This example is a generalization of the on/off problem. It's a common setup for SUSY searches. Imagine that one has two variables "x" and "y" (eg. missing ET and SumET), see figure. The signal region has high values of both of these variables (top right). One can see low values of "x" or "y" acting as side-bands. If we just used "y" as a sideband, we would have the on/off problem.
If tau is known, this model is sufficient, but often tau is not known exactly. So one can use low values of "x" as an additional constraint for tau. Note that this technique critically depends on the notion that the joint distribution for "x" and "y" can be factorized. Generally, these regions have many events, so it the ratio can be measured very precisely there. So we extend the model to describe the left two boxes... denoted with "bar".
One can further expand the model to account for the systematic associated to assuming the distribution of "x" and "y" factorizes (eg. that tau is the same for off/on and offbar/onbar). This can be done in several ways, but here we introduce an additional parameter rho, which so that one set of models will use tau and the other tau*rho. The choice is arbitrary, but it has consequences on the numerical stability of the algorithms. The "bar" measurements typically have more events (& smaller relative errors). If we choose
the product tau*rho will be known very precisely (~1/sqrt(bbar)) and the contour in those parameters will be narrow and have a non-trivial tau~1/rho shape. However, if we choose to put rho on the non/noff measurements (where the product will have an error ~1/sqrt(b)), the contours will be more amenable to numerical techniques. Thus, here we choose to define:
Left in this way, the problem is under-constrained. However, one may have some auxiliary measurement (usually based on Monte Carlo) to constrain rho. Let us call this auxiliary measurement that gives the nominal value of rho "rhonom". Thus, there is a 'constraint' term in the full model: P(rhonom | rho). In this case, we consider a Gaussian constraint with standard deviation sigma.
Note, the covariance matrix of the parameters has large off-diagonal terms. Clearly s,b are anti-correlated. Similarly, since noffbar >> nonbar, one would expect bbar,tau to be anti-correlated.
This can be seen below.
Similarly, since tau*rho appears as a product, we expect rho,tau to be anti-correlated. When the error on rho is significantly larger than 1/sqrt(bbar), tau is essentially known and the correlation is minimal (tau mainly cares about bbar, and rho about b,s). In the alternate parametrization (bbar* tau * rho) the correlation coefficient for rho,tau is large (and negative).
Processing /mnt/vdb/lsf/workspace/root-makedoc-v608/rootspi/rdoc/src/v6-08-00-patches/tutorials/roostats/FourBinInstructional.C...
�[1mRooFit v3.60 -- Developed by Wouter Verkerke and David Kirkby�[0m
Copyright (C) 2000-2013 NIKHEF, University of California & Stanford University
All rights reserved, please read http://roofit.sourceforge.net/license.txt
[#1] INFO:ObjectHandling -- RooWorkspace::import(wspace) importing dataset modelData
[#0] PROGRESS:Minization -- ProfileLikelihoodCalcultor::DoGLobalFit - find MLE
[#0] PROGRESS:Minization -- ProfileLikelihoodCalcultor::DoMinimizeNLL - using Minuit / Migrad with strategy 1
[#1] INFO:Minization -- RooMinimizer::optimizeConst: activating const optimization
[#1] INFO:Minization -- The following expressions will be evaluated in cache-and-track mode: (on,off,onbar,offbar,mcCons)
[#1] INFO:Minization --
RooFitResult: minimized FCN value: 16.2872, estimated distance to minimum: 1.21263e-07
covariance matrix quality: Full, accurate covariance matrix
Status : MINIMIZE=0
Floating Parameter FinalValue +/- Error
-------------------- --------------------------
b 8.3602e+01 +/- 1.39e+01
bbar 9.9301e+02 +/- 3.15e+01
rho 1.2783e+00 +/- 1.99e-01
s 5.5397e+01 +/- 1.78e+01
tau 4.9405e+00 +/- 1.72e-01
Bayesian Calc. only supports on parameter of interest
[#1] INFO:Minization -- RooMinimizer::optimizeConst: activating const optimization
[#1] INFO:Minization -- The following expressions will be evaluated in cache-and-track mode: (on,off,onbar,offbar,mcCons)
**********
** 1 **SET PRINT 1
**********
**********
** 2 **SET NOGRAD
**********
PARAMETER DEFINITIONS:
NO. NAME VALUE STEP SIZE LIMITS
1 b 1.17958e+02 1.38657e+01 0.00000e+00 3.00000e+02
2 bbar 1.00111e+03 3.15028e+01 5.00000e+02 2.00000e+03
3 rho 9.28979e-01 1.98664e-01 0.00000e+00 2.00000e+00
4 s 1.20959e+01 1.78108e+01 0.00000e+00 1.00000e+02
MINUIT WARNING IN PARAMETR
============== VARIABLE4 BROUGHT BACK INSIDE LIMITS.
