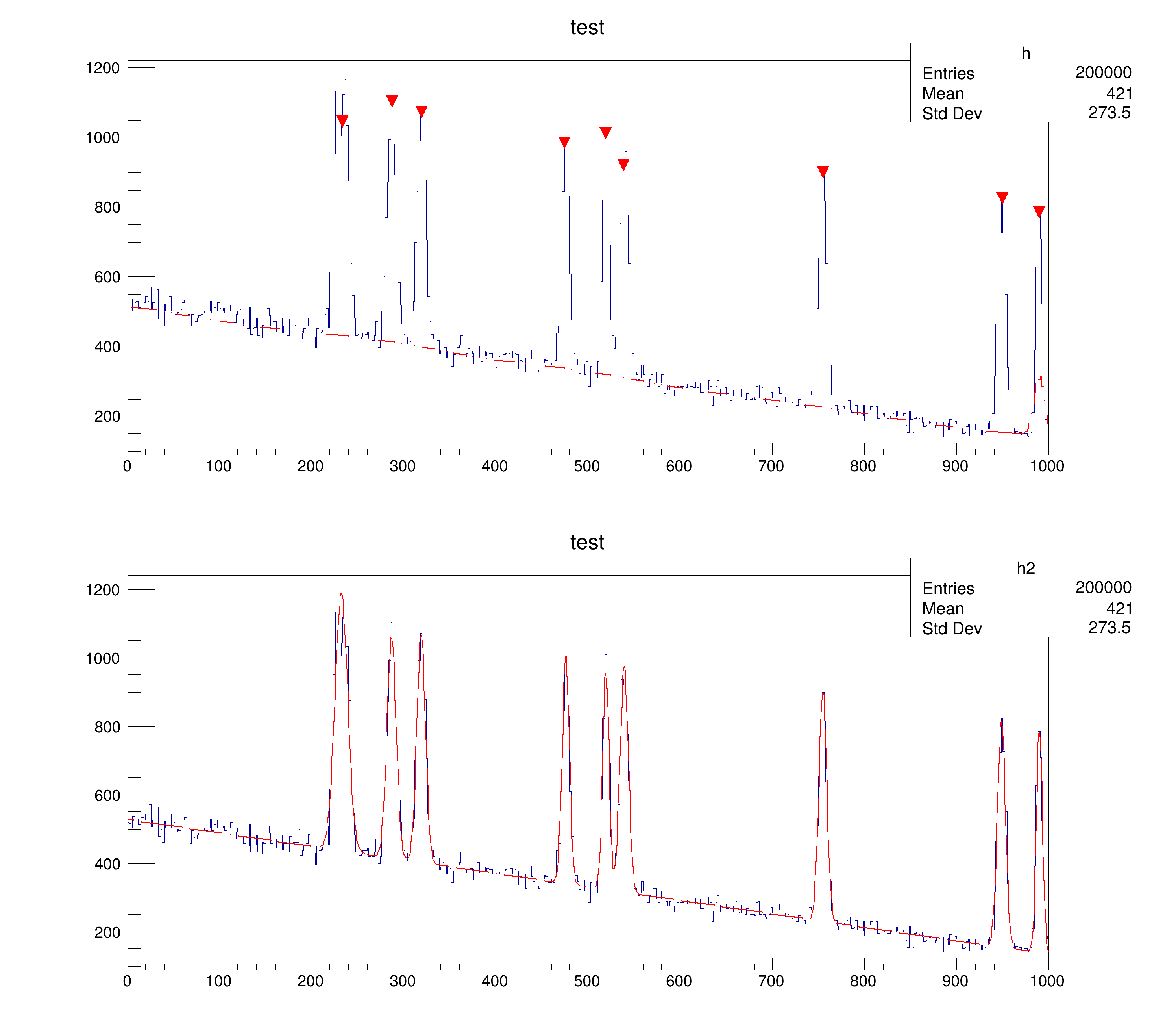
Illustrates how to find peaks in histograms.
This script generates a random number of gaussian peaks on top of a linear background. The position of the peaks is found via TSpectrum and injected as initial values of parameters to make a global fit. The background is computed and drawn on top of the original histogram.
This script can fit "peaks' heights" or "peaks' areas" (comment out or uncomment the line which defines __PEAKS_C_FIT_AREAS__).
