

Multidimensional models: normalization and integration of pdfs, construction of cumulative distribution functions from pdfs in two dimensions
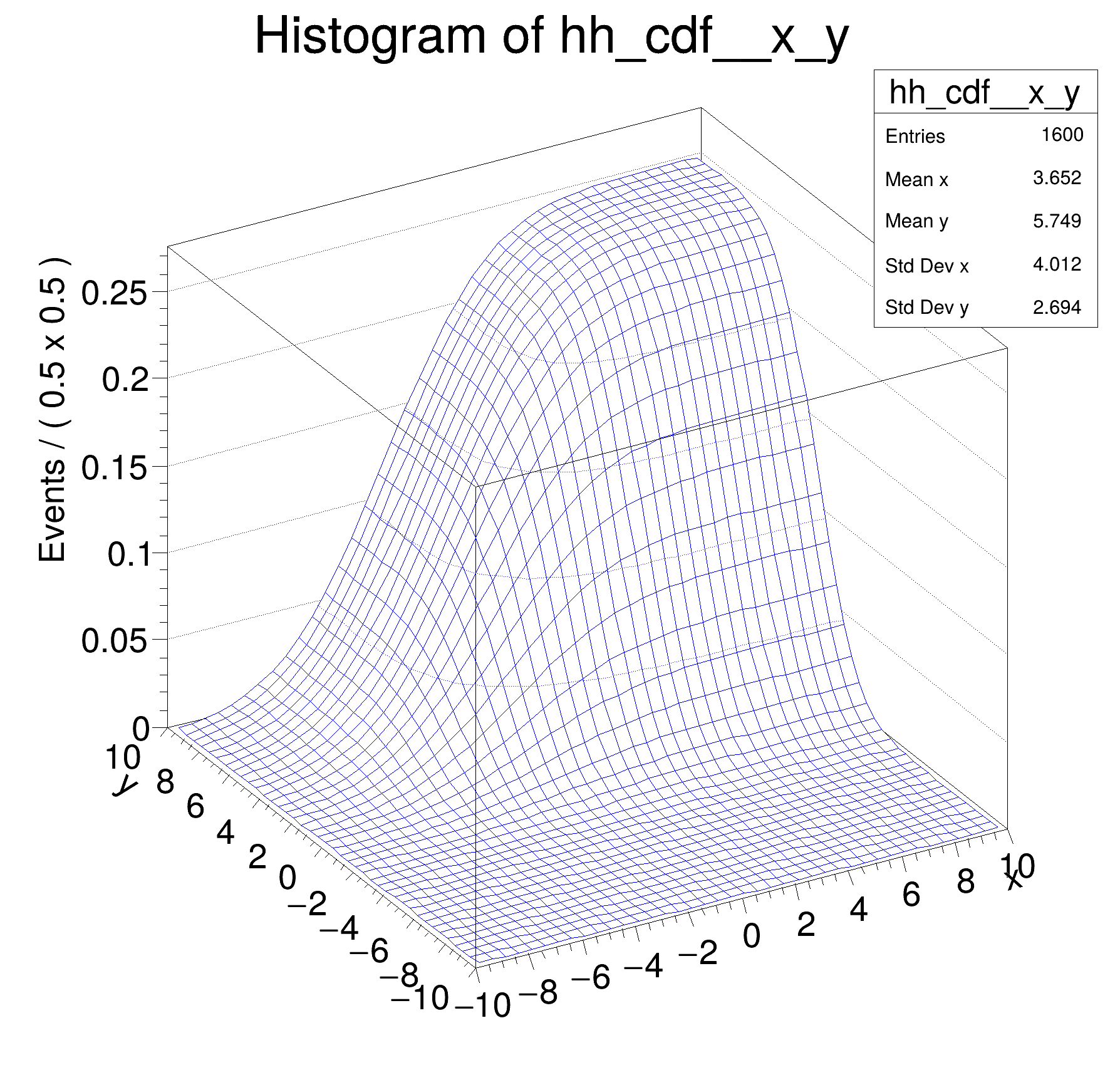
void rf308_normintegration2d()
{
cout <<
"gxy = " <<
gxy.getVal() << endl;
cout <<
"gx_Norm[x,y] = " <<
gxy.getVal(&
nset_xy) << endl;
cout <<
"gx_Int[x,y] = " <<
igxy->getVal() << endl;
cout <<
"gx_Norm[x] = " <<
gxy.getVal(&
nset_x) << endl;
cout <<
"gx_Norm[y] = " <<
gxy.getVal(&
nset_y) << endl;
x.setRange(
"signal", -5, 5);
y.setRange(
"signal", -3, 3);
cout <<
"gx_Int[x,y|signal]_Norm[x,y] = " <<
igxy_sig->getVal() << endl;
new TCanvas(
"rf308_normintegration2d",
"rf308_normintegration2d", 600, 600);
gPad->SetLeftMargin(0.15);
hh_cdf->GetZaxis()->SetTitleOffset(1.8);
}
ROOT::Detail::TRangeCast< T, true > TRangeDynCast
TRangeDynCast is an adapter class that allows the typed iteration through a TCollection.
RooArgSet is a container object that can hold multiple RooAbsArg objects.
Efficient implementation of a product of PDFs of the form.
Variable that can be changed from the outside.
TH1 is the base class of all histogram classes in ROOT.
RooCmdArg YVar(const RooAbsRealLValue &var, const RooCmdArg &arg={})
RooCmdArg NormSet(Args_t &&... argsOrArgSet)
RooCmdArg Binning(const RooAbsBinning &binning)
The namespace RooFit contains mostly switches that change the behaviour of functions of PDFs (or othe...
gxy = 0.485672
gx_Norm[x,y] = 0.0129332
gx_Int[x,y] = 37.5523
gx_Norm[x] = 0.106896
gx_Norm[y] = 0.120989
[#1] INFO:Eval -- RooRealVar::setRange(x) new range named 'signal' created with bounds [-5,5]
[#1] INFO:Eval -- RooRealVar::setRange(y) new range named 'signal' created with bounds [-3,3]
gx_Int[x,y|signal]_Norm[x,y] = 0.572035
- Date
- July 2008
- Author
- Wouter Verkerke
Definition in file rf308_normintegration2d.C.