5 tau 4.89226e+00 1.71714e-01 3.00000e+00 7.00000e+00
**********
** 3 **SET ERR 0.5
**********
**********
** 4 **SET PRINT 1
**********
**********
** 5 **SET STR 1
**********
NOW USING STRATEGY 1: TRY TO BALANCE SPEED AGAINST RELIABILITY
**********
** 6 **MIGRAD 2500 1
**********
FIRST CALL TO USER FUNCTION AT NEW START POINT, WITH IFLAG=4.
START MIGRAD MINIMIZATION. STRATEGY 1. CONVERGENCE WHEN EDM .LT. 1.00e-03
FCN=18.2144 FROM MIGRAD STATUS=INITIATE 20 CALLS 21 TOTAL
EDM= unknown STRATEGY= 1 NO ERROR MATRIX
EXT PARAMETER CURRENT GUESS STEP FIRST
NO. NAME VALUE ERROR SIZE DERIVATIVE
1 b 1.17958e+02 1.38657e+01 9.47846e-02 -1.99668e-02
2 bbar 1.00111e+03 3.15028e+01 4.45472e-02 -1.41126e-01
3 rho 9.28979e-01 1.98664e-01 2.00529e-01 -1.44934e-02
4 s 1.20959e+01 1.78108e+01 5.77645e-01 -2.24297e+00
5 tau 4.89226e+00 1.71714e-01 8.60889e-02 -8.62117e-02
ERR DEF= 0.5
MIGRAD MINIMIZATION HAS CONVERGED.
MIGRAD WILL VERIFY CONVERGENCE AND ERROR MATRIX.
COVARIANCE MATRIX CALCULATED SUCCESSFULLY
FCN=16.2872 FROM MIGRAD STATUS=CONVERGED 190 CALLS 191 TOTAL
EDM=3.60955e-06 STRATEGY= 1 ERROR MATRIX ACCURATE
EXT PARAMETER STEP FIRST
NO. NAME VALUE ERROR SIZE DERIVATIVE
1 b 8.35905e+01 1.38673e+01 7.30675e-05 2.40054e-02
2 bbar 9.93029e+02 3.15025e+01 5.19046e-05 -3.02688e-02
3 rho 1.27859e+00 1.98754e-01 1.58308e-04 1.62267e-02
4 s 5.54105e+01 1.78120e+01 6.70504e-04 3.43707e-04
5 tau 4.94037e+00 1.71702e-01 9.49080e-05 -2.33172e-02
ERR DEF= 0.5
EXTERNAL ERROR MATRIX. NDIM= 25 NPAR= 5 ERR DEF=0.5
1.930e+02 8.358e+01 -2.620e+00 -1.929e+02 -5.000e-01
8.358e+01 9.931e+02 1.329e-04 -8.356e+01 -4.941e+00
-2.620e+00 1.329e-04 4.008e-02 2.619e+00 -7.950e-07
-1.929e+02 -8.356e+01 2.619e+00 3.319e+02 4.998e-01
-5.000e-01 -4.941e+00 -7.950e-07 4.998e-01 2.955e-02
PARAMETER CORRELATION COEFFICIENTS
NO. GLOBAL 1 2 3 4 5
1 0.96819 1.000 0.191 -0.942 -0.762 -0.209
2 0.91196 0.191 1.000 0.000 -0.146 -0.912
3 0.96348 -0.942 0.000 1.000 0.718 -0.000
4 0.76233 -0.762 -0.146 0.718 1.000 0.160
5 0.92088 -0.209 -0.912 -0.000 0.160 1.000
**********
** 7 **SET ERR 0.5
**********
**********
** 8 **SET PRINT 1
**********
**********
** 9 **HESSE 2500
**********
COVARIANCE MATRIX CALCULATED SUCCESSFULLY
FCN=16.2872 FROM HESSE STATUS=OK 31 CALLS 222 TOTAL
EDM=3.61026e-06 STRATEGY= 1 ERROR MATRIX ACCURATE
