1200
if single_canvas
else 600, 600)
if single_canvas:
if single_canvas:
else:
if not single_canvas:
for nll in [nll_gauss, nllr_learned, nll_morph]:
del nll_morph
del nllr_learned
del nll_gauss
del workspace
ROOT::Detail::TRangeCast< T, true > TRangeDynCast
TRangeDynCast is an adapter class that allows the typed iteration through a TCollection.
Option_t Option_t TPoint TPoint const char GetTextMagnitude GetFillStyle GetLineColor GetLineWidth GetMarkerStyle GetTextAlign GetTextColor GetTextSize void char Point_t Rectangle_t WindowAttributes_t Float_t Float_t Float_t Int_t Int_t UInt_t UInt_t Rectangle_t Int_t Int_t Window_t TString Int_t GCValues_t GetPrimarySelectionOwner GetDisplay GetScreen GetColormap GetNativeEvent const char const char dpyName wid window const char font_name cursor keysym reg const char only_if_exist regb h Point_t winding char text const char depth char const char Int_t count const char ColorStruct_t color const char Pixmap_t Pixmap_t PictureAttributes_t attr const char char ret_data h unsigned char height h Atom_t Int_t ULong_t ULong_t unsigned char prop_list Atom_t Atom_t Atom_t Time_t UChar_t len
RooWorkspace() contents
variables
---------
(mu,x)
p.d.f.s
-------
RooGaussian::gauss[ x=x mean=mu sigma=1.5 ] = 0.249352
RooUniform::uniform[ x=(x) ] = 1
RooFitResult: minimized FCN value: 1862.97, estimated distance to minimum: 2.32702e-05
covariance matrix quality: Full, accurate covariance matrix
Status : MINIMIZE=0
Floating Parameter FinalValue +/- Error
-------------------- --------------------------
mu 2.5399e+00 +/- 4.74e-02
RooFitResult: minimized FCN value: -1126.14, estimated distance to minimum: 4.23342e-05
covariance matrix quality: Full, accurate covariance matrix
Status : MINIMIZE=0
Floating Parameter FinalValue +/- Error
-------------------- --------------------------
mu 2.5511e+00 +/- 7.15e-02
RooFitResult: minimized FCN value: 1864.58, estimated distance to minimum: 1.67611e-06
covariance matrix quality: Full, accurate covariance matrix
Status : MINIMIZE=0
Floating Parameter FinalValue +/- Error
-------------------- --------------------------
mu 2.5108e+00 +/- 4.09e-02
- Date
- July 2024
- Author
- Robin Syring
Definition in file rf615_simulation_based_inference.py.