To execute only the first part of the script (without fitting) specify a negative value for the number of peaks, eg
Found 9 candidate peaks to fit
Found 9 useful peaks to fit
Now fitting: Be patient
****************************************
Minimizer is Minuit2 / Migrad
Chi2 = 596.686
NDf = 471
Edm = 1.7299e-05
NCalls = 1747
p0 = 527.684 +/- 2.02282
p1 = -0.395029 +/- 0.00304651
p2 = 634.668 +/- 20.672
p3 = 519.331 +/- 0.111412
p4 = 3.49861 +/- 0.109353
p5 = 664.735 +/- 18.7022
p6 = 319.147 +/- 0.131874
p7 = 4.69145 +/- 0.126752
p8 = 670.916 +/- 17.6455
p9 = 754.806 +/- 0.108202
p10 = 4.29739 +/- 0.101204
p11 = 669.613 +/- 20.0806
p12 = 475.964 +/- 0.113649
p13 = 3.89314 +/- 0.110985
p14 = 648.09 +/- 18.199
p15 = 989.666 +/- 0.0884478
p16 = 3.34535 +/- 0.0786714
p17 = 662.552 +/- 17.8619
p18 = 539.268 +/- 0.122694
p19 = 4.56069 +/- 0.113882
p20 = 659.417 +/- 16.1804
p21 = 948.476 +/- 0.101982
p22 = 4.41156 +/- 0.091998
p23 = 753.529 +/- 15.2593
p24 = 232.585 +/- 0.151403
p25 = 6.95019 +/- 0.122555
p26 = 645.477 +/- 17.9858
p27 = 286.947 +/- 0.140814
p28 = 4.98705 +/- 0.133049
{
#if defined(__PEAKS_C_FIT_AREAS__)
#endif
}
}
{
TH1F *
h =
new TH1F(
"h",
"test", 500, 0, 1000);
par[0] = 0.8;
par[1] = -0.6 / 1000;
#if defined(__PEAKS_C_FIT_AREAS__)
#endif
}
h->FillRandom(
"f", 200000);
return;
par[0] =
fline->GetParameter(0);
par[1] =
fline->GetParameter(1);
continue;
#if defined(__PEAKS_C_FIT_AREAS__)
#endif
}
printf(
"Now fitting: Be patient\n");
h2->Fit("fit");
}
int Int_t
Signed integer 4 bytes (int)
double Double_t
Double 8 bytes.
winID h TVirtualViewer3D TVirtualGLPainter p
Option_t Option_t TPoint TPoint const char GetTextMagnitude GetFillStyle GetLineColor GetLineWidth GetMarkerStyle GetTextAlign GetTextColor GetTextSize void char Point_t Rectangle_t WindowAttributes_t Float_t Float_t Float_t Int_t Int_t UInt_t UInt_t Rectangle_t Int_t Int_t Window_t TString Int_t GCValues_t GetPrimarySelectionOwner GetDisplay GetScreen GetColormap GetNativeEvent const char const char dpyName wid window const char font_name cursor keysym reg const char only_if_exist regb h Point_t np
Option_t Option_t TPoint TPoint const char GetTextMagnitude GetFillStyle GetLineColor GetLineWidth GetMarkerStyle GetTextAlign GetTextColor GetTextSize void char Point_t Rectangle_t WindowAttributes_t Float_t Float_t Float_t Int_t Int_t UInt_t UInt_t Rectangle_t result
R__EXTERN TRandom * gRandom
virtual void SetNpx(Int_t npx=100)
Set the number of points used to draw the function.
virtual void SetParameters(const Double_t *params)
1-D histogram with a float per channel (see TH1 documentation)
TH1 is the base class of all histogram classes in ROOT.
Double_t Rndm() override
Machine independent random number generator.
Advanced Spectra Processing.
virtual Int_t Search(const TH1 *hist, Double_t sigma=2, Option_t *option="", Double_t threshold=0.05)
One-dimensional peak search function.
Double_t * GetPositionX() const
virtual TH1 * Background(const TH1 *hist, Int_t nIter=20, Option_t *option="")
One-dimensional background estimation function.
static TVirtualFitter * Fitter(TObject *obj, Int_t maxpar=25)
Static function returning a pointer to the current fitter.
Double_t Gaus(Double_t x, Double_t mean=0, Double_t sigma=1, Bool_t norm=kFALSE)
Calculates a gaussian function with mean and sigma.
Double_t Sqrt(Double_t x)
Returns the square root of x.
Short_t Abs(Short_t d)
Returns the absolute value of parameter Short_t d.
constexpr Double_t TwoPi()