EXT PARAMETER INTERNAL INTERNAL
NO. NAME VALUE ERROR STEP SIZE VALUE
1 b 8.35905e+01 1.38724e+01 1.46135e-05 -4.58641e-01
2 bbar 9.93029e+02 3.15055e+01 1.03809e-05 -3.49712e-01
3 rho 1.27859e+00 1.98823e-01 3.16616e-05 2.82321e-01
4 s 5.54105e+01 1.78183e+01 1.34101e-04 1.08422e-01
5 tau 4.94037e+00 1.71720e-01 1.89816e-05 -2.98215e-02
ERR DEF= 0.5
EXTERNAL ERROR MATRIX. NDIM= 25 NPAR= 5 ERR DEF=0.5
1.931e+02 8.361e+01 -2.622e+00 -1.931e+02 -5.002e-01
8.361e+01 9.933e+02 -3.075e-05 -8.361e+01 -4.942e+00
-2.622e+00 -3.075e-05 4.011e-02 2.622e+00 1.826e-07
-1.931e+02 -8.361e+01 2.622e+00 3.321e+02 5.001e-01
-5.002e-01 -4.942e+00 1.826e-07 5.001e-01 2.956e-02
PARAMETER CORRELATION COEFFICIENTS
NO. GLOBAL 1 2 3 4 5
1 0.96821 1.000 0.191 -0.942 -0.763 -0.209
2 0.91198 0.191 1.000 -0.000 -0.146 -0.912
3 0.96350 -0.942 -0.000 1.000 0.718 0.000
4 0.76253 -0.763 -0.146 0.718 1.000 0.160
5 0.92090 -0.209 -0.912 0.000 0.160 1.000
[#1] INFO:Minization -- RooMinimizer::optimizeConst: deactivating const optimization
[#1] INFO:Minization -- RooProfileLL::evaluate(nll_model_modelData_Profile[s]) Creating instance of MINUIT
[#1] INFO:Minization -- RooProfileLL::evaluate(nll_model_modelData_Profile[s]) determining minimum likelihood for current configurations w.r.t all observable
[#1] INFO:Minization -- RooProfileLL::evaluate(nll_model_modelData_Profile[s]) minimum found at (s=55.4077)
.
[#1] INFO:Minization -- RooProfileLL::evaluate(nll_model_modelData_Profile[s]) Creating instance of MINUIT
[#1] INFO:Minization -- RooProfileLL::evaluate(nll_model_modelData_Profile[s]) determining minimum likelihood for current configurations w.r.t all observable
[#0] ERROR:InputArguments -- RooArgSet::checkForDup: ERROR argument with name s is already in this set
[#1] INFO:Minization -- RooProfileLL::evaluate(nll_model_modelData_Profile[s]) minimum found at (s=55.4105)
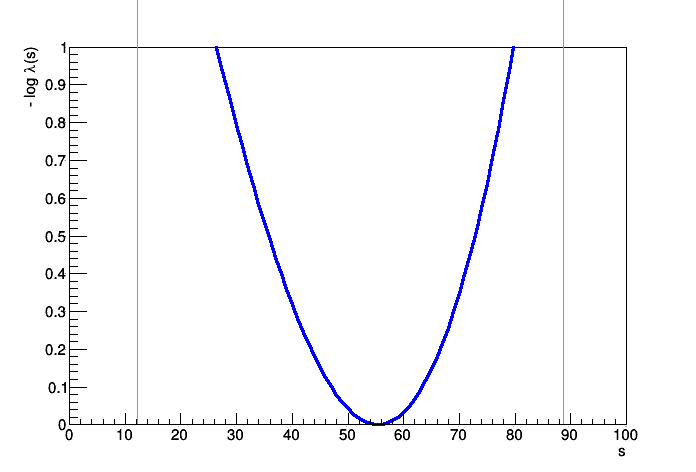
..........................................................................................................................................................................................................Profile Likelihood interval on s = [12.1902, 88.6871]
Real time 0:00:01, CP time 0.680



 This example is a generalization of the on/off problem.
This example is a generalization of the on/off problem.